Linoleoyl Ethanolamide (Synonyms: LEA) |
| Katalog-Nr.GC44072 |
Linoleoyl ethanolamide is an endocannabinoid detected in porcine brain and murine peritoneal macrophages which contains linoleate in place of the arachidonate moiety of arachidonyl ethanolamide (AEA).
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
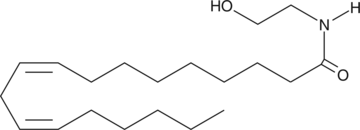
Cas No.: 68171-52-8
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Linoleoyl ethanolamide is an endocannabinoid detected in porcine brain and murine peritoneal macrophages which contains linoleate in place of the arachidonate moiety of arachidonyl ethanolamide (AEA). [1] [2] It has weak affinity for the cannabinoid 1 (CB1) and CB2 receptors, exhibiting Ki values of 10 µM and 25 µM, respectively.[3] However, it is only approximately 4-fold less potent than AEA at causing catalepsy in mice (ED50 of 26.5 mg/kg). [4] In addition, linoleoyl ethanolamide increases ERK phosphorylation and AP-1-dependent transcription approximately 1.5 fold at 15 µM in a CB-receptor-independent manner.[5] However, cellular toxicity is readily apparent at concentrations of 10-20 µM. Linoleoyl ethanolamide inhibits human fatty acid amide hydrolase-dependent hydrolysis of AEA with a Ki value of 9.0 µM, but also is hydrolyzed effectively by the enzyme. [6][7]
Reference:
[1]. Patrono, C., Rotella, C.M., Toccafondi, R.S., et al. Prostacyclin stimulates the adenylate cyclase system of human thyroid tissue. Prostaglandins 22(1), 105-115 (1981).
[2]. Schmid, P.C., Kuwae, T., Krebsbach, R.J., et al. Anandanide and other N-acylethanolamines in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 87, 103-110 (1997).
[3]. Lin, S., Khanolkar, A.D., Fan, P., et al. Novel analogues of arachidonylethanolamide (anandamide): Affinities for the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors and metabolic stability. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 41, 5353-5361 (1998).
[4]. Watanabe, K., Matsunaga, T., Nakamura, S., et al. Pharmacological effects in mice of anandamide and its related fatty acid ethanolamides, and enhancement of cataleptogenic effect of anandamide by phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bullentin 22(4), 366-370 (1999).
[5]. Berdyshev, E.V., Schmid, P.C., Krebsbach, R.J., et al. Cannabinoid-receptor-independent cell signalling by N-acylethanolamines. Biochemistry Journal 360, 67-75 (2001).
[6]. Maccarrone, M., van der Stelt, M., Rossi, A., et al. Anandamide hydrolysis by human cells in culture and brain. The Journal of Biological Chemisty 273, 32332-32339 (1998).
[7]. Bisogno, T., Maurelli, S., Melck, D., et al. Biosynthesis, uptake, and degradation of anandamide and palmitoylethanolamide in leukocytes. The Journal of Biological Chemisty 272, 3315-3323 (1997).
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 8 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















