Epoxomicin (Synonyms: BU 4061T) |
| Katalog-Nr.GC12494 |
Epoxomicin is a selective proteasome inhibitor that effectively inhibits the chymotrypsin-like (CH-L) activity of the 20S proteasome, with an IC50 of approximately 40-80nM.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
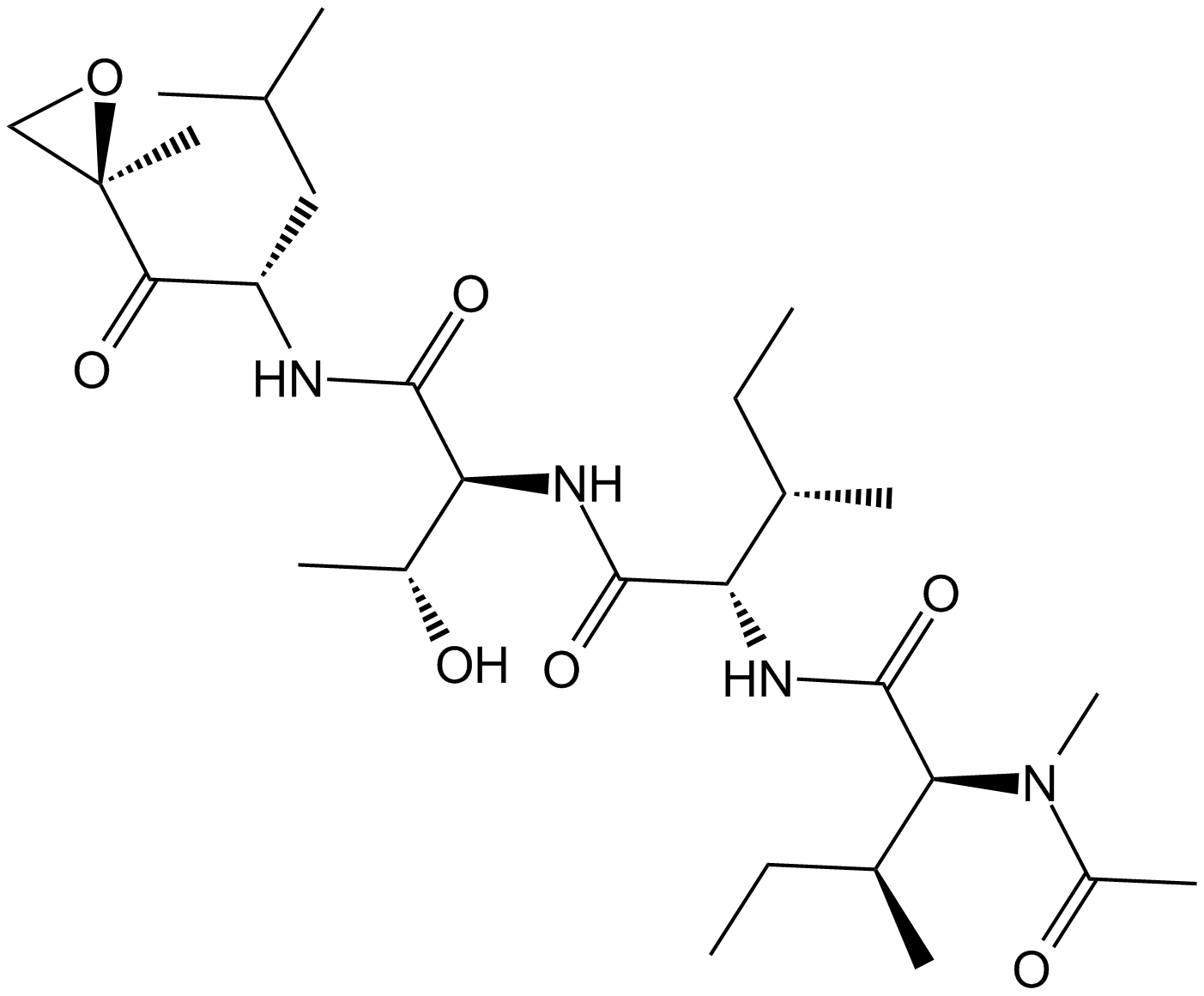
Cas No.: 134381-21-8
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Epoxomicin is a selective proteasome inhibitor that effectively inhibits the chymotrypsin-like (CH-L) activity of the 20S proteasome, with an IC50 of approximately 40-80nM[1]. Epoxomicin covalently binds to the catalytic β subunits LMP 7, X, Z, and MECL 1 of the proteasome, leading to inhibition of the proteasome subunits' CH-L, T-L, and PGPH catalytic activities[2].
In vitro, Epoxomicin shows considerable cytotoxicity against B16-F10, HCT116, Moser, P388, and K562 cells, with IC50 values of 0.002μg/mL, 0.005μg/mL, 0.044μg/mL, 0.002μg/mL, and 0.037μg/mL, respectively[3]. Epoxymycin (0.2 and 2 μM) treated HEK293T cells for 1 hour, inhibiting the expression of proteasome beta-2 and beta-5 subunits in the cells[4]. Epoxomicin (100 nM) for 24 hours in Plasmodium falciparum cells results in a 77% reduction in gametocytes[5].
In vivo, Epoxymycin (0.5mg/kg), administered intraperitoneally, reduced polyubiquitination in GAS muscle of C57BL/6 mice by 23% and increased polyubiquitination in liver by 41%, the latter associated with The inhibitory effect of proteasome β5 is consistent [6]. Epoxymycin (0.5mg/kg/day) was administered to KI and WT mice for 1 week using a subcutaneously implanted osmotic minipump, which reduced the chymotrypsin-like activity of the mice by approximately 50%[7] .
References:
[1] Meng L , Mohan R , Kwok B H B ,et al.Epoxomicin, a potent and selective proteasome inhibitor, exhibits in vivo antiinflammatory activity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1999, 96(18):10403-10408.
[2] Aboulaila M , Nakamura K , Govind Y ,et al.Evaluation of the in vitro growth-inhibitory effect of epoxomicin on Babesia parasites.[J].Veterinary Parasitology, 2010, 167(1):19-27.
[3] Hanada M, Sugawara K, Kaneta K, et al. Epoxomicin, a new antitumor agent of microbial origin.[J] Antibiot (Tokyo). 1992 Nov;45(11):1746-52.
[4] Fricker L D, Gelman J S, Castro L M, et al. Peptidomic analysis of HEK293T cells: effect of the proteasome inhibitor epoxomicin on intracellular peptides[J]. Journal of proteome research, 2012, 11(3): 1981-1990.
[5] Czesny B , Goshu S , Cook J L ,et al. The Proteasome Inhibitor Epoxomicin Has Potent Gametocytocidal Activity[J]. 2009.
[6]Jamart, Cécile, Gomes A V , Dewey S ,et al. Regulation of ubiquitin-proteasome and autophagy pathways after acute LPS and epoxomicin administration in mice[J].Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders, 2014, 15(1):166.
[7]Schlossarek,Saskia,Singh,et al. Proteasome inhibition slightly improves cardiac function in mice with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy[J].Frontiers in Physiology, 2014.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 30 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















