Apoptosis
As one of the cellular death mechanisms, apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, can be defined as the process of a proper death of any cell under certain or necessary conditions. Apoptosis is controlled by the interactions between several molecules and responsible for the elimination of unwanted cells from the body.
Many biochemical events and a series of morphological changes occur at the early stage and increasingly continue till the end of apoptosis process. Morphological event cascade including cytoplasmic filament aggregation, nuclear condensation, cellular fragmentation, and plasma membrane blebbing finally results in the formation of apoptotic bodies. Several biochemical changes such as protein modifications/degradations, DNA and chromatin deteriorations, and synthesis of cell surface markers form morphological process during apoptosis.
Apoptosis can be stimulated by two different pathways: (1) intrinsic pathway (or mitochondria pathway) that mainly occurs via release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria and (2) extrinsic pathway when Fas death receptor is activated by a signal coming from the outside of the cell.
Different gene families such as caspases, inhibitor of apoptosis proteins, B cell lymphoma (Bcl)-2 family, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor gene superfamily, or p53 gene are involved and/or collaborate in the process of apoptosis.
Caspase family comprises conserved cysteine aspartic-specific proteases, and members of caspase family are considerably crucial in the regulation of apoptosis. There are 14 different caspases in mammals, and they are basically classified as the initiators including caspase-2, -8, -9, and -10; and the effectors including caspase-3, -6, -7, and -14; and also the cytokine activators including caspase-1, -4, -5, -11, -12, and -13. In vertebrates, caspase-dependent apoptosis occurs through two main interconnected pathways which are intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. The intrinsic or mitochondrial apoptosis pathway can be activated through various cellular stresses that lead to cytochrome c release from the mitochondria and the formation of the apoptosome, comprised of APAF1, cytochrome c, ATP, and caspase-9, resulting in the activation of caspase-9. Active caspase-9 then initiates apoptosis by cleaving and thereby activating executioner caspases. The extrinsic apoptosis pathway is activated through the binding of a ligand to a death receptor, which in turn leads, with the help of the adapter proteins (FADD/TRADD), to recruitment, dimerization, and activation of caspase-8 (or 10). Active caspase-8 (or 10) then either initiates apoptosis directly by cleaving and thereby activating executioner caspase (-3, -6, -7), or activates the intrinsic apoptotic pathway through cleavage of BID to induce efficient cell death. In a heat shock-induced death, caspase-2 induces apoptosis via cleavage of Bid.
Bcl-2 family members are divided into three subfamilies including (i) pro-survival subfamily members (Bcl-2, Bcl-xl, Bcl-W, MCL1, and BFL1/A1), (ii) BH3-only subfamily members (Bad, Bim, Noxa, and Puma9), and (iii) pro-apoptotic mediator subfamily members (Bax and Bak). Following activation of the intrinsic pathway by cellular stress, pro‑apoptotic BCL‑2 homology 3 (BH3)‑only proteins inhibit the anti‑apoptotic proteins Bcl‑2, Bcl-xl, Bcl‑W and MCL1. The subsequent activation and oligomerization of the Bak and Bax result in mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). This results in the release of cytochrome c and SMAC from the mitochondria. Cytochrome c forms a complex with caspase-9 and APAF1, which leads to the activation of caspase-9. Caspase-9 then activates caspase-3 and caspase-7, resulting in cell death. Inhibition of this process by anti‑apoptotic Bcl‑2 proteins occurs via sequestration of pro‑apoptotic proteins through binding to their BH3 motifs.
One of the most important ways of triggering apoptosis is mediated through death receptors (DRs), which are classified in TNF superfamily. There exist six DRs: DR1 (also called TNFR1); DR2 (also called Fas); DR3, to which VEGI binds; DR4 and DR5, to which TRAIL binds; and DR6, no ligand has yet been identified that binds to DR6. The induction of apoptosis by TNF ligands is initiated by binding to their specific DRs, such as TNFα/TNFR1, FasL /Fas (CD95, DR2), TRAIL (Apo2L)/DR4 (TRAIL-R1) or DR5 (TRAIL-R2). When TNF-α binds to TNFR1, it recruits a protein called TNFR-associated death domain (TRADD) through its death domain (DD). TRADD then recruits a protein called Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD), which then sequentially activates caspase-8 and caspase-3, and thus apoptosis. Alternatively, TNF-α can activate mitochondria to sequentially release ROS, cytochrome c, and Bax, leading to activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 and thus apoptosis. Some of the miRNAs can inhibit apoptosis by targeting the death-receptor pathway including miR-21, miR-24, and miR-200c.
p53 has the ability to activate intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis by inducing transcription of several proteins like Puma, Bid, Bax, TRAIL-R2, and CD95.
Some inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) can inhibit apoptosis indirectly (such as cIAP1/BIRC2, cIAP2/BIRC3) or inhibit caspase directly, such as XIAP/BIRC4 (inhibits caspase-3, -7, -9), and Bruce/BIRC6 (inhibits caspase-3, -6, -7, -8, -9).
Any alterations or abnormalities occurring in apoptotic processes contribute to development of human diseases and malignancies especially cancer.
References:
1.Yağmur Kiraz, Aysun Adan, Melis Kartal Yandim, et al. Major apoptotic mechanisms and genes involved in apoptosis[J]. Tumor Biology, 2016, 37(7):8471.
2.Aggarwal B B, Gupta S C, Kim J H. Historical perspectives on tumor necrosis factor and its superfamily: 25 years later, a golden journey.[J]. Blood, 2012, 119(3):651.
3.Ashkenazi A, Fairbrother W J, Leverson J D, et al. From basic apoptosis discoveries to advanced selective BCL-2 family inhibitors[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2017.
4.McIlwain D R, Berger T, Mak T W. Caspase functions in cell death and disease[J]. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology, 2013, 5(4): a008656.
5.Ola M S, Nawaz M, Ahsan H. Role of Bcl-2 family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis[J]. Molecular and cellular biochemistry, 2011, 351(1-2): 41-58.
What is Apoptosis? The Apoptotic Pathways and the Caspase Cascade
Ziele für Apoptosis
- Pyroptosis(31)
- Caspase(54)
- 14.3.3 Proteins(1)
- Apoptosis Inducers(41)
- Bax(8)
- Bcl-2 Family(108)
- Bcl-xL(8)
- c-RET(8)
- IAP(26)
- KEAP1-Nrf2(68)
- MDM2(13)
- p53(112)
- PC-PLC(4)
- PKD(7)
- RasGAP (Ras- P21)(1)
- Survivin(6)
- Thymidylate Synthase(10)
- TNF-α(131)
- Other Apoptosis(884)
- Apoptosis Detection(0)
- Caspase Substrate(0)
- APC(5)
- PD-1/PD-L1 interaction(61)
- ASK1(3)
- PAR4(2)
- RIP kinase(50)
- FKBP(19)
- Cuproptosis(0)
Produkte für Apoptosis
- Bestell-Nr. Artikelname Informationen
-
GC12545
2-HBA
Bis(2-hydroxybenzylidene)acetone
2-HBA ist ein starker Induktor der NAD(P)H:Chinon-Akzeptor-Oxidoreduktase 1 (NQO1), die auch Caspase-3 und Caspase-10 aktivieren kann.
-
GC38318
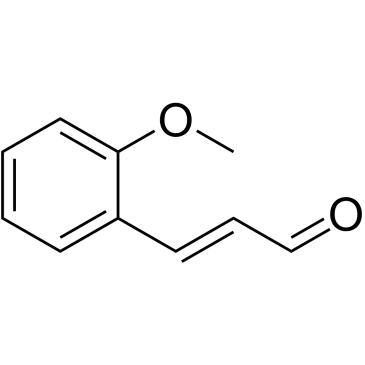
2-Methoxycinnamaldehyde
2-Methoxyzimtaldehyd (o-Methoxyzimtaldehyd) ist eine natÜrliche Verbindung von Cinnamomum cassia mit AntitumoraktivitÄt. 2-Methoxyzimtaldehyd hemmt die Proliferation und induziert Apoptose durch Verlust des mitochondrialen Membranpotentials (δψm), Aktivierung von Caspase-3 und Caspase-9. 2-Methoxyzimtaldehyd hemmt wirksam die durch den BlutplÄttchen-Wachstumsfaktor (PDGF) induzierte HASMC-Migration.
-
GC15084
2-Methoxyestradiol (2-MeOE2)
2Hydroxyestradiol 2methyl ether, 2ME2, NSC 659853, Panzem
2-Methoxyestradiol (2-MeOE2/2-Me) is an HIF-1α inhibitor.
