GGsTop (Synonyms: Nahlsgen) |
| Catalog No.GC16612 |
γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) inhibitor, novel and irreversible
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
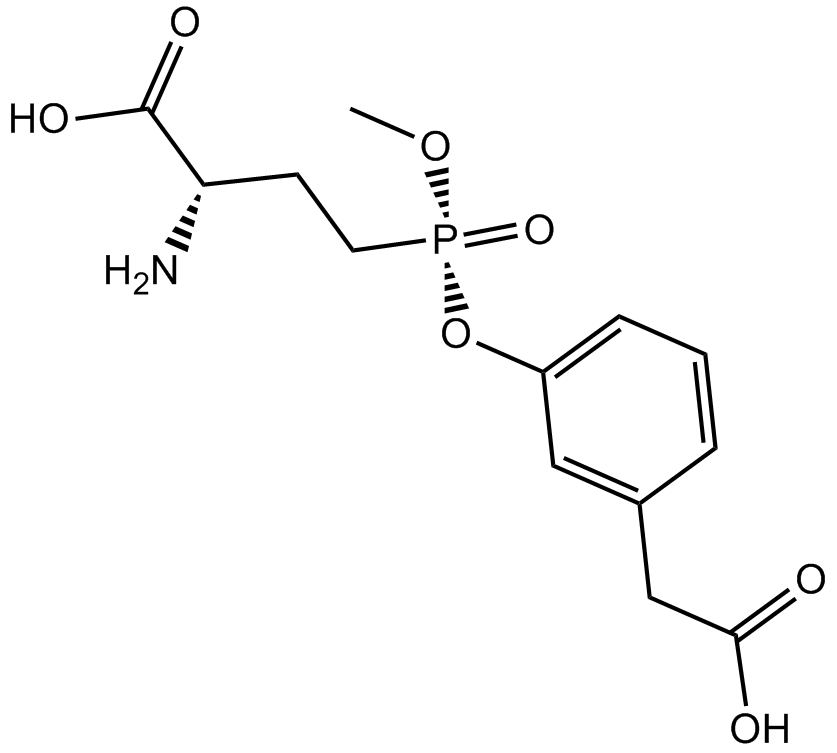
Cas No.: 926281-37-0
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
GGsTop is a novel is a novel, highly selective, and irreversible γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) inhibitor with Ki of 0.17 mM. [1]
GGT plays an important role in the metabolism of plasma glutathione (GSH) and its S-conjugates via the cleavage of the γ-glutamyl amide bond by hydrolysis and/or transpeptidation. GGT exists in the lung as a soluble enzyme in association with surfactant phospholipids and controls turnover of the extracellular pool of glutathione in LLF (lung lining fluid). In the human enzyme, a specific residue in the Cys - Gly binding site played a critical role in recognizing the Cys – Gly moiety or the acceptor molecules by interacting with the C-terminal carboxy group, whereas the Cys side chain and the Cys - Gly amide bond were not recognized significantly. GGsTop was found for its potency against GGT in a series of analogues designed for structure-activity relationships. [1, 2]
The inactivation rates of E. coli and human GGT by GGsTop were studied. GGsTop showed a good potency against GGT in both species. Furthermore, the kinetics of GGsTop for human GGT was also measured and its Ki value is 0.17 mM. [1]
In the IL-13 model, mice treated with IL-13 and GGsTop exhibit a lung inflammatory response similar to that of mice administrated with IL-13 alone. However, mice treated with IL-13 and GGsTop exhibit attenuation of methacholine-stimulated airway hyper-reactivity, inhibitory effect of Muc5ac and Muc5b gene induction, decreased epithelial cell mucous accumulation in the airway and a 4-fold increase in LLF glutathione content compared to mice in IL-13 group. The associated increase in LLF glutathione can protect lung airway epithelial cells against oxidant injury associated with inflammation in asthma. Moreover, ischemic acute kidney injury (AKI) was induced by occlusion of the left renal artery and vein for 45 min followed by reperfusion 2 weeks after contralateral nephrectomy. Renal function in control significantly decreased at 1 day after reperfusion. Rats administrated with GGsTop at doses of 1 and 10 mg per kg i.v. 5 min before ischemia attenuated the I/R-induced renal dysfunction in a dose-dependent manner. Histopathological evaluation of the kidney of AKI rats revealed severe renal damages, whereas they were significantly suppressed by the GGsTop treatment. [2, 3]
References:
[1]. Han, Liyou, et al. "Design, synthesis, and evaluation of γ-phosphono diester analogues of glutamate as highly potent inhibitors and active site probes of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase." Biochemistry 46.5 (2007): 1432-1447.
[2]. Yamamoto, Shinya, et al. "Preventive effect of GGsTop, a novel and selective γ-glutamyl transpeptidase inhibitor, on ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury in rats." Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 339.3 (2011): 945-951.
[3]. Tuzova, Marina, et al. "Inhibiting lung lining fluid glutathione metabolism with GGsTop as a novel treatment for asthma." Frontiers in pharmacology 5 (2014)
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 4 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




