E3330 (Synonyms: APX 3330) |
| Katalog-Nr.GC10620 |
E3330 ist ein niedermolekularer Inhibitor der apurinischen/apyrimidinischen Endonuklease/Redox-Effektor-Funktion (APE1/Ref-1) des Redox-Domänensystems (IC50, 50 µmol/L).
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
Cas No.: 136164-66-4
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
E3330 ist ein niedermolekularer Inhibitor der apurinischen/apyrimidinischen Endonuklease/Redox-Effektor-Funktion (APE1/Ref-1) des Redox-Domänensystems (IC50, 50 µmol/L) [1,2].
E3330 (10-30 µM, 72h) hemmt nicht nur das Wachstum, sondern auch die Migrationsfähigkeiten von Pankreaskrebszellen in vitro [1]. Die gemeinsame Inkubation von E3330 (30 µM, 3 h) und Cisplatin (5-20 µM, 72 h) verringerte die Zellviabilität in der humanen NSCLC-Zelllinie H1975 im Vergleich zu Cisplatin allein signifikant [3]. Die Behandlung mit E3330 verhinderte die funktionelle Aktivierung von NF-κB durch die Veränderung des subzellulären Transports von APE1 und reduzierte die durch TNF-α induzierte Expression von IL-6 und IL-8 [4]. E3330 unterdrückte deutlich die Sekretion von entzündlichen Zytokinen einschließlich Tumornekrosefaktor-α (TNF-α), Interleukin (IL-6) und IL-12 sowie entzündliche Mediatoren wie Stickstoffmonoxid (NO) und Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) aus den LPS-stimulierten RAW264.7-Zellen [5].
Die Behandlung mit E3330 (10-100 mg/kg, oral) 1 Stunde nach der Galaktosamin-Herausforderung verringerte die Leberschädigung. E3330 war wirksam, wenn es p.o. 6 oder 12 Stunden nach der Galaktosamin-Herausforderung im Galaktosamin-induzierten Hepatitis-Modell bei F344-Ratten verabreicht wurde [6]. Die Injektion von TNF in Kombination mit Galaktosamin führte zu schweren Leberschäden. Eine orale Vorbehandlung mit 100 und 300 mg/kg E3330 30 Minuten vor der Injektion von Galaktosamin/TNF verringerte signifikant den Anstieg der Plasma-L-Alanin-Aminotransferase- und L-Aspartat-Aminotransferase-Aktivitäten [7]. Die geschätzte Halbwertszeit (t1/2) von E3330 betrug 3,7 Stunden bei Mäusen [2].
References:
[1]. Zou G M, Maitra A. Small-molecule inhibitor of the AP endonuclease 1/REF-1 E3330 inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth and migration[J]. Molecular cancer therapeutics, 2008, 7(7): 2012-2021.
[2]. Fishel M L, Colvin E S, Luo M, et al. Inhibition of the redox function of APE1/Ref-1 in myeloid leukemia cell lines results in a hypersensitive response to retinoic acid-induced differentiation and apoptosis[J]. Experimental hematology, 2010, 38(12): 1178-1188.
[3]. Manguinhas R, Fernandes A S, Costa J G, et al. Impact of the APE1 redox function inhibitor E3330 in non-small cell lung cancer cells exposed to cisplatin: increased cytotoxicity and impairment of cell migration and invasion[J]. Antioxidants, 2020, 9(6): 550.
[4]. Cesaratto L, Codarin E, Vascotto C, et al. Specific inhibition of the redox activity of ape1/ref-1 by e3330 blocks tnf-α-induced activation of IL-8 production in liver cancer cell lines[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(8): e70909.
[5]. Jedinak A, Dudhgaonkar S, Kelley M R, et al. Apurinic/Apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 regulates inflammatory response in macrophages[J]. Anticancer research, 2011, 31(2): 379-385.
[6]. Nagakawa J, Hirota K, Hishinuma I, et al. Protective effect of E3330, a novel quinone derivative, in galactosamine-induced hepatitis in rats[J]. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 1993, 264(1): 496-500.
[7]. Nagakawa J, Hishinuma I, Hirota K, et al. Protective effects of E3330, a novel quinone derivative, on galactosamine/tumor necrosis factor-α-induced hepatitis in mice[J]. European journal of pharmacology, 1992, 229(1): 63-67.