-
GC68043
2-tert-Butyl-1,4-benzoquinone
-
GC15355
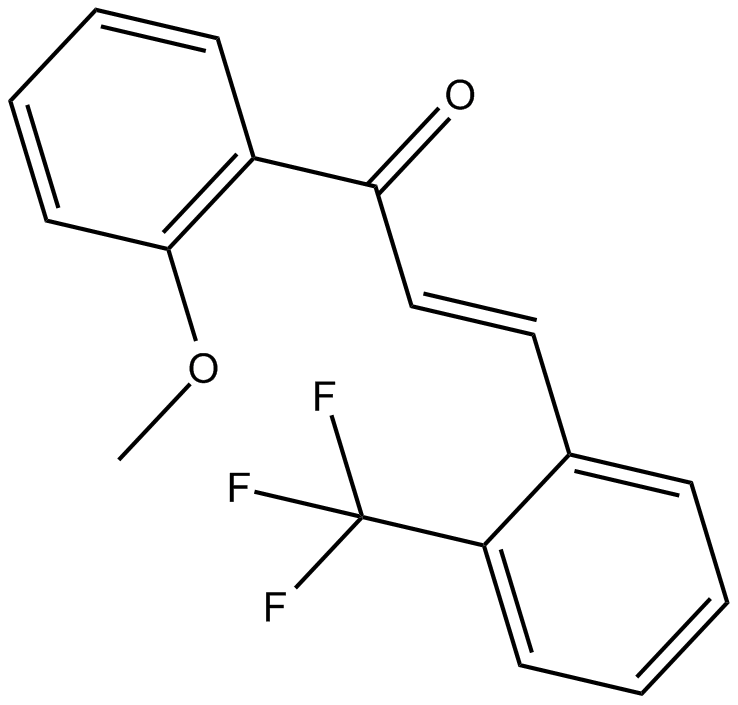
2-Trifluoromethyl-2'-methoxychalcone
Nrf2 activator
-
GN10800
20(S)-NotoginsenosideR2
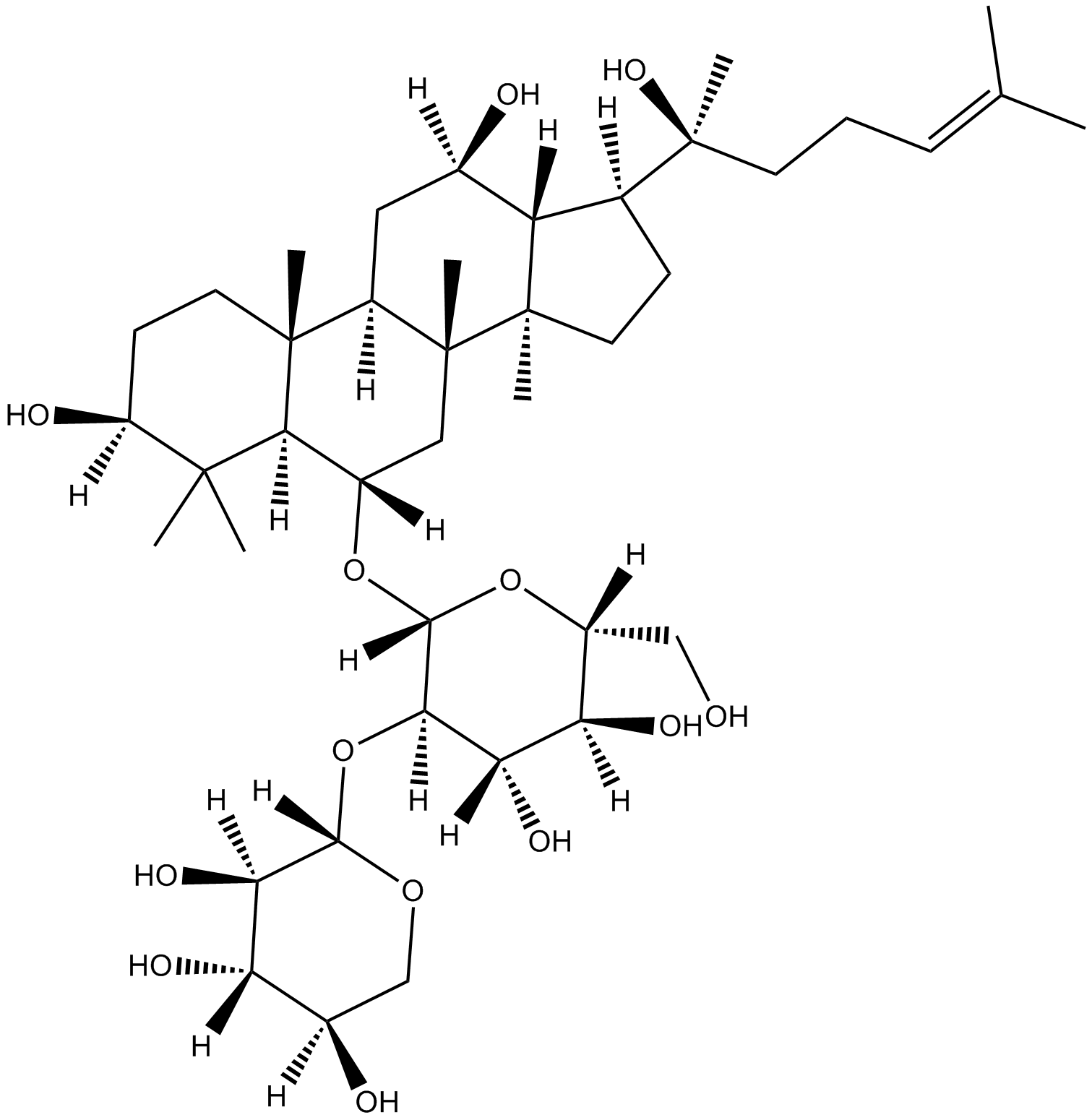
-
GC46528
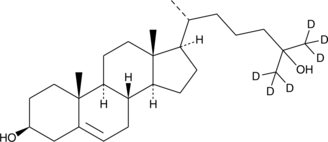
25-hydroxy Cholesterol-d6
An internal standard for the quantification of 25hydroxy cholesterol
-
GC48482
28-Acetylbetulin
28-acetoxy Betulin, 28-O-Acetylbetulin, C-28-Acetylbetulin
A lupane triterpenoid with anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities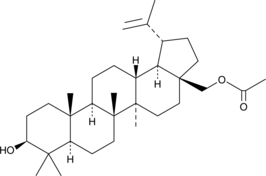
-
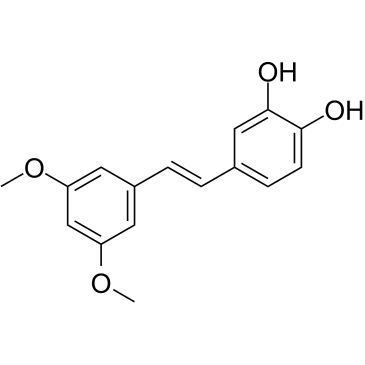
GC35112
3'-Hydroxypterostilbene
3'-Hydroxypterostilben ist ein Pterostilben-Analogon. 3'-Hydroxypterostilben hemmt das Wachstum von COLO 205-, HCT-116- und HT-29-Zellen mit IC50-Werten von 9,0, 40,2 bzw. 70,9 μM. 3'-Hydroxypterostilben reguliert die PI3K/Akt- und MAPK-Signalwege signifikant herunter und hemmt wirksam das Wachstum menschlicher Dickdarmkrebszellen, indem es Apoptose und Autophagie induziert. 3'-Hydroxypterostilben kann fÜr die Krebsforschung verwendet werden.
-
GC12791
3,3'-Diindolylmethane
DIM
A phytochemical with antiradiation and chemopreventative effects
-
GC42237
3,5-dimethyl PIT-1
PtdIns-(3,4,5)-P3 (PIP3) serves as an anchor for the binding of signal transduction proteins bearing pleckstrin homology (PH) domains such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) or PTEN.
-
GC64762
3,6-Dihydroxyflavone
3,6-Dihydroxyflavon ist ein Antikrebsmittel. 3,6-Dihydroxyflavon verringert dosis- und zeitabhÄngig die ZelllebensfÄhigkeit und induziert Apoptose durch Aktivierung der Caspase-Kaskade, Spaltung der Poly(ADP-Ribose)-Polymerase (PARP). 3,6-Dihydroxyflavon erhÖht den intrazellulÄren oxidativen Stress und die Lipidperoxidation.
-
GC46583
3-Amino-2,6-Piperidinedione
α-Aminoglutarimide, 3-Aminoglutarimide, Glutamimide
An active metabolite of (±)-thalidomide
-
GC49849
3-Aminosalicylic Acid
3-ASA, NSC 285111
A salicylic acid derivative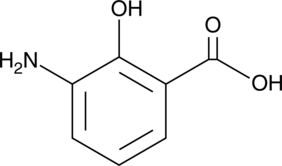
-
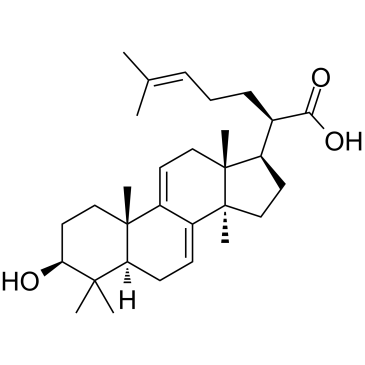
GC35106
3-Dehydrotrametenolic acid
3-DehydrotrametenolsÄure, isoliert aus dem Sclerotium von Poria cocos, ist ein Lactatdehydrogenase (LDH)-Hemmer. 3-DehydrotrametenolsÄure fÖrdert die Adipozytendifferenzierung in vitro und wirkt in vivo als Insulinsensibilisator. 3-DehydrotrametenolsÄure induziert Apoptose und wirkt gegen Krebs.
-
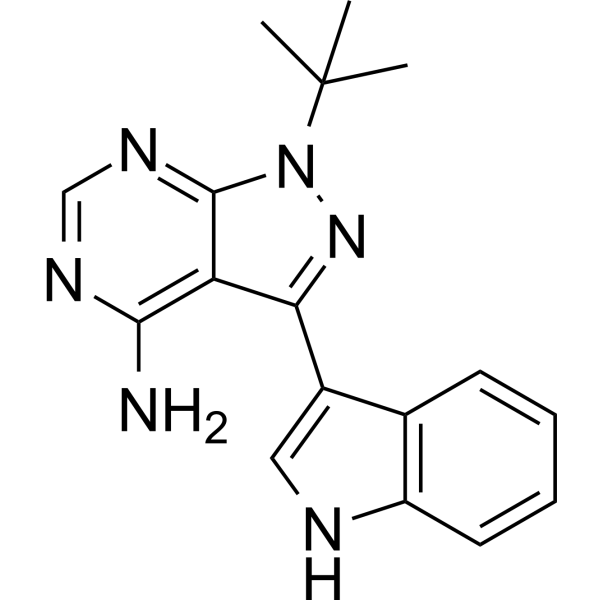
GC68537
3-IN-PP1
3-IN-PP1 ist ein Protein-Kinase-D (PKD)-Inhibitor. 3-IN-PP1 hat eine breite PKD-Inhibitionsaktivität gegenüber PKD1, PKD2 und PKD3 mit IC50-Werten von jeweils 108, 94 und 108 nM. Es ist auch ein Breitspektrum-Antitumorwirkstoff und hemmt das Wachstum verschiedener Krebszellen. 3-IN-PP1 kann für die Krebsforschung verwendet werden.
-
GC17394
3-Nitropropionic acid
β-Nitropropionic Acid, 3-NP, NSC 64266
3-NitropropionsÄure (β-NitropropionsÄure) ist ein irreversibler Inhibitor der Succinatdehydrogenase.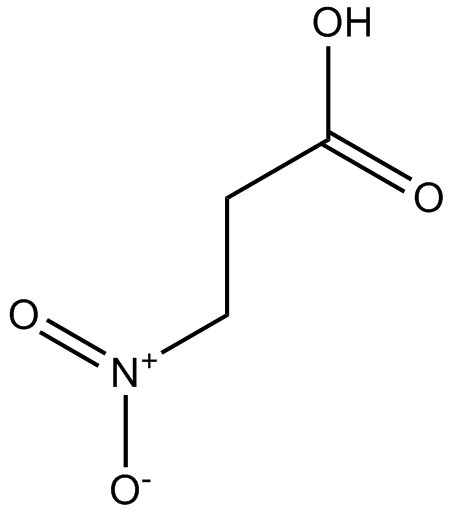
-
GC35099
3-O-Acetyloleanolic acid
3-Acetyloleanolic Acid
3-O-Acetyloleanolsäure (3AOA), ein aus den Samen von Vigna sinensis K. isoliertes Oleanolsäurederivat, induziert Krebs und zeigt auch Anti-Angiogenese-Aktivität.
-
GC60507
3-O-Methylgallic acid
3-O-MethylgallussÄure (3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoesÄure) ist ein Anthocyanin-Metabolit und hat eine starke antioxidative Wirkung. 3-O-MethylgallussÄure hemmt die Caco-2-Zellproliferation mit einem IC50-Wert von 24,1 μM. 3-O-MethylgallussÄure induziert auch Zellapoptose und hat Anti-Krebs-Wirkungen.
-
GC32767
3BDO
3-Benzyl-5-((2-nitrophenoxy)methyl)dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one
3BDO ist ein neuer mTOR-Aktivator, der auch die Autophagie hemmen kann.
-
GC45354
4β-Hydroxywithanolide E
NSC 212509
4β-Hydroxywithanolide E, isoliert aus Physalis peruviana L.
-
GC48437
4'-Acetyl Chrysomycin A
A bacterial metabolite with antibacterial and anticancer activities
-
GC42346
4-bromo A23187
4-Bromocalcimycin
4-Bromo A23187 ist ein halogeniertes Analogon des hochselektiven Calciumionophors A-23187.
-
GC42401
4-hydroperoxy Cyclophosphamide
4-OOH-CY
Ein aktiviertes Analogon von Cyclophosphamid.
-
GC30896
4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol
NSC 227926, p-Hydroxybenzyl Alcohol
4-Hydroxybenzylalkohol ist eine phenolische Verbindung, die in verschiedenen Pflanzenarten weit verbreitet ist.
-
GC33815
4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid
4-HPAA, p-HPAA, para-HPAA, p-Hydroxyphenylacetic Acid, para-Hydroxyphenylacetic Acid, NSC 25066, NSC 27460
4-HydroxyphenylessigsÄure, ein wichtiger, von Mikrobiota stammender Metabolit von Polyphenolen, ist an der antioxidativen Wirkung beteiligt.
-
GC35138
4-Methyldaphnetin
4-Methyldaphnetin ist ein VorlÄufer bei der Synthese von Derivaten von 4-Methylcumarin. 4-Methyldaphnetin hat starke, selektive antiproliferative und Apoptose-induzierende Wirkungen auf mehrere Krebszelllinien. 4-Methyldaphnetin besitzt radikalfangende Eigenschaften und hemmt stark die Lipidperoxidation der Membran.
