Z-Ile-Leu-aldehyde (Synonyms: Z-IL-CHO; GSI-XII; γ-Secretase inhibitor XII) |
| Catalog No.GC15896 |
Le Z-Ile-Leu-aldéhyde (Z-IL-CHO) est un inhibiteur peptidique puissant et compétitif de la γ-sécrétase et de l'encoche.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
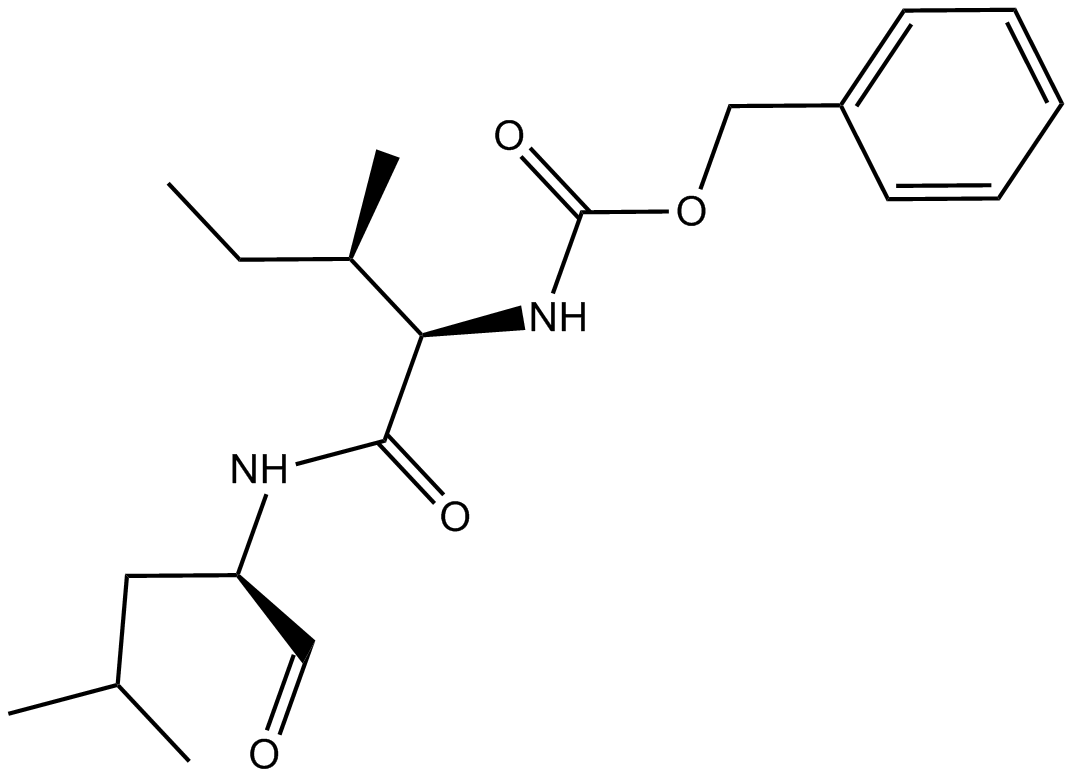
Cas No.: 161710-10-7
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Z-Ile-Leu-aldehyde (gamma-Secretase inhibitor XII /GSI XII, Z-IL-CHO) is a potent gamma-Secretase inhibitor and Notch signaling inhibitor.
Notch signaling impinges on many cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and maintenance of stem cells. It is also involved in many developmental systems, including neurogenesis, angiogenesis, hematopoiesis, and myogenesis. Deregulation of Notch signaling leads to developmental syndromes and cancer [3]. In order to transmit a signal, Notch receptors undergo a series of proteolytic cleavages after binding their cognate ligands of the Delta-like and Jagged family. γ-Secretase is a large protease complex that cleaves the membrane-bound form of Notch and releases the intracellular domain of the Notch receptor. This step in Notch signaling is pivotal in the activation of this signaling cascade [1] [2].
In vitro: GSI XII (10~15 µM) blocked the Notch signaling, reduced cell viability and induced apoptosis in MOPC315.BM murine multiple myeloma cells in vitro. GSI XII (10 µM) impaired murine osteoclast differentiation of receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)-stimulated RAW264.7 murine monocyte/macrophage cell line [1]. GSI XII (8 μM ~ 15 μM) potently triggered an apoptotic response through inhibition of Notch activity in the breast cancer cells. GSI XII also targets mammary cancer stem-like cells because it dramatically prevented in vitro mammosphere formation [3].
In vivo: Notch inhibition through GSI XII (intraperitoneal injection, 10 mg/kg) reduced myeloma-specific paraprotein levels, bone loss and diminished osteolytic lesions in the MOPC315.BM mice model[1]. Notch inhibition using GSI XII (intraperitoneal injection, 5 mg/kg) blocked embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma tumorigenesis in mice[2].
ex vivo: A model of 3D culture of human breast cancer tissues was developed to study a series of 30 consecutive primary tumors from patients with untreated breast cancer for their sensitivity to the Notch inhibitor GSI XII (15 μM). The results indicated that 24 tumors are sensitive to apoptosis induction by GSIXII.
References:
[1]. Schwarzer R, Nickel N, Godau J, et al. Notch pathway inhibition controls myeloma bone disease in the murine MOPC315. BM model[J]. Blood cancer journal, 2014, 4(6): e217.
[2]. Belyea B C, Naini S, Bentley R C, et al. Inhibition of the Notch-Hey1 axis blocks embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma tumorigenesis[J]. Clinical Cancer Research, 2011, 17(23): 7324-7336.
[3]. Séveno C, Loussouarn D, Bréchet S, et al. γ-Secretase inhibition promotes cell death, Noxa upregulation, and sensitization to BH3 mimetic ABT-737 in human breast cancer cells[J]. Breast Cancer Research, 2012, 14(3): R96.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 16 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















