D-Pantothenic acid |
| Catalog No.GC17311 |
water-soluble vitamin
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
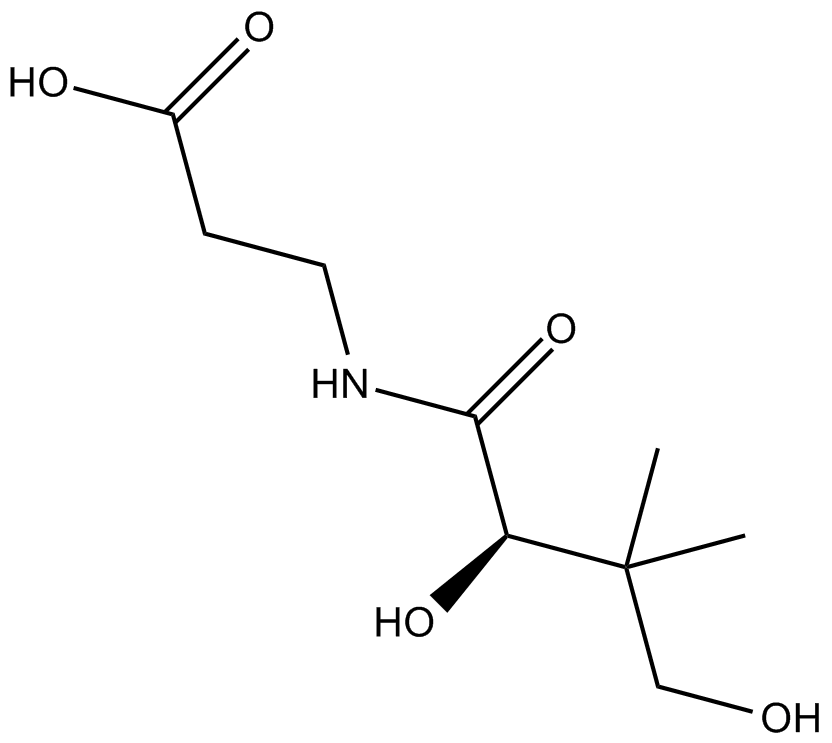
Cas No.: 79-83-4
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
D-Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) is a water-soluble vitamin and is an essential nutrient to synthesize coenzyme-A, fats, proteins and carbohydrates.
D-Pantothenic acid is a water-soluble vitamin. In rabbits, pentothenate (20 mg/kg) significantly increased aponeurosis strength after surgery and improved the strength of the skin. Also, pentothenate significantly increased the fibroblast content of the scar during the fibroblast proliferation phase [1]. Pantothenic acid deficiency increased occurrence of hypertension due to adrenal regeneration [2]. In rabbits, cerebellar and forebrain slices were able to accumulate and phosphorylate pantothenic acid. However, medium-chain fatty acids, probenecid and ouabain inhibited pantothenic acid accumulation by forebrain slices and inhibited conversion to CoA [3]. In ICR mice, pantothenic acid significantly reduced valproic acid (VPA)-induced exencephaly, which suggested that pantothenic acid inhibited neural tube defects induced by VPA [4].
References:
[1]. Aprahamian M, Dentinger A, Stock-Damgé C, et al. Effects of supplemental pantothenic acid on wound healing: experimental study in rabbit. Am J Clin Nutr, 1985, 41(3): 578-589.
[2]. Schwabedal PE, Pietrzik K, Wittkowski W. Pantothenic acid deficiency as a factor contributing to the development of hypertension. Cardiology, 1985, 72 Suppl 1: 187-189.
[3]. Spector R. Development and characterization of pantothenic acid transport in brain. J Neurochem, 1986, 47(2): 563-568.
[4]. Sato M, Shirota M, Nagao T. Pantothenic acid decreases valproic acid-induced neural tube defects in mice (I). Teratology, 1995, 52(3): 143-148.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 25 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















