E-64 |
| Katalog-Nr.GC13418 |
Ein Pilzmetabolit mit vielfältigen biologischen Aktivitäten.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
Cas No.: 66701-25-5
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
E-64 is a potent and irreversible inhibitor of cysteine proteases with an IC50 of 9nM for papain[1]. E-64 can inhibit the cysteine proteases cathepsin B, H, L and papain, but has no effect on serine proteases or metalloproteinases[2]. E-64 has antiparasitic activity in vitro and can induce oxidative stress and apoptosis in filarial parasites[3]. E-64 can improve the preimplantation development of bovine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos[4].
In vitro, E-64 (0-50μM) treatment of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells for 24h increased the amount of intracellular active cathepsin S and reduced the amount of cathepsin L in a dose-dependent manner[5]. E-64 (4mM) treatment of porcine alveolar macrophages (PAM) for 48h upregulated the mRNA levels of IFNγ, IL-12 and IFN-α in cells without cytotoxicity[6].
In vivo, daily intravenous infusion of E-64 (1mg) in Dahl salt-sensitive rats significantly increased the mature forms of the lysosomal proteases Cath B and Cath L in the renal cortex of rats, but had no effect on high-salt diet-induced hypertension and renal damage[7].
References:
[1] Matsumoto K, Mizoue K, Kitamura K, et al. Structural basis of inhibition of cysteine proteases by E‐64 and its derivatives[J]. Peptide Science, 1999, 51(1): 99-107.
[2] Barrett A J, Kembhavi A A, Brown M A, et al. L-trans-Epoxysuccinyl-leucylamido (4-guanidino) butane (E-64) and its analogues as inhibitors of cysteine proteinases including cathepsins B, H and L[J]. Biochemical Journal, 1982, 201(1): 189-198.
[3] Wadhawan M, Singh N, Rathaur S. Inhibition of cathepsin B by E-64 induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in filarial parasite[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(3): e93161.
[4] Min S H, Song B S, Yeon J Y, et al. A cathepsin B inhibitor, E-64, improves the preimplantation development of bovine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos[J]. Journal of Reproduction and Development, 2014, 60(1): 21-27.
[5] Wilder C L, Walton C, Watson V, et al. Differential cathepsin responses to inhibitor-induced feedback: E-64 and cystatin C elevate active cathepsin S and suppress active cathepsin L in breast cancer cells[J]. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 2016, 79: 199-208.
[6] Liu B, Cui Y, Lu G, et al. Small molecule inhibitor E-64 exhibiting the activity against African swine fever virus pS273R[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2021, 35: 116055.
[7] Blass G, Levchenko V, Ilatovskaya D V, et al. Chronic cathepsin inhibition by E‐64 in Dahl salt‐sensitive rats[J]. Physiological reports, 2016, 4(17): e12950.
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
Cell lines | MDA-MB-231 cells |
Preparation Method | Confluent MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with E-64 concentrations ranging from 0 to 50μM for 24h. Cells were lysed and subjected to multiplex cathepsin zymography to detect changes in the amount of active material. |
Reaction Conditions | 0-50μM; 24h |
Applications | E-64 treatment significantly increased the amount of active cathepsin S, while significantly decreased the amount of cathepsin L in cell lysates. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
Animal models | Dahl Salt Sensitive rats (SS/JrHsdMcwi) |
Preparation Method | Dahl Salt Sensitive rats (SS/JrHsdMcwi) had their left femoral artery and vein catheterized. Both catheters were fixed and exteriorized from the back of the neck and the arterial line was connected to a heparinized saline infusion pump that was in line with a blood pressure transducer, and the venous line was connected to a saline infusion pump. Animals were allowed 360° movement using a tether-swivel system. A stable baseline blood pressure was obtained for 4 days prior to switching both groups to an 8.0% NaCl diet and the simultaneous addition of N-[N-(L-3-trans-carboxyox-irane-2-carbonyl)-L-leucyl]-agmatine (E-64, 1mg/day; 280mM stock in DMSO) or the vehicle control to the venous catheter. Daily mean arterial pressure (MAP) was calculated by averaging MAP taken every min over the beginning 3 h period of the rat sleep cycle. |
Dosage form | 1mg/day; i.v. |
Applications | A significant increase in the renal cortical mature form of Cath B and Cath L were measured in E-64 treated rats. |
References: [1]Wilder C L, Walton C, Watson V, et al. Differential cathepsin responses to inhibitor-induced feedback: E-64 and cystatin C elevate active cathepsin S and suppress active cathepsin L in breast cancer cells[J]. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 2016, 79: 199-208. [2]Blass G, Levchenko V, Ilatovskaya D V, et al. Chronic cathepsin inhibition by E‐64 in Dahl salt‐sensitive rats[J]. Physiological reports, 2016, 4(17): e12950. | |
| Cas No. | 66701-25-5 | SDF | |
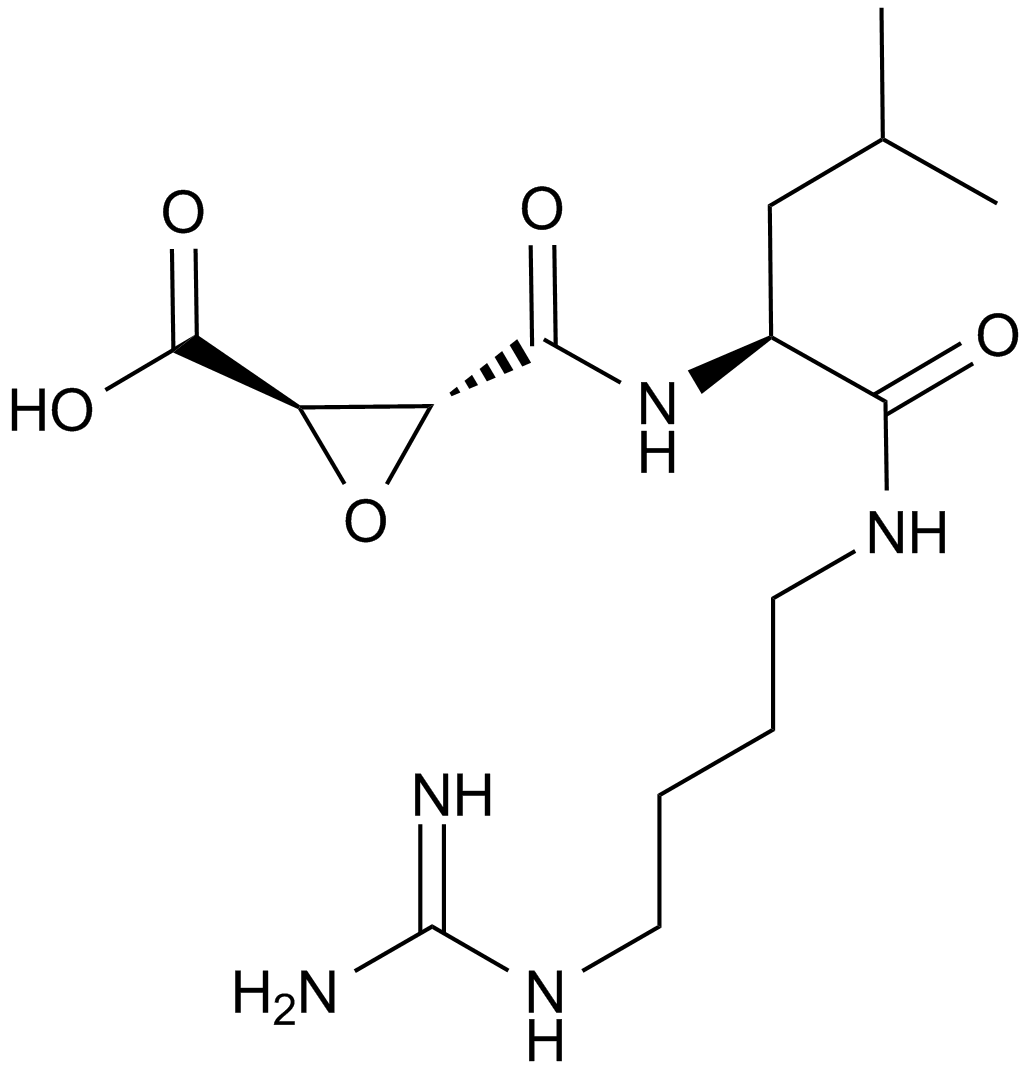
| Chemical Name | (2S,3S)-3-[[(2S)-1-[4-(diaminomethylideneamino)butylamino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]carbamoyl]oxirane-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| Canonical SMILES | CC(C)CC(C(=O)NCCCCN=C(N)N)NC(=O)C1C(O1)C(=O)O | ||
| Formula | C15H27N5O5 | M.Wt | 357.41 |
| Löslichkeit | ≥ 53.6mg/mL in DMSO | Storage | Store at 2-8°C |
| General tips | Please select the appropriate solvent to prepare the stock solution according to the
solubility of the product in different solvents; once the solution is prepared, please store it in
separate packages to avoid product failure caused by repeated freezing and thawing.Storage method
and period of the stock solution: When stored at -80°C, please use it within 6 months; when stored
at -20°C, please use it within 1 month. To increase solubility, heat the tube to 37°C and then oscillate in an ultrasonic bath for some time. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Evaluation sample solution: shipped with blue ice. All other sizes available: with RT, or with Blue Ice upon request. | ||
| Prepare stock solution | |||

|
1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg |
| 1 mM | 2.7979 mL | 13.9895 mL | 27.9791 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5596 mL | 2.7979 mL | 5.5958 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2798 mL | 1.399 mL | 2.7979 mL |
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
 g
g
 μL
μL

Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
3. All of the above co-solvents are available for purchase on the GlpBio website.
Quality Control & SDS
- View current batch:
- Purity: >98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- SDS (Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 30 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *



















