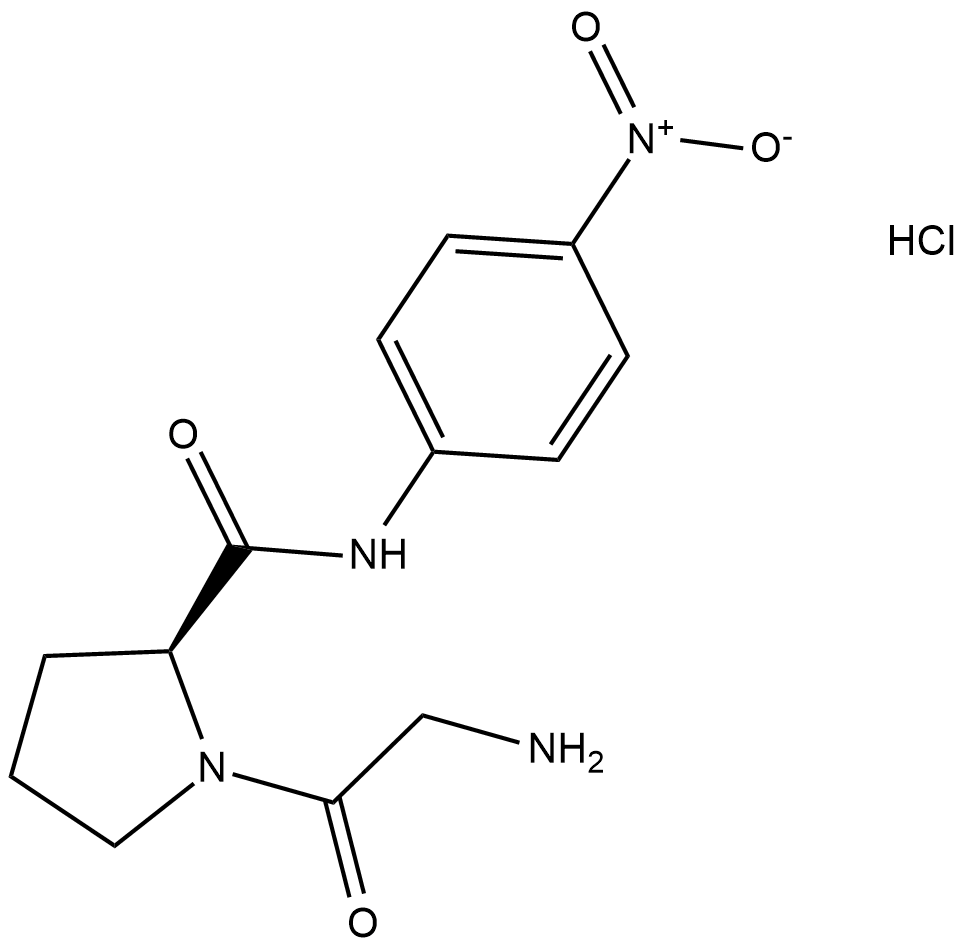
Gly-Pro-pNA (hydrochloride) (Synonyms: Gly-Pro pnitroanilide, GP-pNA) |
| Katalog-Nr.GC18201 |
Gly-Pro-pNA (hydrochloride) ist ein chromogenes Substrat, das durch das zirkulierende Enzym Dipeptidylpeptidase IV (DPP IV) gespalten werden kann.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
Cas No.: 103213-34-9
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Gly-Pro-pNA (hydrochloride) ist ein chromogenes Substrat, das durch das zirkulierende Enzym Dipeptidylpeptidase IV (DPP IV) gespalten werden kann. Die Enzymaktivität kann durch kolorimetrische Detektion von freiem p-Nitroanilid bei 405 nm quantifiziert werden. Dieses Substrat kann verwendet werden, um nach DPP-IV-Inhibitoren zu suchen.[5].
Stutenmolkenproteine zeigen in vitro eine gute DPP-IV-hemmende Aktivität und sind in der Lage, DPP-IV daran zu hindern, Gly-Pro-pNA (hydrochloride) abzubauen. [1]. Die in vitro DPP-IV-hemmenden Aktivitäten von Quinoa-Protein-Hydrolysaten können mit Gly-Pro-pNA (hydrochloride) als Substrat bestimmt werden[2]. Gly-Pro-pNA (hydrochloride) kann auch zur Bewertung der Aktivität von DPP-IV im menschlichen Serum verwendet werden[3]. Es zeigt sich, dass DPP IV bei Diabetikern nicht sehr unterschiedlich im Vergleich zu normalen Bedingungen ist[4]. Gly-pro p-Nitroanilid Hydrochlorid wurde als Substrat verwendet, um den DPPIV-Spiegel bei Patienten mit polyzystischem Ovarialsyndrom (PCOS) zu bestimmen. Eine Deregulierung der DPP4-Serumspiegel könnte ein zusätzliches Merkmal der mit PCOS verbundenen metabolischen Ungleichgewichte sein[5].
Die Verwendung von Gly-Pro-pNA (hydrochloride) als Substrat kann die enzymatische Aktivität und den biochemischen Status der Dipeptidylpeptidase IV (DPP IV) bei Patienten mit rheumatoider Arthritis bewerten[6].
References:
[1]. Song JJ, Wang Q, et,al. Identification of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides from mare whey protein hydrolysates. J Dairy Sci. 2017 Sep;100(9):6885-6894. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-11828. Epub 2017 Jul 12. PMID: 28711271.
[2]. You H, Wu T, et,al. Preparation and identification of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptides from quinoa protein. Food Res Int. 2022 Jun;156:111176. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111176. Epub 2022 Mar 19. PMID: 35651037.
[3]. Yeganeh F, Mousavi SMJ, et,al. Association of CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV mRNA level in peripheral blood mononuclear cells with disease activity and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Dec;37(12):3183-3190. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4268-y. Epub 2018 Aug 22. PMID: 30136129.
[4]. Sun AL, Deng JT, et,al. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV is a potential molecular biomarker in diabetic kidney disease. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2012 Oct;9(4):301-8. doi: 10.1177/1479164111434318. Epub 2012 Mar 2. PMID: 22388283.
[5]. Blauschmidt S, Greither T, et,al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 serum activity and concentration are increased in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2017 Dec;87(6):741-747. doi: 10.1111/cen.13444. Epub 2017 Sep 13. PMID: 28799235.
[6]. Mavropoulos JC, Cuchacovich M, et,al. Anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy augments dipeptidyl peptidase IV activity and decreases autoantibodies to GRP78/BIP and phosphoglucose isomerase in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2005 Nov;32(11):2116-24. PMID: 16265688.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 38 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















