Demethyleneberberine |
| رقم الكتالوجGC38101 |
Demethyleneberberine (DMB), as a natural active component of medicinal plant Cortex phellodendri chinensis, has favorable bioactivity.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
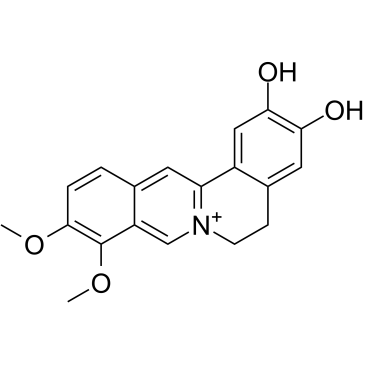
Cas No.: 25459-91-0
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Demethyleneberberine (DMB), as a natural active component of medicinal plant Cortex phellodendri chinensis, has favorable bioactivity[1]. Demethyleneberberine also, as a natural mitochondria-targeted antioxidant, can inhibit oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and steatosis in an alcoholic hepatic disease model[2].
In vitro experiment it shown that with 0, 10, 20, 40, 80, and 160 µmol/L DMB (Demethyleneberberine) obviously inhibit proliferation of HSCs in a concentration dependent manner. The IC50 of DMB(Demethyleneberberine) for HSC-T6 cells at 48 h was 36.7 µmol/L[3]. In vitro, Demethyleneberberine has the inhibition of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) with IC50 of 9.06 µM[4].
In vivo efficacy test it demonstrated that mice were administrated 50 mg/kg/d orally Demethyleneberberine for 98 days markedly improved colon atrophy, colonic tissue mass score, neutrophil infiltration and histological damage, which was mainly attributed to the anti-inflammatory effect of Demethyleneberberine[5]. In vivo, methionine and choline deficient (MCD) high-fat diet feeding mice and db/db mice were injected with 20 or 40 mg/kg intraperitoneally can reduce hepatic lipid accumulation. In addition, DMB treatmentthe can obviously attenuate oxidative damage and inflammation induced by NAFLD(Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease)[6]. In vivo, inflammatory colitis mice were administrated with 150 and 300 mg/kg orally Demethyleneberberine caused the reduction of weight loss and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, while significantly decrease the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and inhibited the activation of NF-κB signaling pathway[7].
References:
[1] Liu J, et al. Demethyleneberberine induces cell cycle arrest and cellular senescence of NSCLC cells via c-Myc/HIF-1α pathway. Phytomedicine. 2021 Oct;91:153678.
[2] Zhang P., et al. Demethyleneberberine, a natural mitochondria-targeted antioxidant, inhibits mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and steatosis in alcoholic liver disease mouse model. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015;352:139–147.
[3] Wang Y, et al. Demethyleneberberine Protects against Hepatic Fibrosis in Mice by Modulating NF-κB Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 30;17(7):1036.
[4] Tao C, et al. Highly efficient synthesis and monoamine oxidase B inhibitory profile of demethyleneberberine, columbamine and palmatine. Neurochem Int. 2020 Oct;139:104807.
[5] Zhao Y, et al. Demethyleneberberine blocked the maturation of IL-1β in inflammation by inhibiting TLR4-mitochondria signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Dec;113(Pt A):109319.
[6] Qiang X, et al. Demethyleneberberine attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with activation of AMPK and inhibition of oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Apr 15;472(4):603-9.
[7] Chen YY, et al. Demethyleneberberine alleviates inflammatory bowel disease in mice through regulating NF-κB signaling and T-helper cell homeostasis. Inflamm Res. 2017 Feb;66(2):187-196.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 15 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















