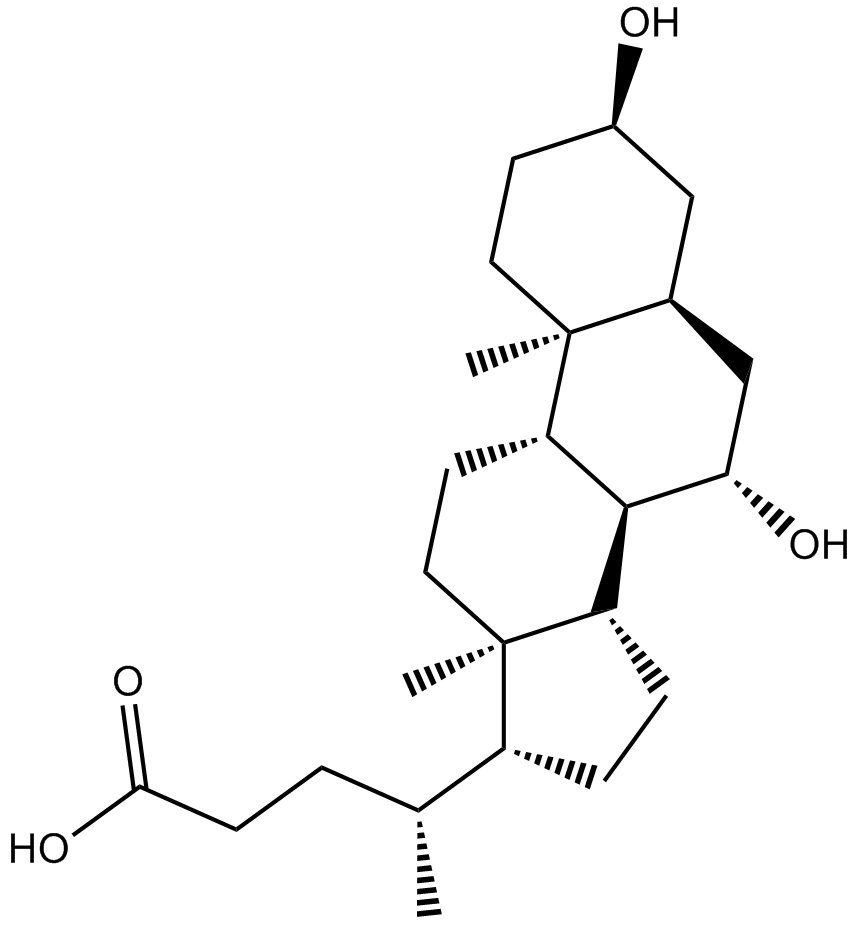
Ursodiol (Synonyms: NSC 683769, UDCA, Ursodiol) |
| Katalog-Nr.GC13363 |
Ursodiol (Ursodeoxycholat) ist eine sekundÄre GallensÄure, die bei der Umwandlung von (Cheno)desoxycholsÄure durch Darmbakterien entsteht und als SchlÜsselregulator fÜr die IntegritÄt der Darmbarriere fungiert und fÜr den Fettstoffwechsel unerlÄsslich ist.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
Cas No.: 128-13-2
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Ursodiol (UDCA) is a secondary bile acid derived from the 7α/β isomerization of the primary bile acid chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) by microorganisms. Ursodiol can be used in the study of various liver diseases and gastrointestinal diseases. Ursodiol has cytoprotective, anti-apoptotic, membrane-stabilizing, antioxidant and immunomodulatory effects[1-3].
Ursodiol can inhibit the viability of HepG2 and BEL7402 cells with IC50 of 0.92 mmol/L and 0.86 mmol/L, respectively, but Ursodiol has no effect on the viability of normal hepatocytes L-02. After Ursodiol (1.0 mmol/L) treatment, the apoptosis rate of HepG2 and BEL7402 cells was significantly increased in a concentration-dependent manner, whereas the apoptosis rate of L-02 cells did not change significantly.Ursodiol inhibits Bcl-2 expression and promotes Bax expression [2].
Mice treated with low and high doses (50 and 450 mg/kg/day) of Ursodiol showed significant weight loss, whereas 150 mg/kg/day had no significant effect on mouse body weight. After 21 days of ursodiol treatment, the microbial community structure and bile acid pool in the ileum and cecum contents and feces of mice were significantly changed compared with those before treatment. Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA), Glycoursodeoxycholic acid (GUDCA) and Lithocholic acid (LCA) levels were significantly elevated in the ileum of mice treated with Ursodiol 450 mg/kg[1]. Ursodiol treatment at 416 mg/kg reduces SARS-CoV-2 transmission in a Syrian golden hamster SARS-CoV-2 infection model[4].
References:
[1]Winston JA, Rivera A, Cai J, Patterson AD, Theriot CM. Secondary bile acid ursodeoxycholic acid alters weight, the gut microbiota, and the bile acid pool in conventional mice. PLoS One. 2021 Feb 18;16(2):e0246161.
[2] Liu H, Qin CY, Han GQ, Xu HW, Meng M, Yang Z. Mechanism of apoptotic effects induced selectively by ursodeoxycholic acid on human hepatoma cell lines. World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Mar 21;13(11):1652-8.
[3] Kumar D, Tandon RK. Use of ursodeoxycholic acid in liver diseases. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001 Jan;16(1):3-14.
[4] Brevini T, Maes M, Webb G J, et al. FXR inhibition may protect from SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing ACE2[J]. Nature, 2023, 615(7950): 134-142.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 26 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