-
GC68231
4-Methylsalicylic acid
-
GC31648
4-Octyl Itaconate
4-Octyl-Itakonat (4-OI) ist ein zellpermeables Itakonat-Derivat. Itakonat und 4-Octyl-Itakonat hatten eine ähnliche Thiol-Reaktivität, wodurch sich 4-Octyl-Itakonat als geeigneter Ersatz für Itakonat zur Untersuchung seiner biologischen Funktion eignet.
-
GC49127
4-oxo Cyclophosphamide
4-keto CP, 4-keto Cyclophosphamide, NSC 139488, 4-oxo CP
An inactive metabolite of cyclophosphamide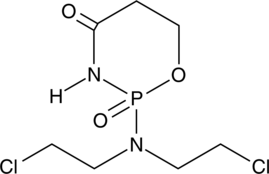
-
GC45352
4-oxo Withaferin A
4-Dehydrowithaferin A
4-oxo Withaferin A ist das Analogon von Withaferin A. Withaferin A ist ein aus Withania somnifera isoliertes Withanolid. 4-Oxo-Withaferin A hat das Potenzial fÜr die Erforschung des multiplen Myeloms.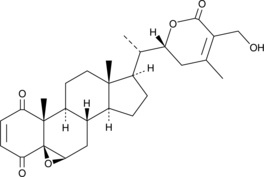
-
GC45353
4-oxo-27-TBDMS Withaferin A
4-oxo-27-TBDMS Withaferin A, ein Withaferin A-Derivat, zeigt starke antiproliferative Wirkungen auf die Tumorzellen. 4-oxo-27-TBDMS Withaferin A induziert die Apoptose von Tumorzellen. 4-Oxo-27-TBDMS Withaferin A ist ein Antikrebsmittel.
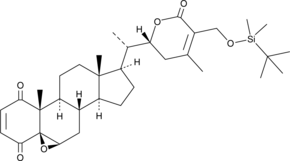
-
GC60525
4-Vinylphenol (10%w/w in propylene glycol)
4-Vinylphenol kommt in der Heilpflanze Hedyotis diffusa Willd, Wildreis vor und ist auch der Metabolit von p-CumarinsÄure und FerulasÄure durch MilchsÄurebakterien im Wein. 4-Vinylphenol induziert Apoptose und hemmt die Bildung von BlutgefÄßen und unterdrÜckt das invasive Wachstum von Brusttumoren in vivo.
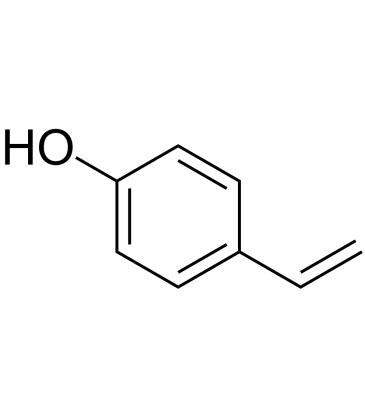
-
GC10468
4EGI-1
eIF4E/eIF4G Interaction Inhibitor
4EGI-1 ist ein Inhibitor der eIF4E/eIF4G-Interaktion mit einer Kd von 25 μM gegen die eIF4E-Bindung.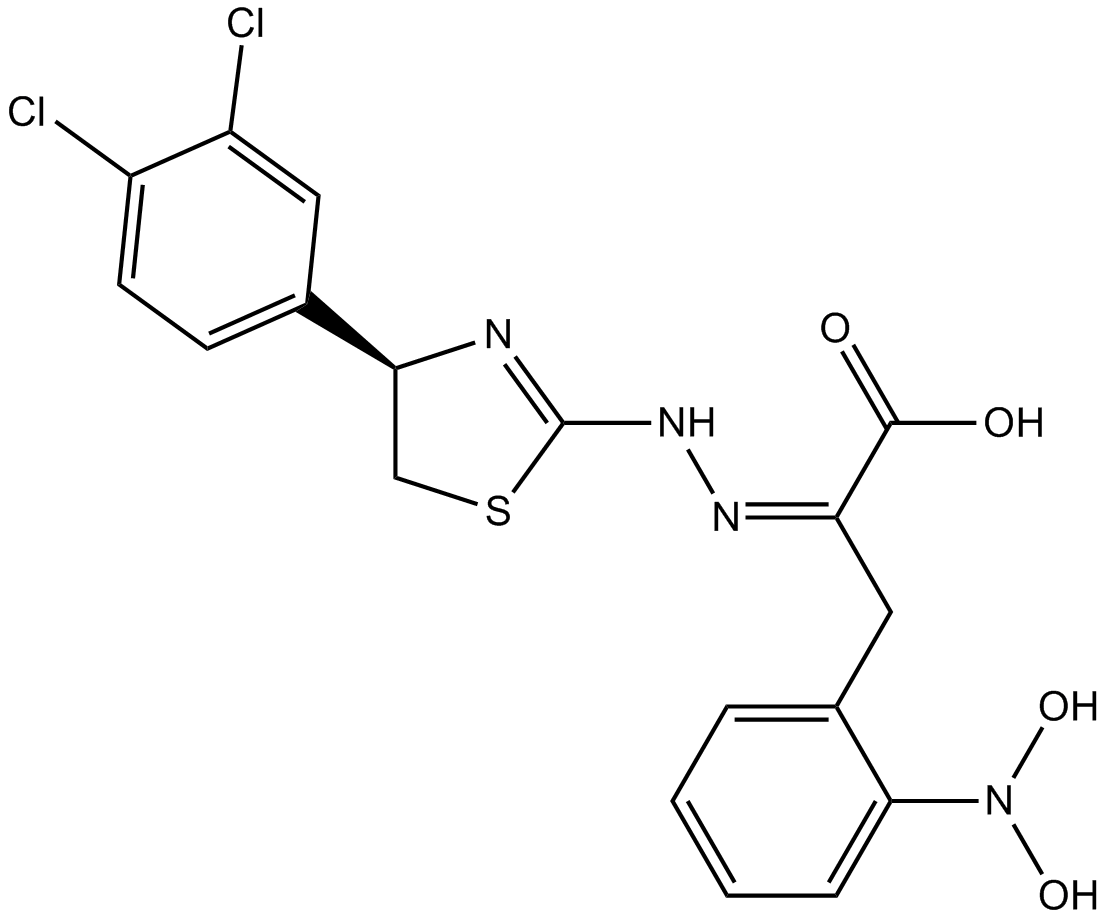
-
GC71507
5'-Methylthioadenosine-13C6
5'-Methylthioadenosine-13C6 ist das 13C-markierte 5'-Methylthiodenosin.
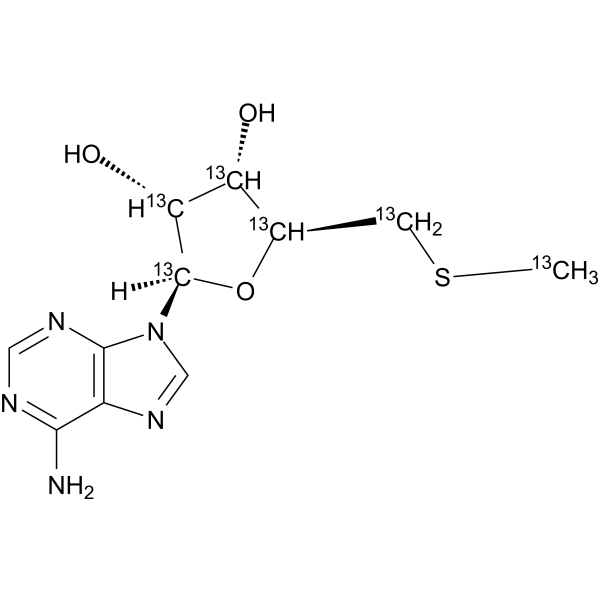
-
GC35150
5,7,4'-Trimethoxyflavone
5,7,4'-Trimethoxyflavon wird aus Kaempferia parviflora (KP) isoliert, einer berühmten Heilpflanze aus Thailand. 5,7,4'-Trimethoxyflavon induziert Apoptose, wie durch Inkremente der Sub-G1-Phase, DNA-Fragmentierung, Annexin-V/PI-Färbung, das Bax/Bcl-xL-Verhältnis, proteolytische Aktivierung von Caspase-3 und Abbau von Poly belegt wird (ADP-Ribose)-Polymerase (PARP)-Protein.5,7,4'-Trimethoxyflavon ist bei der konzentrationsabhängigen Hemmung der Proliferation von menschlichen SNU-16-Magenkrebszellen signifikant wirksam.
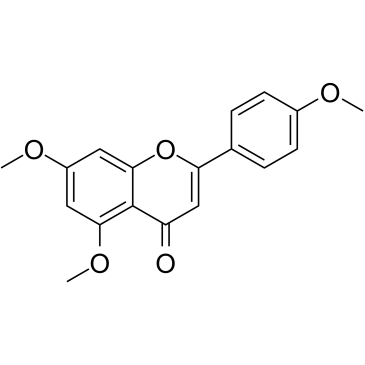
-
GN10629
5,7-dihydroxychromone
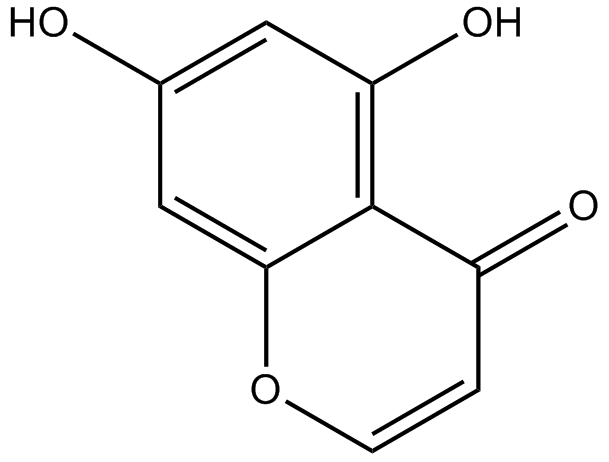
-
GC63972
5,7-Dimethoxyflavanone
5,7-Dimethoxyflavanon zeigt starke antimutagene AktivitÄt gegen MeIQ-Mutagenese im Ames-Test unter Verwendung des S.
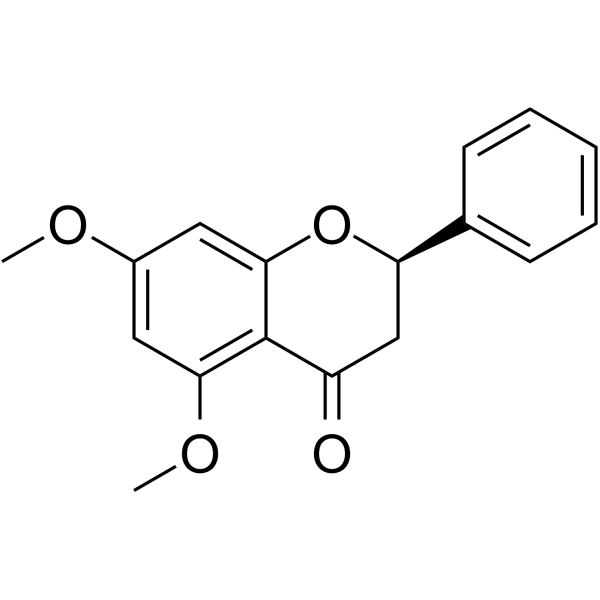
-
GC52227
5-(3',4'-Dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-Valerolactone
(±)-δ-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-Valerolactone, 5-(3',4'-Dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-VL
An active metabolite of various polyphenols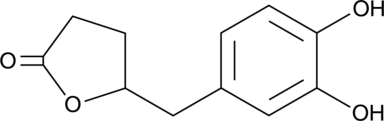
-
GC35147
5-(N,N-Hexamethylene)-amiloride
HMA
5-(N,N-Hexamethylen)-amilorid (Hexamethylenamilorid) leitet sich von einem Amilorid ab und ist ein potenter Na+/H+-Austauscher-Inhibitor, der den intrazellulÄren pH-Wert (pHi) senkt und Apoptose bei LeukÄmie induziert Zellen.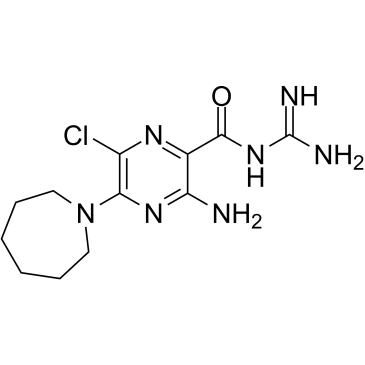
-
GC45356
5-Aminolevulinic Acid (hydrochloride)
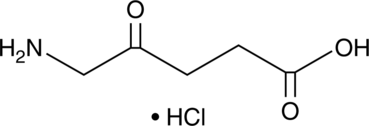
-
GC68562
5-Aminolevulinic acid-13C-1 hydrochloride
5-ALA-13C-1 hydrochloride; δ-Aminolevulinic acid-13C-1 hydrochloride; 5-Amino-4-oxopentanoic acid-13C-1 hydrochloride
5-Aminolevulinsäure-13C-1 (5-ALA-13C-1) Hydrochlorid ist eine mit 13C markierte Form von 5-Aminolevulinsäurehydrochlorid. 5-Aminolevulinsäurehydrochlorid (5-ALA-Hydrochlorid) ist ein Zwischenprodukt der Biosynthese von Hämoglobin im Körper und dient als Vorläufer des Tetrapyrrols.
