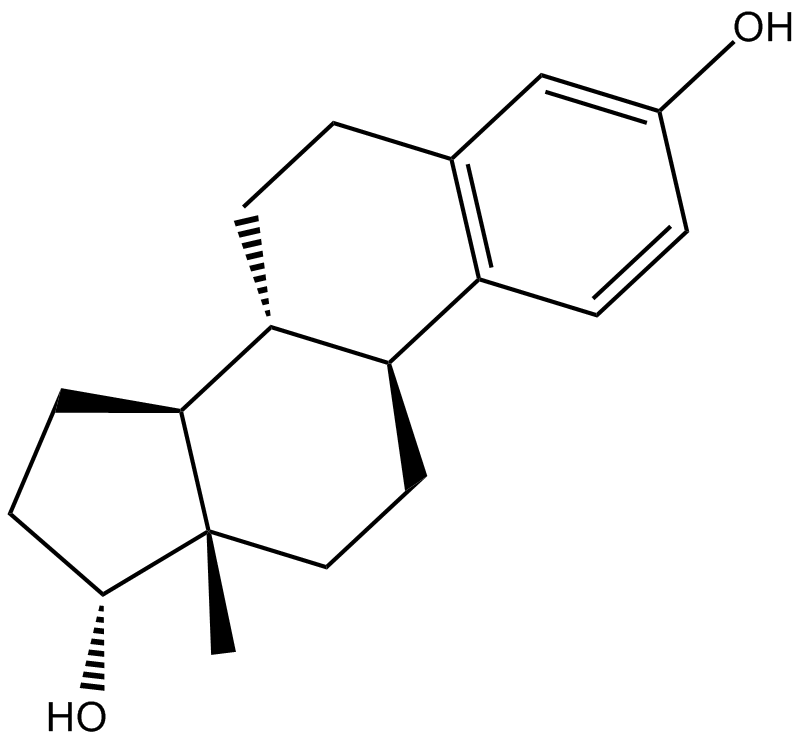
α-Estradiol (Synonyms: Alfatradiol, α-Estradiol, 17-epi Estradiol, NSC 20293, 17α-Oestradiol) |
| Katalog-Nr.GC15975 |
α-Estradiol ist ein schwaches Östrogen und ein 5&7#945;-Reduktasehemmer, der als topisches Medikament bei der Behandlung von androgener Alopezie verwendet wird.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
Cas No.: 57-91-0
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Alpha-Estradiol is a weak estrogen and a 5α-reductase inhibitor which is used as a topical medication in the treatment of androgenic alopecia.
Alpha-Estradiol (17 alpha-Estradiol) is a 5α-reductase inhibitor, and inhibits testosterone metabolism catalyzed by 5 alpha-reductase[1]. Alpha-Estradiol (17 Alpha-estradiol, 10 μM) attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory markers in both C57BL/6J male and female mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells, primary pre-adipocytes and differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes in an ERα-dependent manner, and such effects are through decreased NFκB-p65 and increased ERα protein expression[2].
Alpha-Estradiol (17-alpha-estradiol, 0.01, 0.1, 1 μg) significantly reduces the percentage of central avascular/total retina area of the mouse pups. Alpha-Estradiol (1 μg) markedly decreasesmalondialdehyde (MDA) levels on postnatal days (PND) 9, 13, and 17 in retinas of hyperoxia-exposed pups. Alpha-Estradiol (1 μg) also decreases the number of NADPH-oxidase-positive cells, NADPH oxidase concentration and activity in retinas of the pups. In the 1.0-μg Alpha-Estradiol-treated pups, VEGF retinal concentrations are high on PND 9 but lower on PND 14 and 17. The best effect in retinas of 1.0-μg Alpha-Estradiol-treated pups is partly reversed by ICI182780 on PND 14 and 17[3].
References:
[1]. Schriefers H, et al. Inhibition of testosterone metabolism by 17-alpha-estradiol in rat liver slices. Arzneimittelforschung. 1991 Nov;41(11):1186-9.
[2]. Santos RS, et al. The effects of 17 alpha-estradiol to inhibit inflammation in vitro. Biol Sex Differ. 2017 Sep 6;8:30.
[3]. Zhang HB, et al. 17-Alpha-estradiol ameliorating oxygen-induced retinopathy in a murine model. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2012 Jul;56(4):407-15.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 24 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