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
Cell lines | Pancreatic cancer PaCa-2 and Panc-1 cells |
Preparation Method | Cells were were maintained at 37 ⊿in 5% CO2 and grown in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium with 10% cosmic calf serum. PaCa-2 and Panc-1 cells were treated with E3330 for 72 and 48 hours, respectively. |
Reaction Conditions | 0-135 µM for 48, 72 h |
Applications | E3330 was found to effectively slow the growth rate of cells in a dose-dependent manner, with an ED50 of 135 and 87 µmol/L for PaCa-2 and Panc-1, respectively. |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
Animal models | Nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient mice (NOD/SCID) mice |
Preparation Method | PaCa-2 cells (2.5 × 106) in 0.2 mL of DMEM media were implanted s.c. into the right flanks of NOD/SCID mice. E3330 was dissolved in 4% CremophorEL:EtOH (1:1)/saline solution or methylcellulose (0.5%). When tumor volumes were greater than 100 mm3, E3330 was administered orally twice daily, 8 hours apart, at 25 mg/kg for 10 to 12 days (5 days on 2 days off schedule). Tumors were measured biweekly and followed for approximately 6 weeks. |
Dosage form | 25 mg/kg, orally twice daily, for 10 to 12 days (5 days on 2 days off schedule) |
Applications | In contrast to vehicle-control tumors, PaCa-2 xenografts showed a significant tumor growth delay. |
References: | |
| Cas No. | 136164-66-4 | SDF | |
| Überlieferungen | APX 3330 | ||
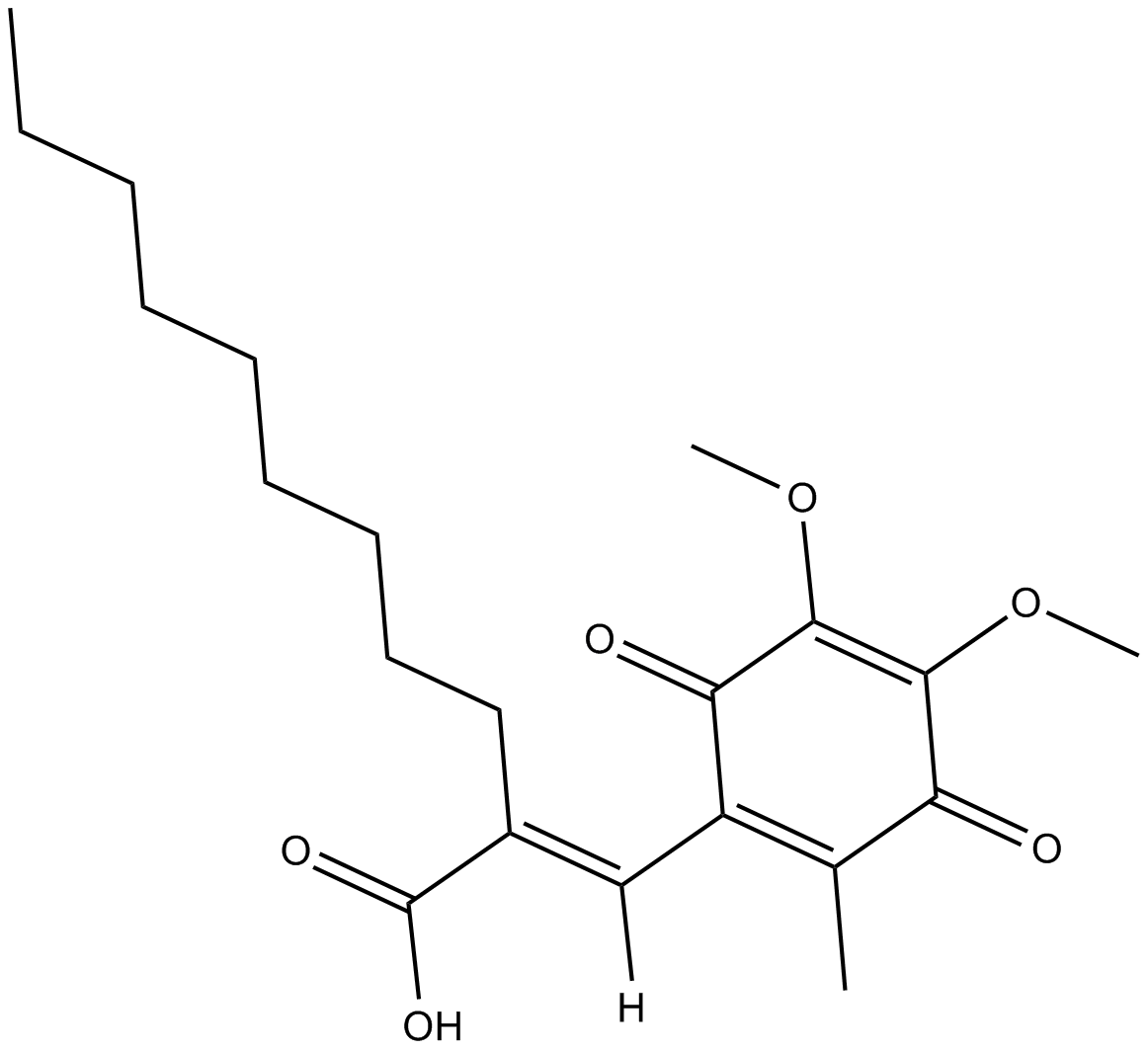
| Chemical Name | (E)-2-((4,5-dimethoxy-2-methyl-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl)methylene)undecanoic acid | ||
| Canonical SMILES | CCCCCCCCC/C(C(O)=O)=C([H])\C(C1=O)=C(C(C(OC)=C1OC)=O)C | ||
| Formula | C21H30O6 | M.Wt | 378.46 |
| Löslichkeit | ≥ 75.4mg/mL in DMSO, ≥ 75.4mg/mL in EtOH | Storage | Store at -20°C |
| General tips | Please select the appropriate solvent to prepare the stock solution according to the
solubility of the product in different solvents; once the solution is prepared, please store it in
separate packages to avoid product failure caused by repeated freezing and thawing.Storage method
and period of the stock solution: When stored at -80°C, please use it within 6 months; when stored
at -20°C, please use it within 1 month. To increase solubility, heat the tube to 37°C and then oscillate in an ultrasonic bath for some time. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Evaluation sample solution: shipped with blue ice. All other sizes available: with RT, or with Blue Ice upon request. | ||
| Prepare stock solution | |||

|
1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg |
| 1 mM | 2.6423 mL | 13.2114 mL | 26.4229 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5285 mL | 2.6423 mL | 5.2846 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2642 mL | 1.3211 mL | 2.6423 mL |
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
 g
g
 μL
μL

Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
3. All of the above co-solvents are available for purchase on the GlpBio website.
Quality Control & SDS
- View current batch:
- Purity: >98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- SDS (Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 16 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *