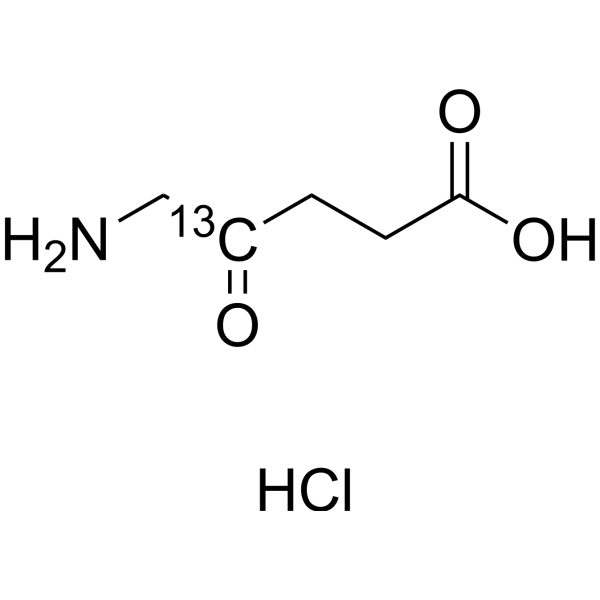
-
GC71833
5-Aminolevulinic acid-d2 hydrochloride
5-Aminolevulinic acid-d2 hydrochloride ist deuterium markiertes 5-Aminolevulinsäurehydrochlorid.
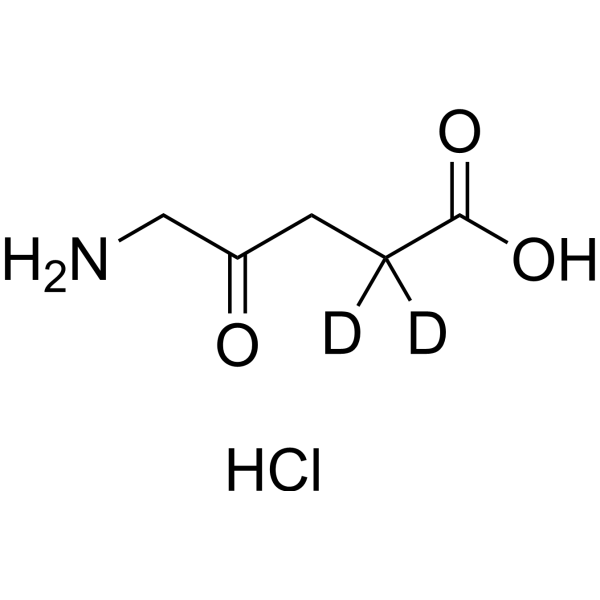
-
GC46681
5-Bromouridine
(–)-5-Bromouridine, BrU, BrUrd, NSC 38296
A brominated uridine analog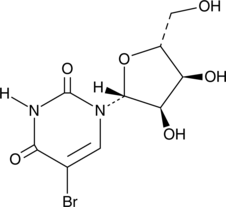
-
GC42545
5-Fluorouracil-13C,15N2
5-FU-13C,15N2
5-Fluorouracil-13C,15N2 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of 5-flurouracil by GC- or LC-MS.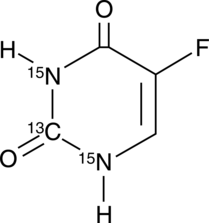
-
GC46705
5-Methoxycanthinone
5-Methoxycanthin-6-one, NSC 88929
5-Methoxycanthinon ist ein oral aktiver Inhibitor von Leishmania-StÄmmen.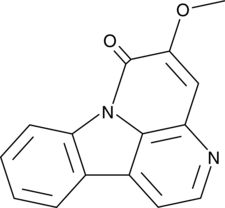
-
GC42586
6α-hydroxy Paclitaxel
6α-hydroxy Taxol
6α-Hydroxy Paclitaxel ist ein primÄrer Metabolit von Paclitaxel. 6α-hydroxy Paclitaxel behÄlt eine zeitabhÄngige Wirkung auf die organischen Anionen-transportierenden Polypeptide 1B1/SLCO1B1 (OATP1B1) mit Ähnlicher Hemmkraft wie Paclitaxel, wÄhrend es keine zeitabhÄngige Hemmung von OATP1B3 mehr zeigte. 6α-Hydroxy-Paclitaxel kann fÜr die Krebsforschung verwendet werden.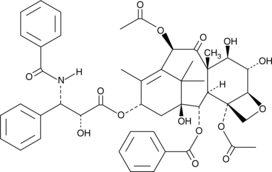
-
GC45772
6(5H)-Phenanthridinone
NSC 11021, NSC 40943, NSC 61083
An inhibitor of PARP1 and 2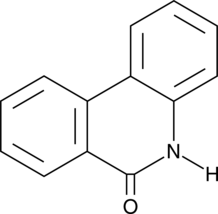
-
GN10093
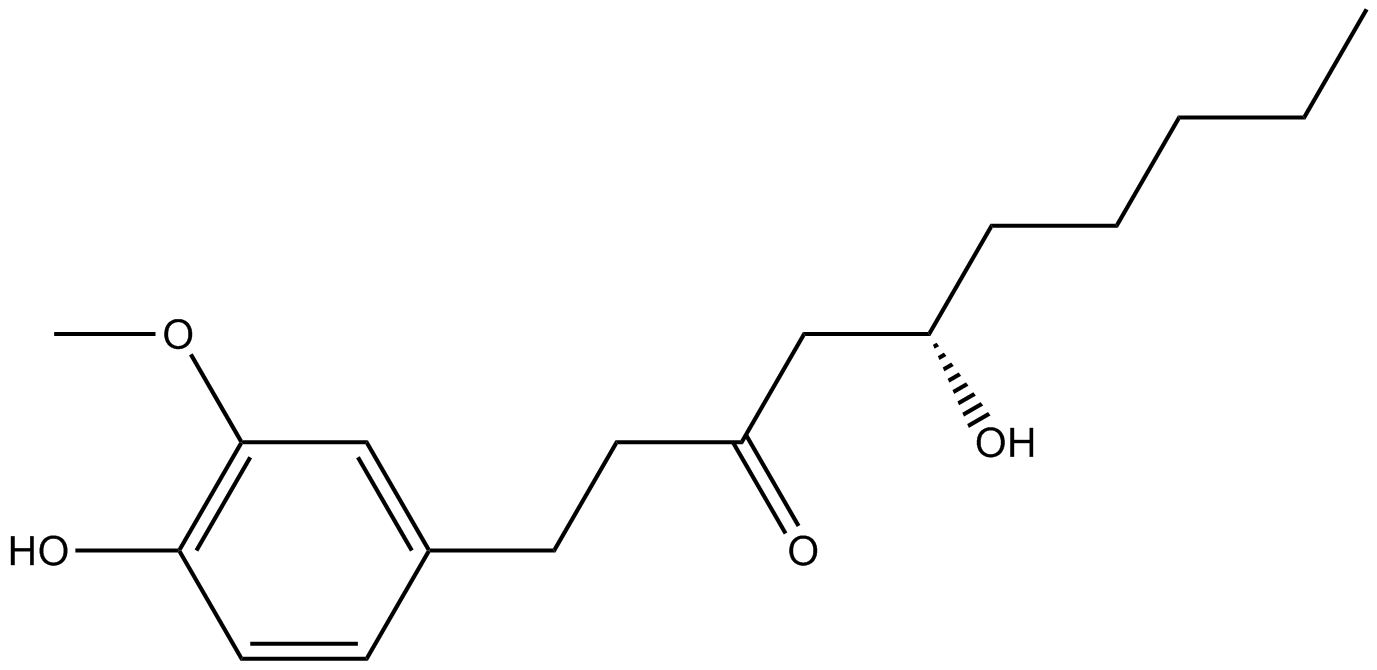
6-gingerol
-
GC49429
6-keto Lithocholic Acid
5β-Cholanic Acid-3α-ol-6-one, 6-KLCA, 6-keto LCA, 6-oxo LCA, 6-oxo Lithocholic Acid, 6-keto Lithocholate, 6-oxo Lithocholate
A metabolite of lithocholic acid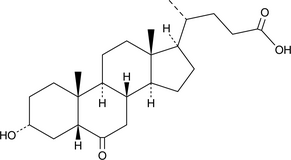
-
GC35184
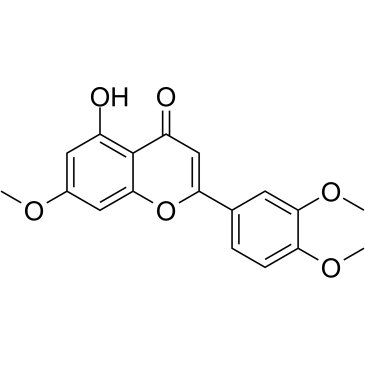
7,3',4'-Tri-O-methylluteolin
7,3',4'-Tri-O-methylluteolin (5-Hydroxy-3',4',7-trimethoxyflavon), eine Flavonoidverbindung, besitzt starke entzÜndungshemmende Wirkungen in LPS-induzierten Makrophagen-Zelllinien, vermittelt durch Hemmung von Freisetzung von EntzÜndungsmediatoren, NO, PGE2 und entzÜndungsfÖrdernden Zytokinen.
-
GC45673
7,8-Dihydroneopterin
D-erythro-7,8-Dihydroneopterin
7,8-Dihydroneopterin, ein EntzÜndungsmarker, induziert zellulÄre Apoptose in Astrozyten und Neuronen durch VerstÄrkung der Stickoxid-Synthase (iNOS)-Expression.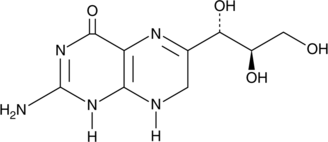
-
GC16853
7,8-Dihydroxyflavone
7,8-DHF
7,8-Dihydroxyflavon ist ein potenter und selektiver TrkB-Agonist, der die physiologischen Wirkungen des aus dem Gehirn stammenden neurotrophen Faktors (BDNF) nachahmt.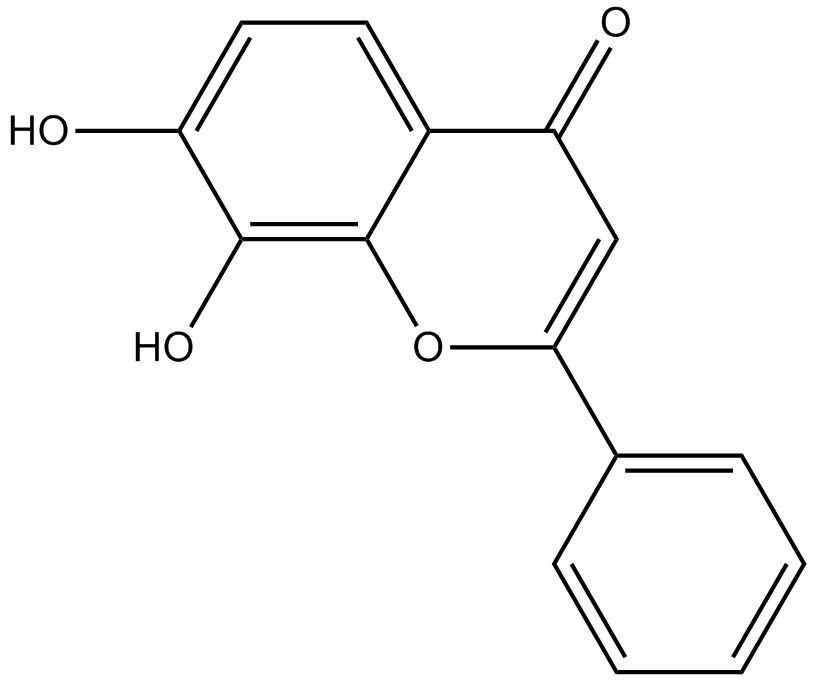
-
GC42616
7-oxo Staurosporine
BMY 41950, RK-1409
7-oxo Staurosporine is an antibiotic originally isolated from S.
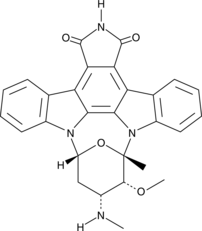
-
GC16037
7BIO
7-Bromoindirubin-3’-oxime
7BIO (7-Bromoindirubin-3-Oxime) ist das Derivat von Indirubin.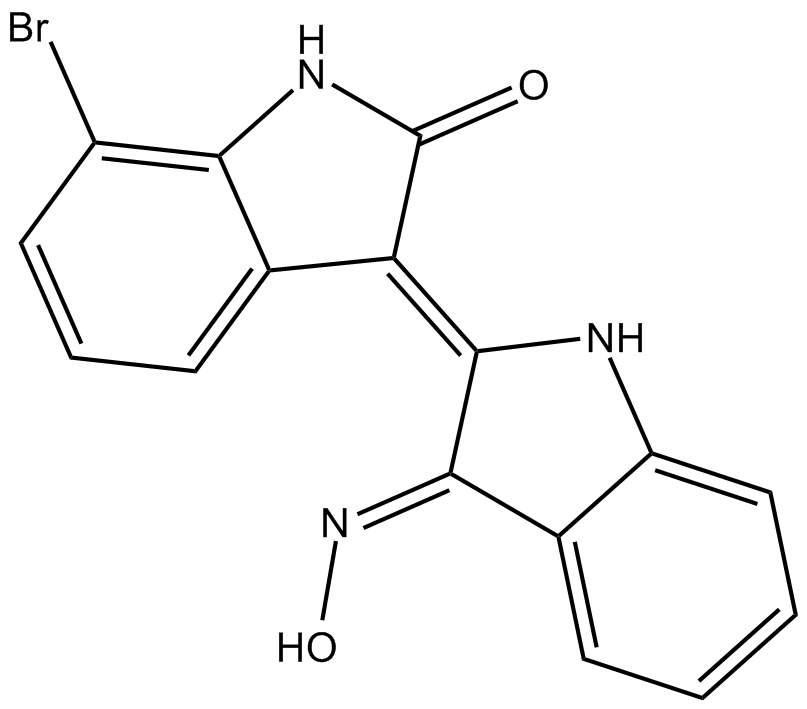
-
GC46741
8(E),10(E),12(Z)-Octadecatrienoic Acid
α-Calendic Acid, Calendic Acid, Calendulic Acid, trans,trans,cis-8,10,12-Octadecatrienoic Acid
A conjugated PUFA
-
GC42622
8-bromo-Cyclic AMP
8-Bromoadenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate, 8-Br-cAMP, 8-bromo-cAMP, NSC 171719
8-bromo-Cyclic AMP is a brominated derivative of cAMP that remains long-acting due to its resistance to degradation by cAMP phosphodiesterase.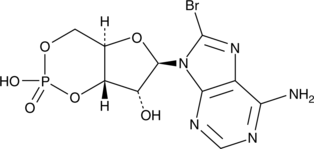
-
GC49275
8-Oxycoptisine
8-Oxocoptisine
8-Oxycoptisin ist ein natÜrliches Protoberberin-Alkaloid mit Anti-Krebs-AktivitÄt.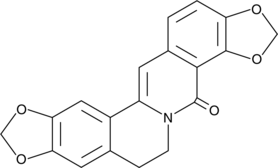
-
GC17119
8-Prenylnaringenin
Flavaprenin,8-PN
8-Prenylnaringenin ist ein aus Hopfenzapfen (Humulus lupulus) isoliertes Prenylflavonoid mit Zytotoxizität. 8-Prenylnaringenin hat eine antiproliferative Aktivität gegen HCT-116-Kolonkrebszellen durch Induktion von intrinsischer und extrinsischer Signalweg-vermittelter Apoptose. 8-Prenylnaringenin fördert auch die Erholung von einer immobilisierungsinduzierten Muskelatrophie durch Nichtgebrauch durch Aktivierung des Akt-Phosphorylierungswegs bei Mäusen.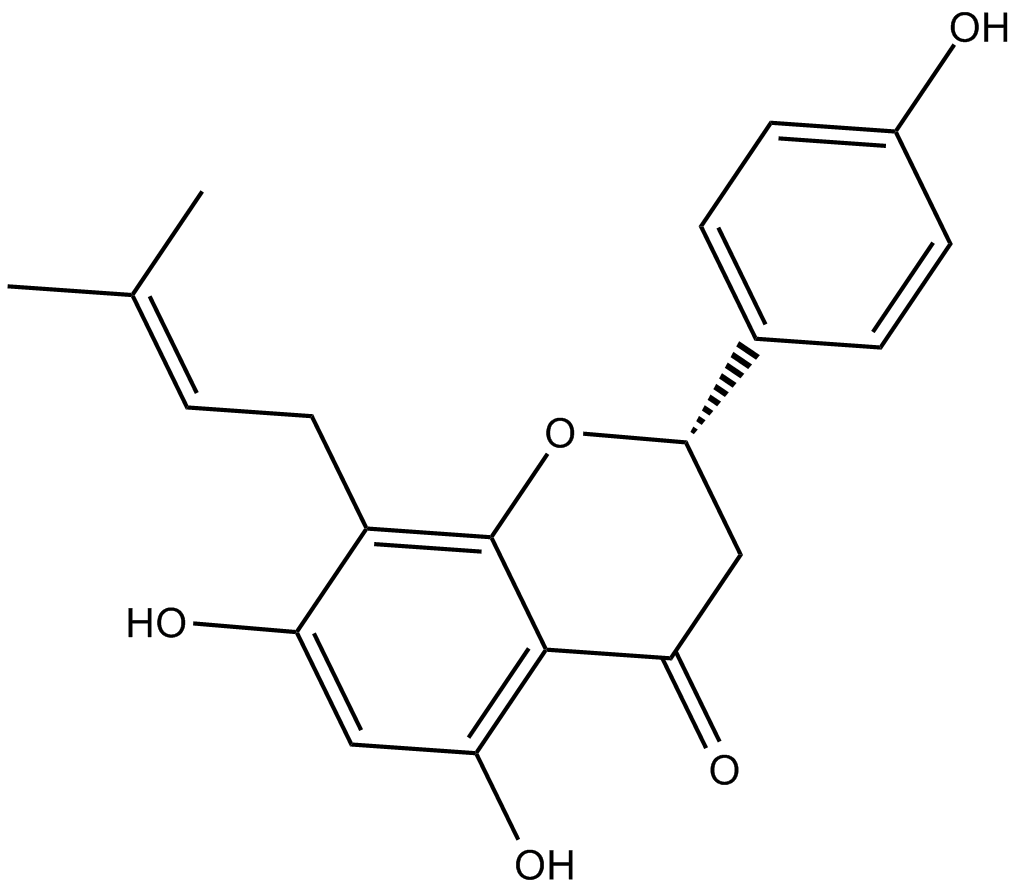
-
GC41642
9(E),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic Acid
β-Eleostearic Acid, β-ESA
9(E),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic acid (β-ESA) is a conjugated polyunsaturated fatty acid that is found in plant seed oils and in mixtures of conjugated linolenic acids synthesized by the alkaline isomerization of linolenic acid.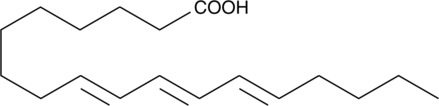
-
GC41643
9(Z),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic Acid
αEleostearic Acid, αESA, LAF 237
9(Z),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic Acid (α-ESA) is a conjugated polyunsaturated fatty acid commonly found in plant seed oil.
-
GC40785
9(Z),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic Acid ethyl ester
αESA ethyl ester, Ethyl αeleostearate
9(Z),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic Acid ethyl ester (α-ESA) is a conjugated polyunsaturated fatty acid commonly found in plant seed oil.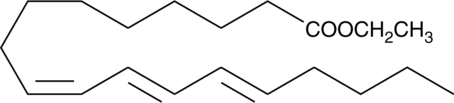
-
GC40710
9(Z),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic Acid methyl ester
αESA methyl ester, Methyl αeleostearate
9Z,11E,13E-octadecatrienoic acid (α-ESA) is a conjugated polyunsaturated fatty acid commonly found in plant seed oil.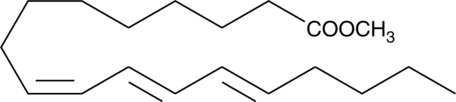
-
GC70659
9-cis-Retinoic acid-d5
9-cis-Retinoic acid-d5 ist die Deuterium markierte 9-cis-Retinosäure.

-
GC39152
9-ING-41
Elraglusib
9-ING-41 ist ein Maleimid-basierter ATP-kompetitiver und selektiver Glykogen-Synthase-Kinase-3β (GSK-3β)-Inhibitor mit einem IC50 von 0,71 μM. 9-ING-41 fÜhrt signifikant zu Zellzyklusstillstand, Autophagie und Apoptose in Krebszellen. 9-ING-41 hat AntikrebsaktivitÄt und hat das Potenzial, die Antitumorwirkung von Chemotherapeutika zu verstÄrken.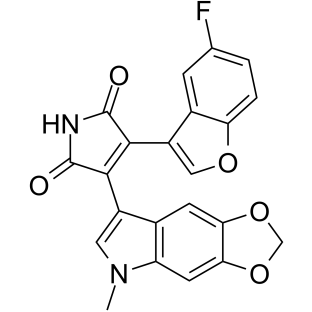
-
GN10035
9-Methoxycamptothecin
-
GC45960
9c(i472)
15-LOX-1 Inhibitor i472
9c(i472) ist ein potenter Inhibitor von 15-LOX-1 (15-Lipoxygenase-1) mit einem IC50-Wert von 0,19 μM.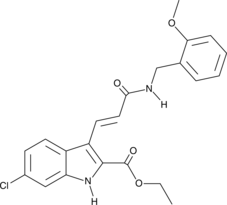
-
GC50465
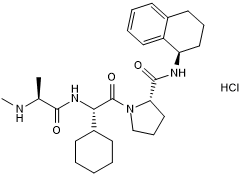
A 410099.1
High affinity XIAP antagonist; active in vivo
-
GC17512
A-1155463
A-1155463 ist ein hochwirksamer und selektiver BCL-XL-Inhibitor mit einem EC50-Wert von 70 nM in Molt-4-Zellen.
-
GC16278
A-1210477
A-1210477 ist ein potenter und selektiver Inhibitor von MCL-1 mit einem Ki von 0,45 nM. A-1210477 bindet spezifisch MCL-1 und fÖrdert die Apoptose von Krebszellen auf MCL-1-abhÄngige Weise.
-
GC17513
A-1331852
A-1331852 ist ein oral verfÜgbarer selektiver BCL-XL-Inhibitor mit einem Ki von weniger als 10 pM.
-
GC60544
A-192621
A-192621 ist ein potenter, nicht peptidischer, oral aktiver und selektiver Endothelin B (ETB)-Rezeptorantagonist mit einem IC50 von 4,5 nM und einem Ki von 8,8 nM.
-
GC32981
A-385358
A-385358 ist ein selektiver Inhibitor von Bcl-XL mit Kis von 0,80 und 67 nM fÜr Bcl-XL bzw. Bcl-2.
-
GC11200
A23187
Calcimycin
A23187 (A-23187) ist ein Antibiotikum und ein einzigartiger Divalent-Kationen-Ionophor (wie Calcium und Magnesium).
-
GC42659
A23187 (calcium magnesium salt)
Calcimycin
A23187 is a divalent cation ionophore.
-
GC35216
AAPK-25
AAPK-25 ist ein potenter und selektiver Aurora/PLK-Doppelinhibitor mit Anti-Tumor-AktivitÄt, der eine mitotische VerzÖgerung verursachen und Zellen in einer Prometaphase anhalten kann, was durch die Phosphorylierung des Biomarkers Histon H3Ser10 widergespiegelt wird, gefolgt von einem Anstieg der Apoptose. AAPK-25 zielt auf Aurora-A, -B und -C mit Kd-Werten im Bereich von 23-289 nM sowie PLK-1, -2 und -3 mit Kd-Werten im Bereich von 55-456 nM ab.
-
GC13805
Abacavir
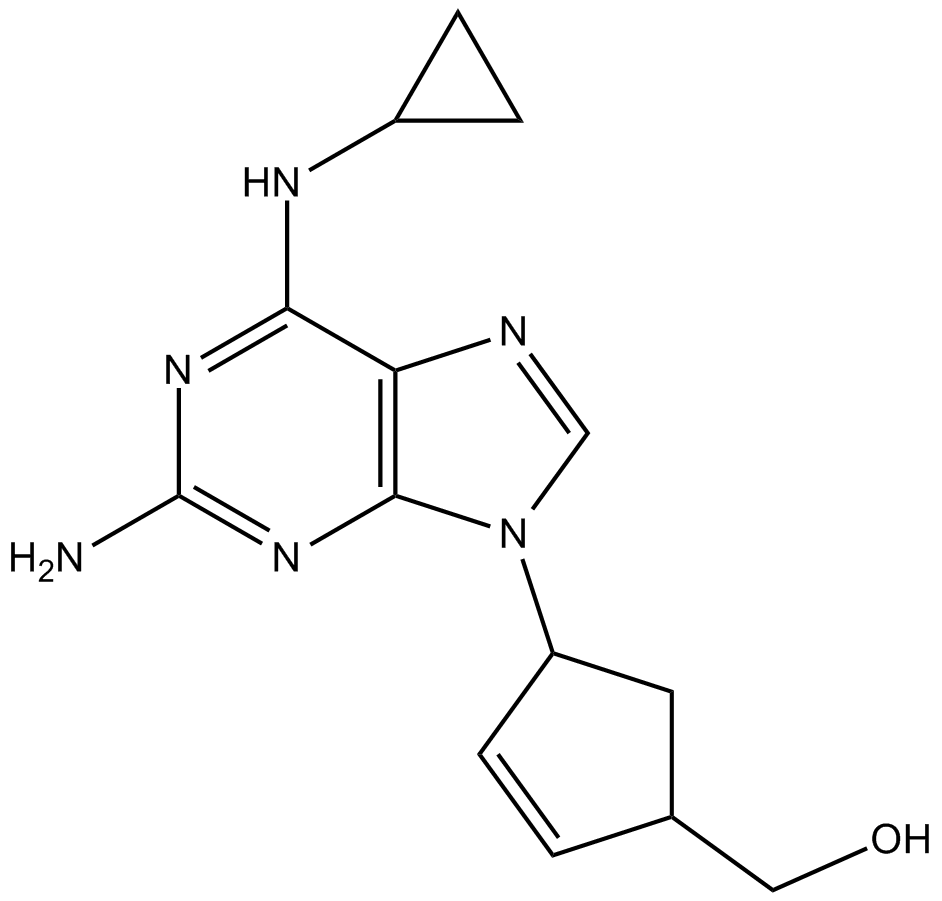
-
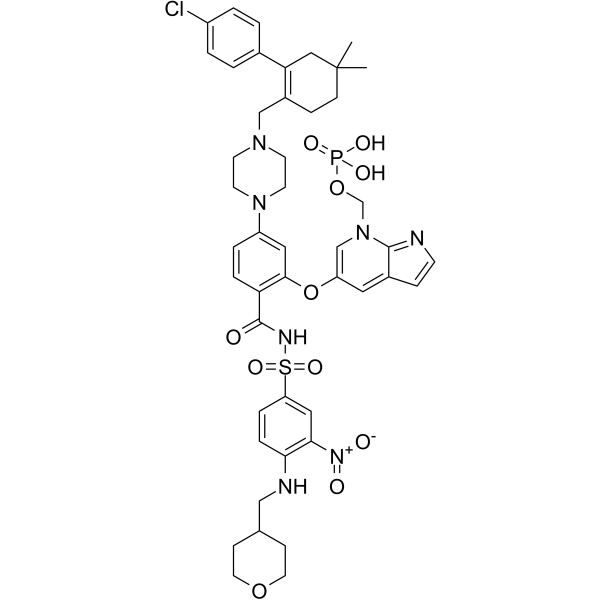
GC64674
ABBV-167
ABBV-167 ist ein Phosphat-Prodrug des BCL-2-Inhibitors Venetoclax.
-
GC60548
ABT-100
ABT-100 ist ein potenter, hochselektiver und oral aktiver Farnesyltransferase-Inhibitor. ABT-100 hemmt die Zellproliferation (IC50s von 2,2 nM, 3,8 nM, 5,9 nM, 6,9 nM, 9,2 nM, 70 nM und 818 nM fÜr EJ-1, DLD-1, MDA-MB-231, HCT-116, MiaPaCa- 2-, PC-3- bzw. DU-145-Zellen), erhÖht die Apoptose und verringert die Angiogenese. ABT-100 besitzt eine Breitband-AntitumoraktivitÄt.
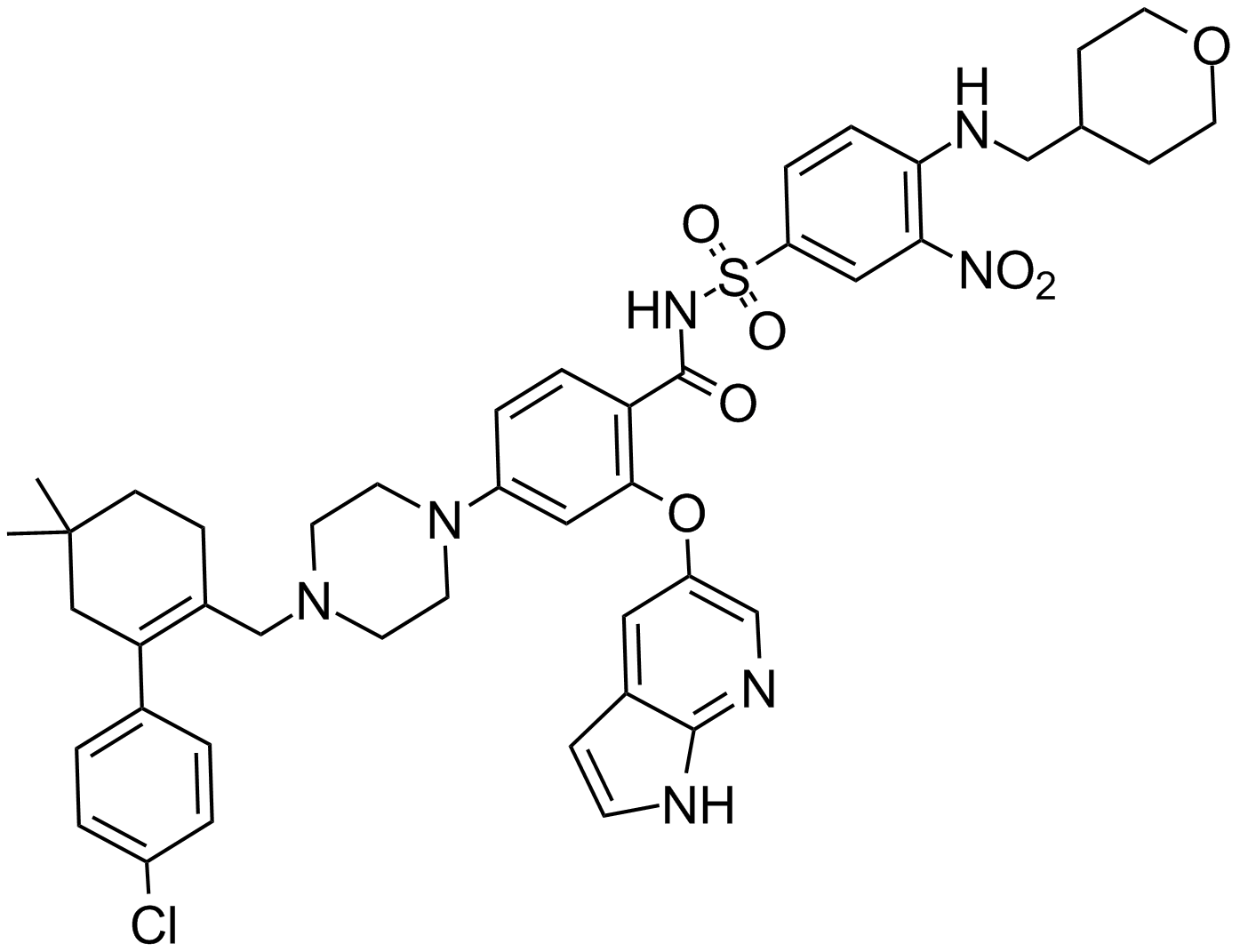
-
GC14069
ABT-199
GDC 0199, Venetoclax
Ein Bcl-2-Inhibitor
-
GC12405
ABT-263 (Navitoclax)
Navitoclax,ABT-263,ABT263,ABT 263
Ein Hemmstoff von Bcl-2-Familienproteinen.
-
GC49745
ABT-263-d8
Navitoclax-d8
ABT-263-d8 ist das Deuterium mit der Bezeichnung Navitoclax. Navitoclax (ABT-263) ist ein potenter und oral aktiver Proteininhibitor der Bcl-2-Familie, der an mehrere anti-apoptotische Proteine der Bcl-2-Familie wie Bcl-xL, Bcl-2 und Bcl-w mit einem Ki von weniger bindet als 1 nM.
-
GC70733
ABT-510 acetate
ABT-510 acetate ist ein anti-angiogenes TSP-Peptid (Thrombospondin-1-Analogon), das Apoptose induziert und das Wachstum von Eierstocktumoren in einem orthotopischen syngenen Modell des epithelialen Eierstockkrebs hemmt.
-
GC17234
ABT-737
ABT 737, ABT737
An inhibitor of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins
-
GA20494
Ac-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-pNA
Ac-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-pNA
The cleavage of the chromogenic caspase-3 substrate Ac-DEVD-pNA can be monitored at 405 nm.
-
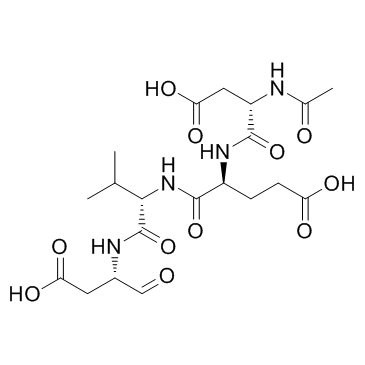
GC17602
Ac-DEVD-AFC
N-Acetyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-7-amido-4-Trifluoromethylcoumarin,Caspase-3 Substrate (Fluorogenic)
Ac-DEVD-AFC ist ein fluorogenes Substrat (Λex=400 nm, Λem=530 nm).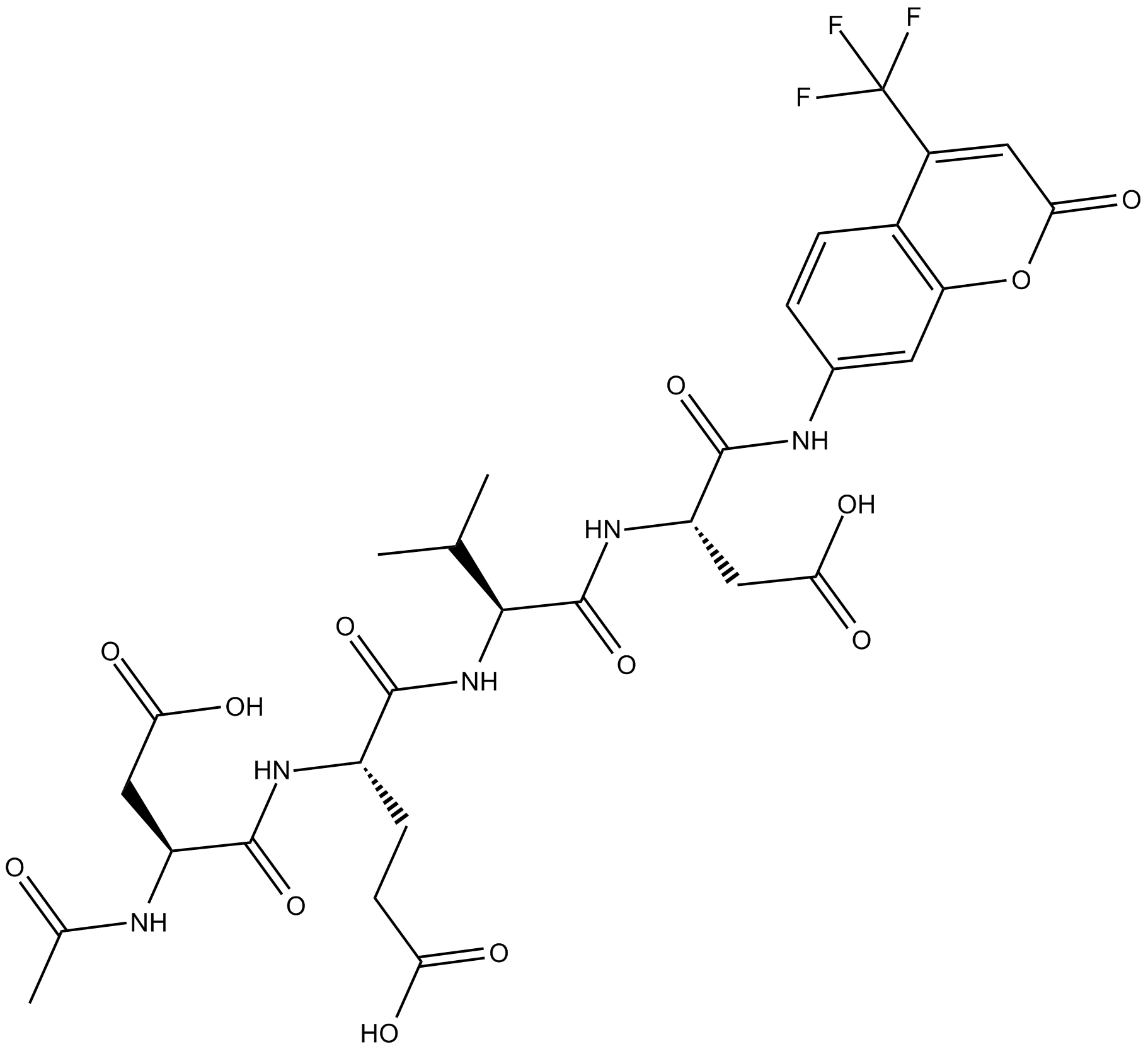
-
GC32695
Ac-DEVD-CHO
Ac-DEVD-CHO ist ein spezifischer Caspase-3-Inhibitor mit einem Ki-Wert von 230 pM.
-
GC48470
Ac-DEVD-CHO (trifluoroacetate salt)
N-Ac-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-CHO
A dual caspase3/caspase7 inhibitor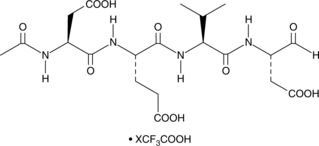
-
GC10951
Ac-DEVD-CMK
Ac-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-CMK,Caspase-3 Inhibitor III
cell-permeable, and irreversible inhibitor of caspase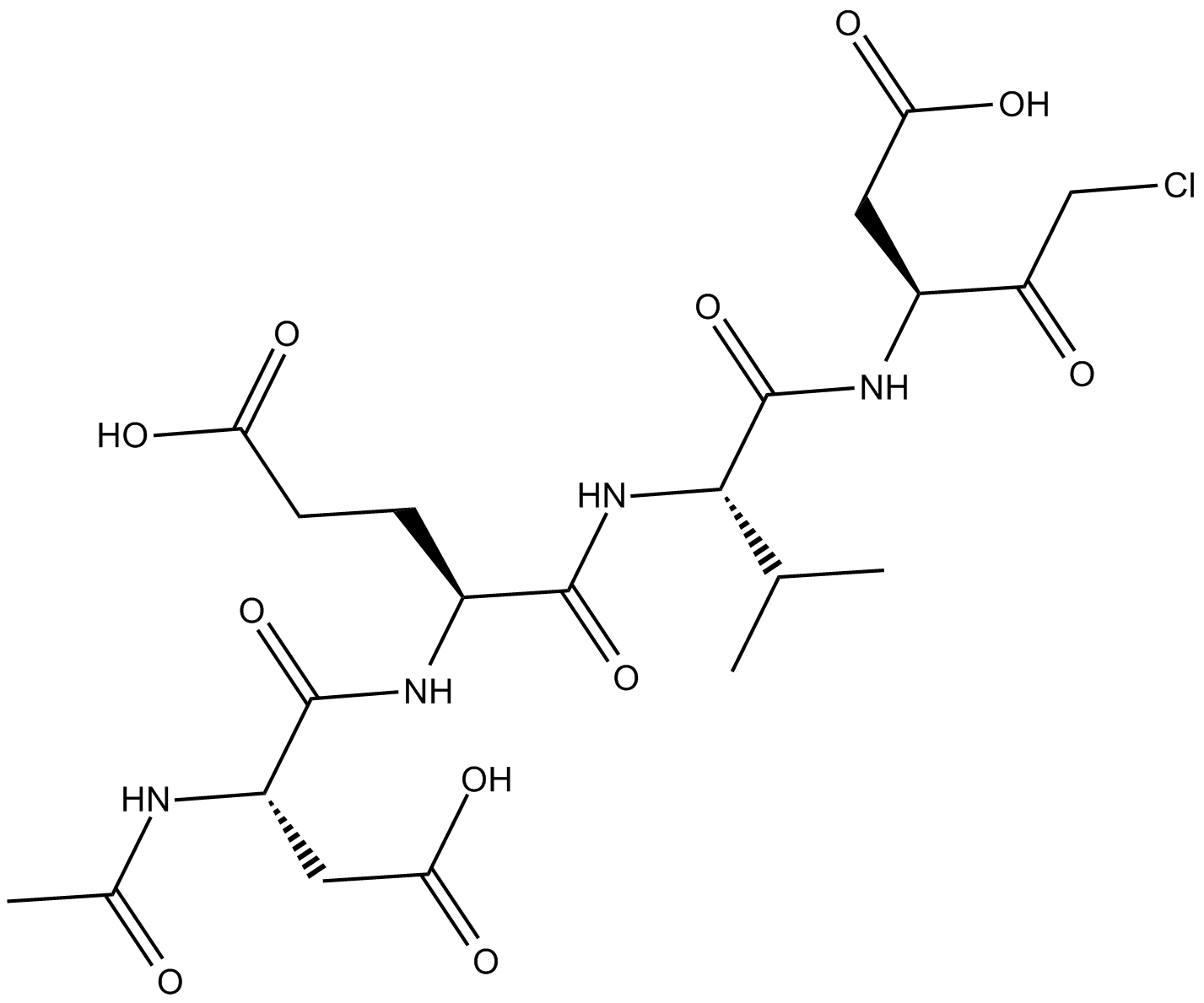
-
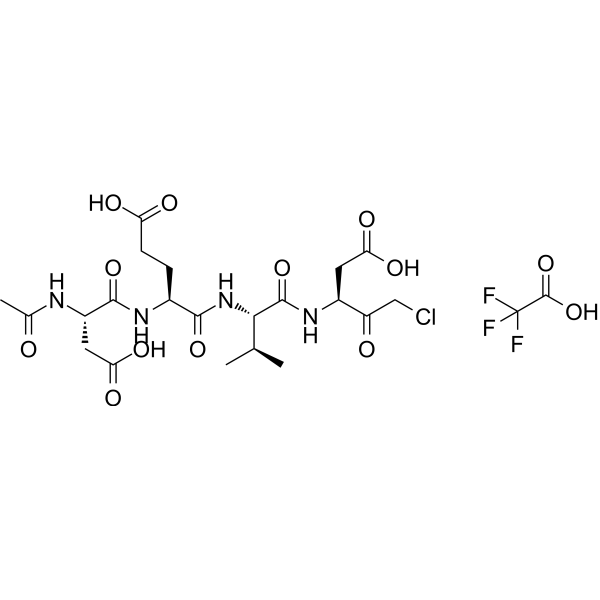
GC68600
Ac-DEVD-CMK TFA
Caspase-3 Inhibitor III TFA
Ac-DEVD-CMK (Caspase-3 Inhibitor III) TFA ist ein selektiver und irreversibler Caspase-3-Inhibitor. Ac-DEVD-CMK TFA hemmt signifikant die Apoptose, die durch hohe Glukose oder 3,20-Dibenzoat (IDB; 5) induziert wird. Ac-DEVD-CMK TFA kann in verschiedenen Experimenten eingesetzt werden, um die Zellapoptose zu hemmen.
-
GC42689
Ac-DNLD-AMC
Ac-Asp-Asn-Leu-Asp-MCA, N-Acetyl-Asp-Asn-Leu-Asp-7-amido-Methylcoumarin, Caspase-3 Substrate
Ac-WLA-AMC ist ein fluorogenes Substrat von Caspase-3.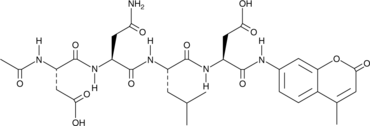
-
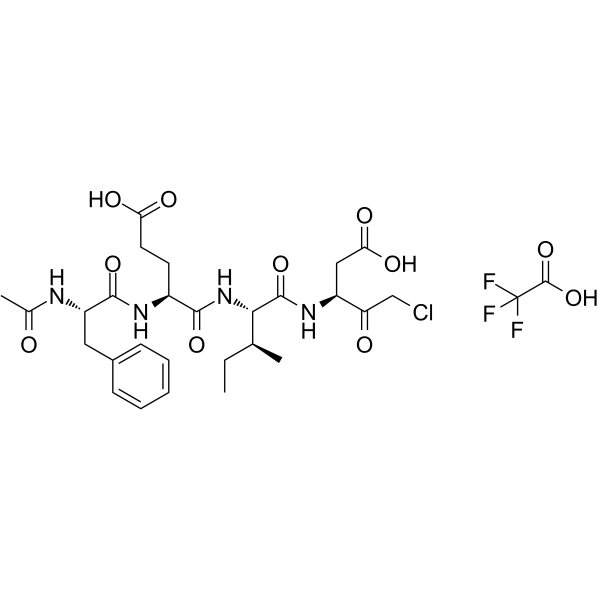
GC65107
Ac-FEID-CMK TFA
Ac-FEID-CMK TFA ist ein potenter Zebrafisch-spezifischer, von GSDMEb abgeleiteter Peptid-Inhibitor.
-
GC60558
Ac-FLTD-CMK
Ac-FLTD-CMK, ein von Gasdermin D (GSDMD) abgeleiteter Inhibitor, ist ein spezifischer entzÜndlicher Caspasen-Inhibitor.
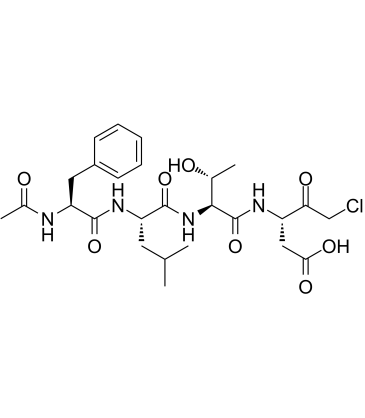
-
GC49704
Ac-FLTD-CMK (trifluoroacetate salt)
Ac-Phe-Leu-Thr-Asp-CMK
An inhibitor of caspase-1, -4, -5, and -11
-
GC18226
Ac-LEHD-AMC (trifluoroacetate salt)
Ac-Leu-Glu-His-Asp-AMC, Caspase-9 Substrate
Ac-LEHD-AMC (Trifluoracetatsalz) ist ein fluorogenes Substrat fÜr Caspase-9 (Anregung: 341 nm; Emission: 441 nm).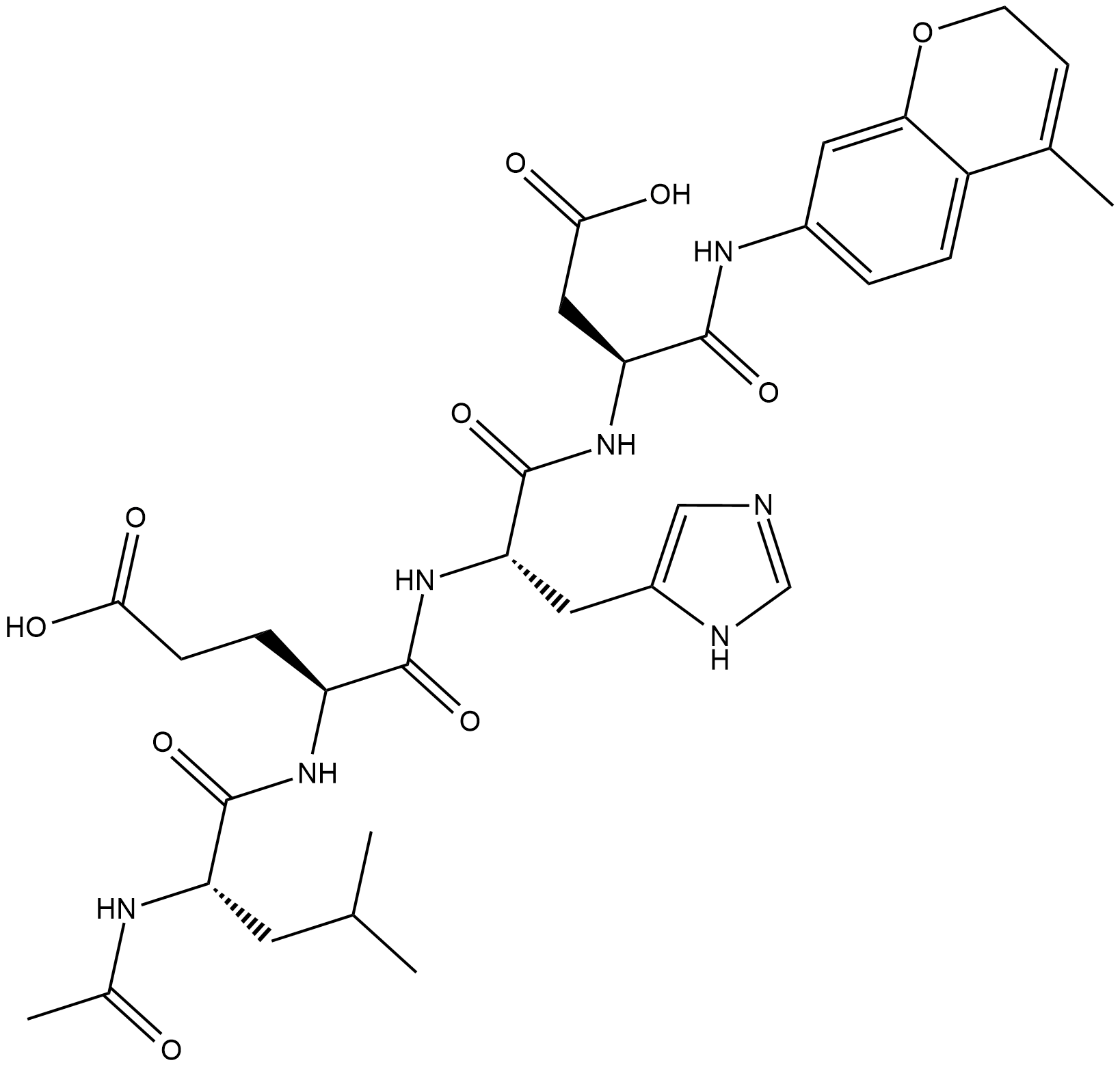
-
GC40556
Ac-LETD-AFC
NAcetylLeuGluThrAsp7amino4Trifluoromethylcoumarin, Caspase8 Substrate (Fluorogenic)
Ac-LETD-AFC ist ein Caspase-8-fluorogenes Substrat.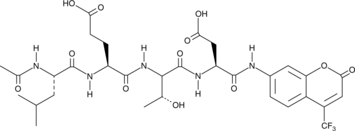
-
GC13400
Ac-VDVAD-AFC
N-Acetyl-Val-Asp-Val-Ala-Asp-7-amino-4-Trifluoromethylcoumarin Caspase-2 Substrate (Fluorogenic)
Ac-VDVAD-AFC ist ein Caspase-spezifisches fluoreszierendes Substrat. Ac-VDVAD-AFC kann Caspase-3-Ähnliche AktivitÄt und Caspase-2-AktivitÄt messen und kann fÜr die Erforschung von Tumoren und Krebs verwendet werden.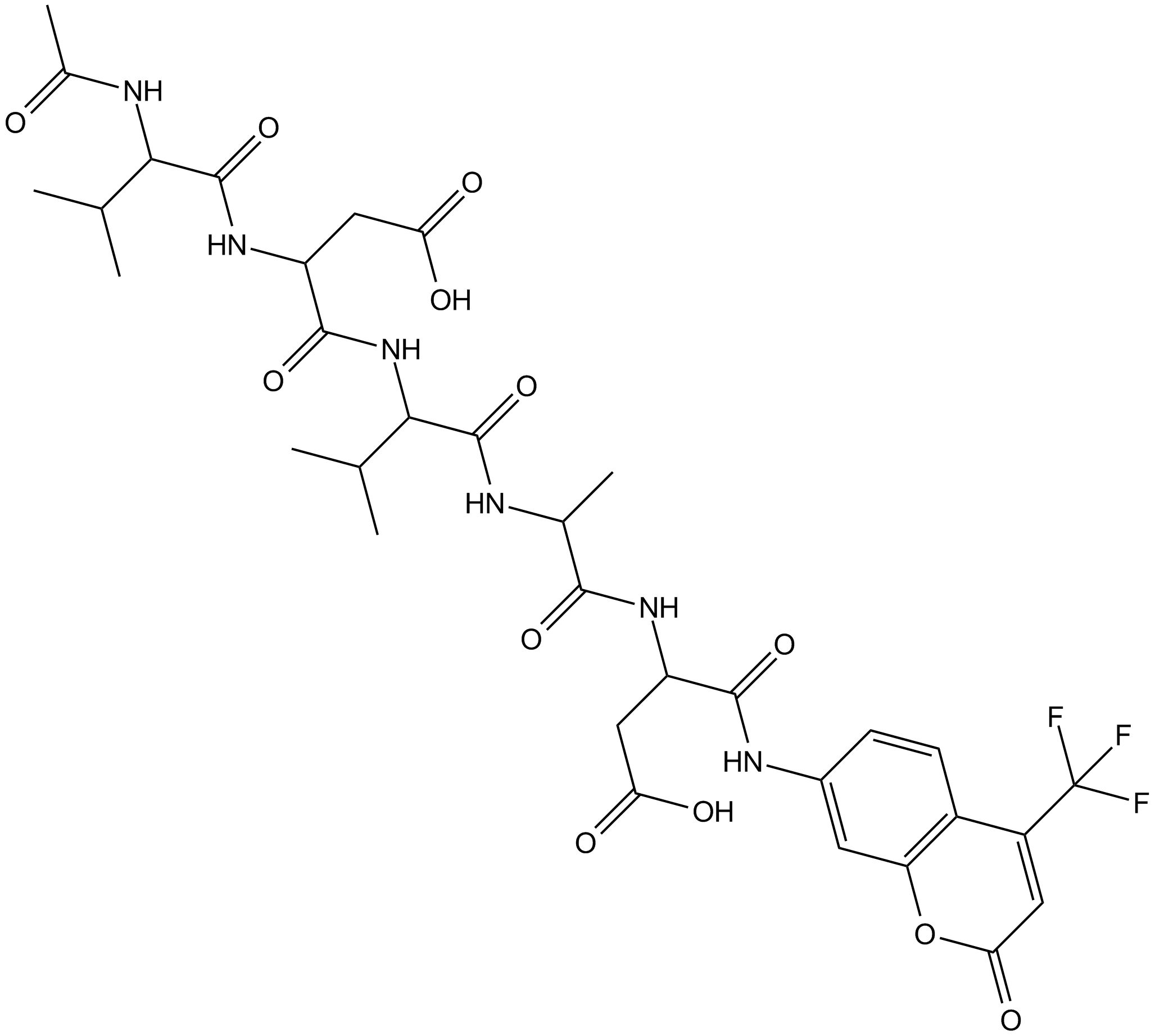
-
GC52372
Ac-VDVAD-AFC (trifluoroacetate salt)
N-Acetyl-Val-Asp-Val-Ala-Asp-AFC, N-Acetyl-Val-Asp-Val-Ala-Asp-7-amino-4-Trifluoromethylcoumarin, Caspase-2 Substrate (Fluorogenic)
A fluorogenic substrate for caspase-2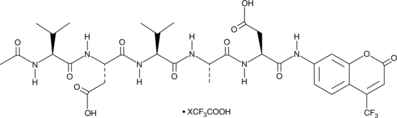
-
GC48974
Ac-VEID-AMC (ammonium acetate salt)
NAcetylValGluIleAsp7amido4Methylcoumarin, Caspase6 Substrate (Fluorogenic)
A caspase-6 fluorogenic substrate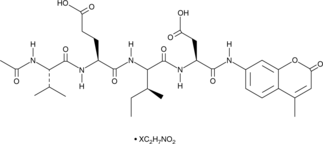
-
GC70289
AC-VEID-CHO TFA
AC-VEID-CHO TFA ist ein Peptid-abgeleiteter Caspase-Inhibitor und hat eine Hemmkraft für Caspase-6, Caspase-3 und Caspase-7 mit IC50 Werten von 16.2 nM, 13.6 nM und 162.1 nM.