Docetaxel |
| Katalog-Nr.GC16684 |
Docetaxel ist ein antineoplastisches Medikament, das die Depolymerisation von Mikrotubuli hemmt und die Auswirkungen der Genexpression von bcl-2 und bcl-xL abschwächt.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
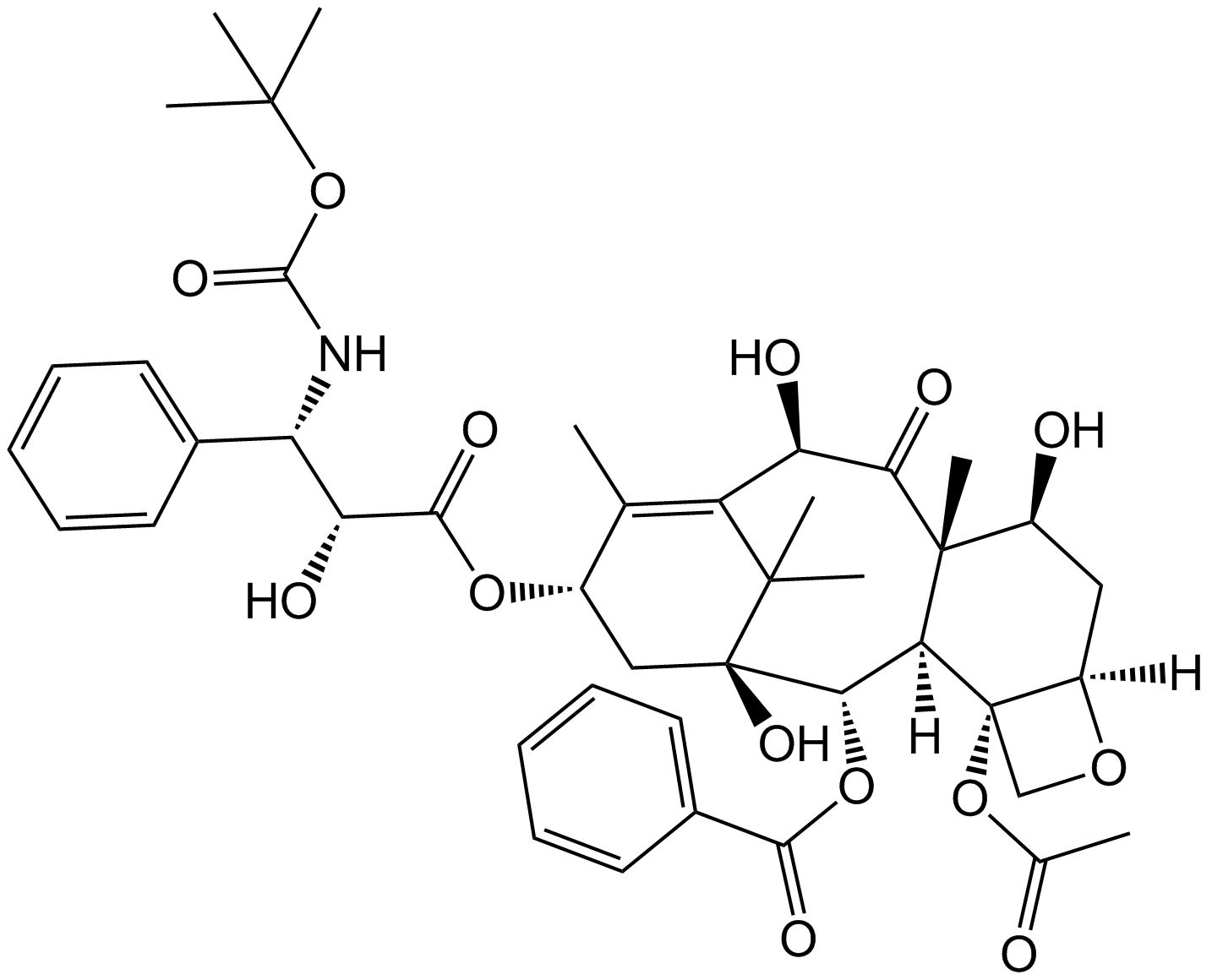
Cas No.: 114977-28-5
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Docetaxel is a taxane class of anti-mitotic chemotherapeutic agents with an IC50 of 0.2 µM. It preferentially binds to β-tubulin, suppresses microtubule dynamics, disrupts cell division, and therefore effectively induces apoptosis. Docetaxel has anti-cancer activity[1-3].
Docetaxel(5 uM;24-72h) suppressed PC-3M IE8 cell proliferation and aerobic glycolysis[4]. Docetaxel(50 nM; 12-48 h) inhibited the proliferation while it enhanced the apoptosis of human CD133 expressing HCC stem cells[5]. Docetaxel treatment activates lysosomal function and promotes its fusion with autophagosome[6].
Docetaxel-based(10 mg/kg Docetaxel per injection;i.p; once per week for two consecutive weeks) chemohormonal therapy prompted the intratumoral infiltration of T cells and upregulated the abundance of PD1 and PD-L1, thereby sensitizing mouse tumors to the anti-PD1 blockade in a xenograft mouse model[7-8].
References:
[1]. James ND, Sydes MR, et,al. Addition of docetaxel, zoledronic acid, or both to first-line long-term hormone therapy in prostate cancer (STAMPEDE): survival results from an adaptive, multiarm, multistage, platform randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016 Mar 19;387(10024):1163-77. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01037-5. Epub 2015 Dec 21. PMID: 26719232; PMCID: PMC4800035.
[2]. Sweeney CJ, Chen YH, et,al. Chemohormonal Therapy in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015 Aug 20;373(8):737-46. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1503747. Epub 2015 Aug 5. PMID: 26244877; PMCID: PMC4562797.
[3]. Buey RM, DÍaz JF, et,al. Interaction of epothilone analogs with the paclitaxel binding site: relationship between binding affinity, microtubule stabilization, and cytotoxicity. Chem Biol. 2004 Feb;11(2):225-36. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.01.014. PMID: 15123284.
[4]. Peng J, He Z, et,al. Docetaxel suppressed cell proliferation through Smad3/HIF-1α-mediated glycolysis in prostate cancer cells. Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Dec 19;20(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00950-z. PMID: 36536346; PMCID: PMC9762006.
[5]. Zhang X, Shao J, et,al. Docetaxel promotes cell apoptosis and decreases SOX2 expression in CD133‑expressing hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells by suppressing the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 2019 Feb;41(2):1067-1074. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6891. Epub 2018 Nov 27. PMID: 30483804.
[6]. Zhang J, Wang J, et,al. Docetaxel enhances lysosomal function through TFEB activation. Cell Death Dis. 2018 May 23;9(6):614. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0571-4. PMID: 29795139; PMCID: PMC5966422.
[7]. Ma Z, Zhang W, et,al. Docetaxel remodels prostate cancer immune microenvironment and enhances checkpoint inhibitor-based immunotherapy. Theranostics. 2022 Jun 27;12(11):4965-4979. doi: 10.7150/thno.73152. PMID: 35836810; PMCID: PMC9274752.
[8]. Yu Y, Yang FH, et,al. Mesenchymal stem cells desensitize castration-resistant prostate cancer to docetaxel chemotherapy via inducing TGF-beta1-mediated cell autophagy. Cell Biosci. 2021;11(1):7.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 30 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




