Cyclophosphamide |
| Catalog No.GC11145 |
Cyclophosphamide is a frequently used chemotherapy, often in combination with other chemotherapy types, for the treatment of breast cancer, malignant lymphomas, multiple myeloma, and neuroblastom.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
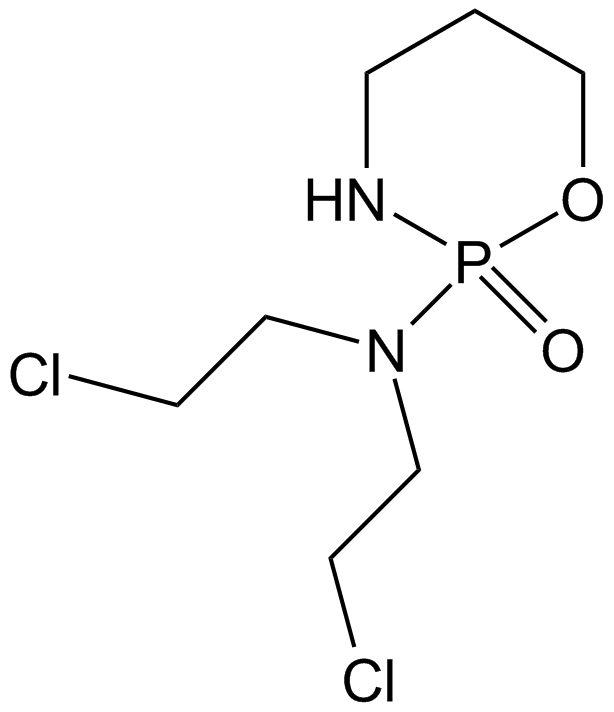
Cas No.: 50-18-0
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Cyclophosphamide is a frequently used chemotherapy, often in combination with other chemotherapy types, for the treatment of breast cancer, malignant lymphomas, multiple myeloma, and neuroblastoma[1].
Cyclophosphamide’s immunomodulatory function was investigated by conditioning macrophages with tumor cell secretome collected from cyclophosphamide treated MM cell lines. CTX-TCS conditioning augmented the migratory capacity of macrophages and increased CD32 and CD64 Fcγ receptor expression on their cell surface. Daratumumab-specific tumor clearance was increased by conditioning macrophages with CTX-TCS in a dose-dependent manner[2]
In vivo,Cyclophosphamide induces early nonapoptotic death of superficial cells, followed by apoptotic death of deeper layers. H&E staining was performed over several days to determine the global urothelial injury and regeneration pattern after cyclophosphamide injection. Compared with uninjured mice, significant sloughing of urothelial cell layers as well as submucosal hemorrhage and inflammation were observed 1 day after cyclophosphamide. cyclophosphamide induces nonapoptotic death of superficial cells starting at 2 hours, followed by apoptotic loss of intermediate and basal cells starting at 4 hours[3]
References:
[1]. Gernaat SAM, von Stedingk H, et al. Cyclophosphamide exposure assessed with the biomarker phosphoramide mustard-hemoglobin in breast cancer patients: The TailorDose I study. Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 1;11(1):2707.
[2]. Naicker SD, Feerick CL, et al. Cyclophosphamide alters the tumor cell secretome to potentiate the anti-myeloma activity of daratumumab through augmentation of macrophage-mediated antibody dependent cellular phagocytosis. Oncoimmunology. 2021 Jan 25;10(1):1859263.
[3]. Narla ST, Bushnell DS, et al. Keratinocyte Growth Factor Reduces Injury and Leads to Early Recovery from Cyclophosphamide Bladder Injury. Am J Pathol. 2020 Jan;190(1):108-124.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 27 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *





