Staurosporine(CGP 41251) (Synonyms: Stsp) |
| رقم الكتالوجGC15299 |
Staurosporin, a small kinase inhibitor, is an alkaloid derived from the bacterium Streptomyces staurosporeus.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.

Cas No.: 62996-74-1
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
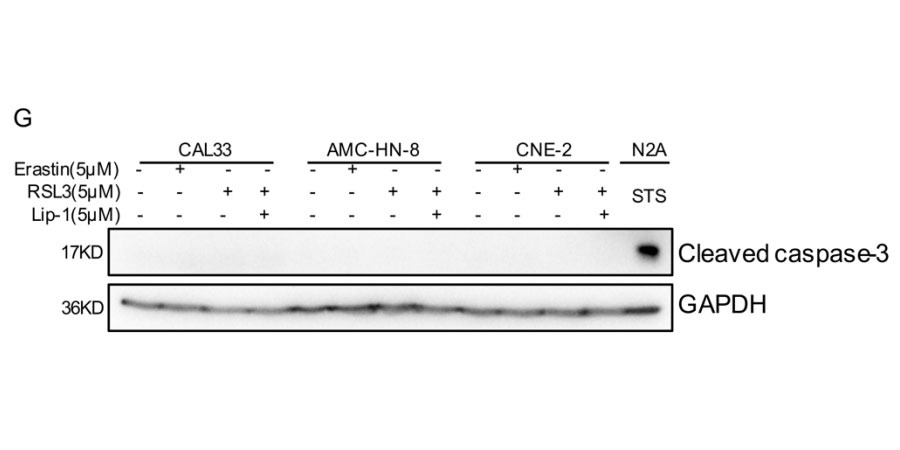
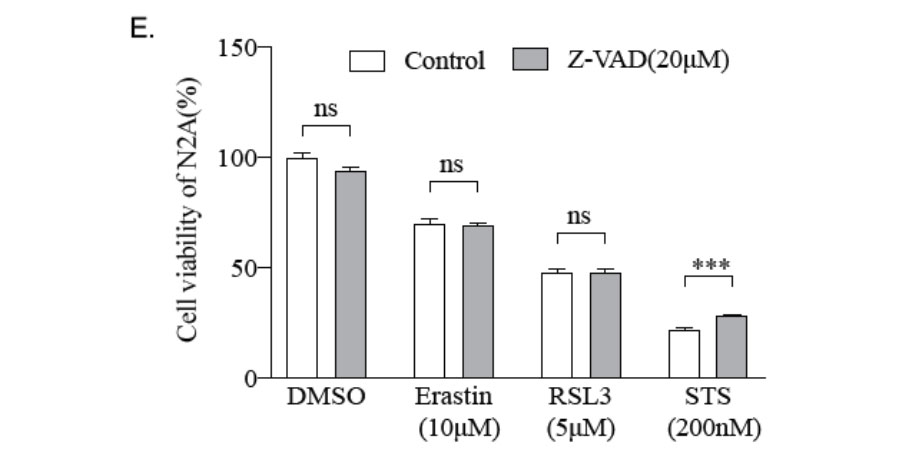
Staurosporin, a small kinase inhibitor, is an alkaloid derived from the bacterium Streptomyces staurosporeus.[1] Staurosporine can block the ATP-binding site of the enzimes and induce apoptosis by activation of caspase-3 in higher eukaryotes.[2]
In vitro experiment it shown that treatment with 50 nM of Staurosporin, there is a single-cell migration of breast carcinoma cells on plastic, fibronectin, or laminin surfaces.[1] Staurosporine killed Acanthamoeba trophozoites in a dose dependent way with IC50 and IC90 values of 0.265?±?0.057 and 1.27?±?0,007?μg/mL, respectively.[2] In vitro, treatment with a low concentration (10(-7) M) of staurosporine in cultured rat astrocytes, there is a significantly increased proportion of early apoptotic cells after regeneration in a staurosporine free medium. However, treatment with a higher (10(-6) M) concentration of staurosporine, there is further obviously increased necroptosis after regeneration in a staurosporine free medium.[3] In vitro efficacy test it indicated that 1 μM STS was able to activate the autophagy pathway in SH-SY5Y cells.[4] In addition, treatment with 5 to 50 μM of staurosporine, conidial cell viability decreased in a concentration-dependent manner, suggesting that staurosporine has potent antifungal activity against N. crassa conidia.[5]
In vivo efficacy study it demonstrated that mice were treated with 3 mg/kg staurosporine via oral gavage twice a week has no effects on tumor growth. But mice were treated with the combination of 3 mg/kg staurosporine and 50 mg/kg lapatinib inhibited the tumor growth obviously.[6]
References:
[1].Meyer FAH, et al. The Presence of Yin-Yang Effects in the Migration Pattern of Staurosporine-Treated Single versus Collective Breast Carcinoma Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 4;22(21):11961.
[2].Cartuche L, et al. Staurosporine from Streptomyces sanyensis activates Programmed Cell Death in Acanthamoeba via the mitochondrial pathway and presents low in vitro cytotoxicity levels in a macrophage cell line. Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 12;9(1):11651.
[3].?imenc J, et al. Staurosporine induces apoptosis and necroptosis in cultured rat astrocytes. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2012 Oct;35(4):399-405.
[4].Brunelli F, et al. PINK1 Protects against Staurosporine-Induced Apoptosis by Interacting with Beclin1 and Impairing Its Pro-Apoptotic Cleavage. Cells. 2022 Feb 15;11(4):678.
[5].Castro A, et al. Rotenone enhances the antifungal properties of staurosporine. Eukaryot Cell. 2010 Jun;9(6):906-14.
[6].Zambrano JN, et al. Staurosporine, an inhibitor of hormonally up-regulated neu-associated kinase. Oncotarget. 2018 Nov 13;9(89):35962-35973.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 30 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *