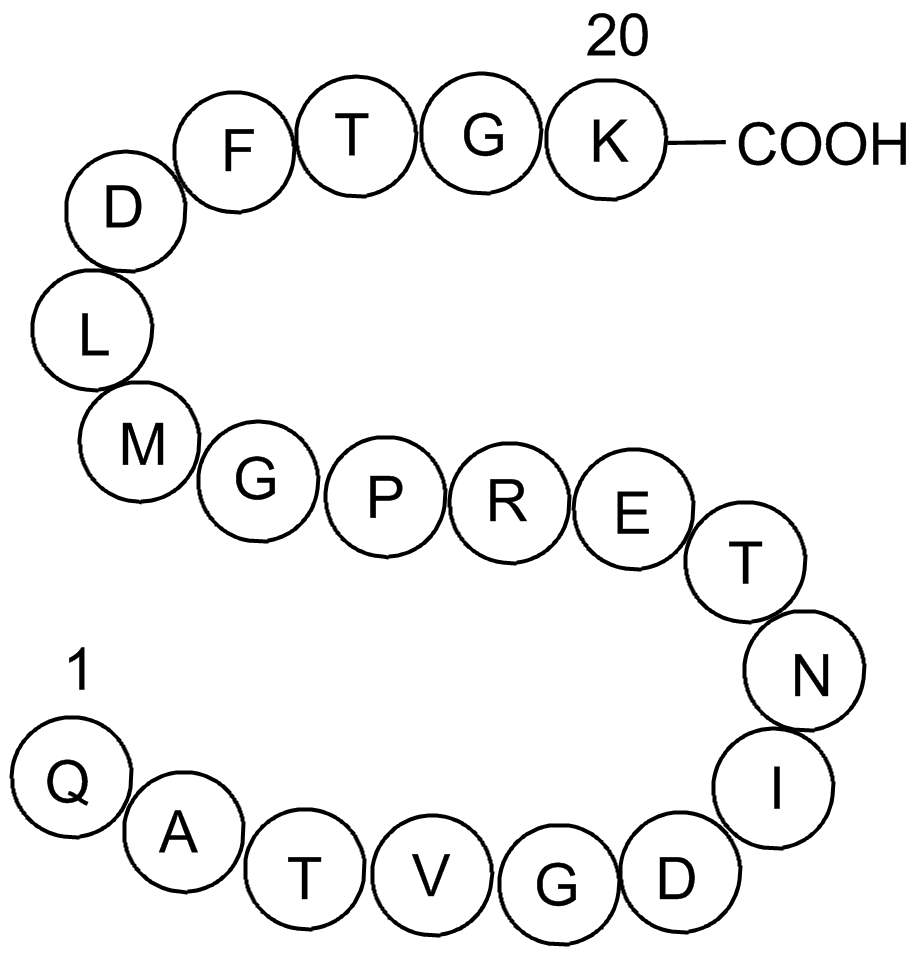
Diazepam-Binding Inhibitor Fragment, human (Synonyms: H2N-Gln-Ala-Thr-Val-Gly-Asp-Ile-Asn-Thr-Glu-Arg-Pro-Gly-Met-Leu-Asp-Phe-Thr-Gly-Lys-OH ) |
| Katalog-Nr.GP10126 |
Diazepam-Binding Inhibitor (DBI) Fragment is encoded by the DBI gene in human.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
Cas No.: 104360-70-5
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Diazepam-Binding Inhibitor (DBI) Fragment is encoded by the DBI gene in human. [1][2] It is a protein regulated by hormones and is involved in lipid metabolism and the displacement of beta-carbolines and benzodiazepines, which modulate signal transduction at type A gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors located in brain synapses. The protein is conserved from yeast to mammals, with the most highly conserved domain consisting of seven contiguous residues that constitute the hydrophobic binding site for medium- and long-chain acyl-Coenzyme A esters.
Diazepam binding inhibitor also mediates the feedback regulation of pancreatic secretion and the postprandial release of cholecystokinin, in addition to its role as a mediator in corticotropin-dependent synthesis of steroids in the adrenal gland. [2]

Fig 1. Structure of the DBI protein
Ref:
1. Todd S, Naylor SL (Dec 1992). "New chromosomal mapping assignments for argininosuccinate synthetase pseudogene 1, interferon-beta 3 gene, and the diazepam binding inhibitor gene". Somat Cell Mol Genet 18 (4): 381–5
2. Entrez Gene: DBI diazepam binding inhibitor (GABA receptor modulator, acyl-Coenzyme A binding protein)
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 30 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















