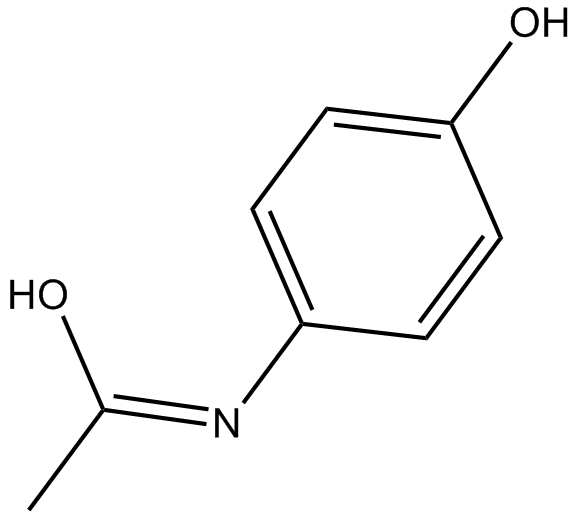
Acetaminophen (Synonyms: 4-Acetamidophenol, APAP, 4'-Hydroxyacetanilide, NSC 3991, NSC 109028, Paracetamol) |
| Katalog-Nr.GC12917 |
Ein COX-Inhibitor
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
Cas No.: 103-90-2
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Acetaminophen (paracetamol) is a selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor with an IC50 of 25.8 μM; is a widely used antipyretic and analgesic drug.
n vitro, acetaminophen elicites a 4.4-fold selectivity toward COX-2 inhibition (IC50 113.7 μM for COX-1; IC50 25.8 μM for COX-2). Following oral administration of the drug, maximal ex vivo inhibitions are 56% (COX-1) and 83% (COX-2). Acetaminophen plasma concentrations remaine above the in vitro IC50 for COX-2 for at least 5 h postadministration. Ex vivo IC50 values (COX-1: 105.2 μM; COX-2: 26.3 μM) of acetaminophen compared favorably with its in vitro IC50 values. In contrast to previous concepts, acetaminophen inhibited COX-2 by more than 80%, i.e., to a degree comparable to nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and selective COX-2 inhibitors. However, a >95% COX-1 blockade relevant for suppression of platelet function is not achieved[1]. MTT assay shows that Acetaminophen (APAP) in a dose of 50 mM significantly (p<0.001) reduces cell viability to 61.5±6.65%. Interestingly, the significant (p<0.01) increase in cell viability to 79.7±2.47% is observed in the Acetaminophen/HV110 co-treated cells, compared to Acetaminophen treated cells[2].
Administering Acetaminophen (250 mg/kg, orally) to the mice causes significant (p<0.001) liver damage and necrosis of cells as evidenced by the elevated serum hepatic enzymes alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (γGT) compared with normal group. Conversely, effects of pretreatment with different doses of citral (125, 250, and 500 mg/kg) exhibited a significant (p<0.05) decrease in serum activities of ALT (91.79%, 93.07%, and 95.61%, resp.), AST (93.40%, 91.89%, and 96.52%, resp.), ALP (39.29%, 37.07%, and 59.80%, resp.), and γGT (92.83%, 91.59%, and 93.0%, resp.), when compared to the Acetaminophen group. Similar results were found in pretreatment with SLM on the activity of ALT (95.90%), AST (95.03%), ALP (70.52%), and γGT (92.69%)[3].
Reference:
[1]. Hinz, B, et al. Acetaminophen (paracetamol) is a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor in man. FASEB J, 2008. 22(2): p. 383-90.
[2]. Dini? M, et al. Lactobacillus fermentum Postbiotic-induced Autophagy as Potential Approach for Treatment ofAcetaminophen Hepatotoxicity. Front Microbiol. 2017 Apr 6;8:594.
[3]. Uchida NS, et al. Hepatoprotective Effect of Citral on Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Toxicity in Mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:1796209.
n vitro, acetaminophen elicites a 4.4-fold selectivity toward COX-2 inhibition (IC50 113.7 μM for COX-1; IC50 25.8 μM for COX-2). Following oral administration of the drug, maximal ex vivo inhibitions are 56% (COX-1) and 83% (COX-2). Acetaminophen plasma concentrations remaine above the in vitro IC50 for COX-2 for at least 5 h postadministration. Ex vivo IC50 values (COX-1: 105.2 μM; COX-2: 26.3 μM) of acetaminophen compared favorably with its in vitro IC50 values. In contrast to previous concepts, acetaminophen inhibited COX-2 by more than 80%, i.e., to a degree comparable to nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and selective COX-2 inhibitors. However, a >95% COX-1 blockade relevant for suppression of platelet function is not achieved[1]. MTT assay shows that Acetaminophen (APAP) in a dose of 50 mM significantly (p<0.001) reduces cell viability to 61.5±6.65%. Interestingly, the significant (p<0.01) increase in cell viability to 79.7±2.47% is observed in the Acetaminophen/HV110 co-treated cells, compared to Acetaminophen treated cells[2].
Administering Acetaminophen (250 mg/kg, orally) to the mice causes significant (p<0.001) liver damage and necrosis of cells as evidenced by the elevated serum hepatic enzymes alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (γGT) compared with normal group. Conversely, effects of pretreatment with different doses of citral (125, 250, and 500 mg/kg) exhibited a significant (p<0.05) decrease in serum activities of ALT (91.79%, 93.07%, and 95.61%, resp.), AST (93.40%, 91.89%, and 96.52%, resp.), ALP (39.29%, 37.07%, and 59.80%, resp.), and γGT (92.83%, 91.59%, and 93.0%, resp.), when compared to the Acetaminophen group. Similar results were found in pretreatment with SLM on the activity of ALT (95.90%), AST (95.03%), ALP (70.52%), and γGT (92.69%)[3].
Reference:
[1]. Hinz, B, et al. Acetaminophen (paracetamol) is a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor in man. FASEB J, 2008. 22(2): p. 383-90.
[2]. Dini? M, et al. Lactobacillus fermentum Postbiotic-induced Autophagy as Potential Approach for Treatment ofAcetaminophen Hepatotoxicity. Front Microbiol. 2017 Apr 6;8:594.
[3]. Uchida NS, et al. Hepatoprotective Effect of Citral on Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Toxicity in Mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:1796209.
Review for Acetaminophen
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 36 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
Review for Acetaminophen
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















