ALW-II-41-27 (Synonyms: Eph receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor;) |
| カタログ番号GC11134 |
多機能キナーゼ阻害剤
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
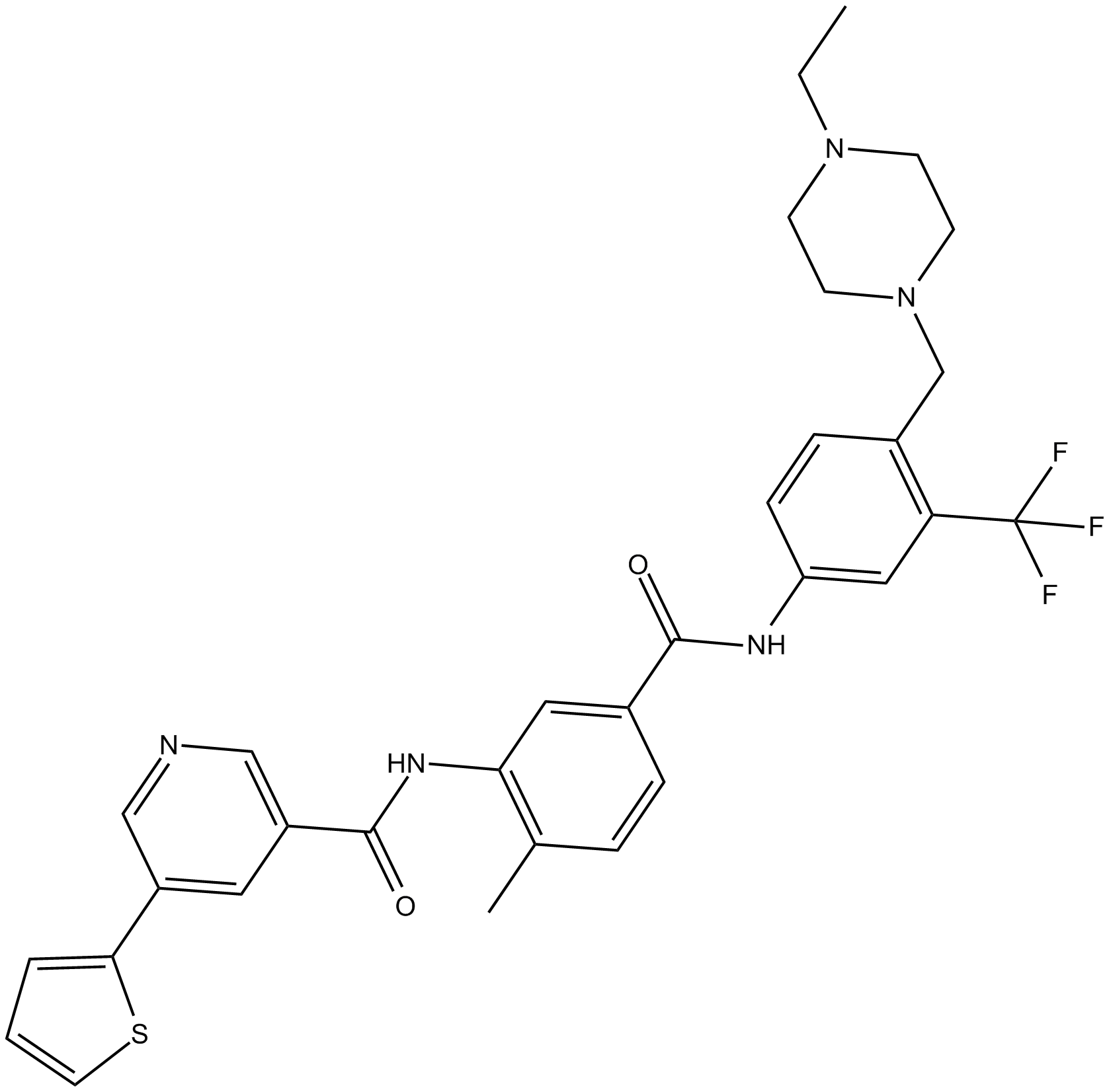
Cas No.: 1186206-79-0
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
ALW-II-41-27 is an Eph family tyrosine kinase inhibitor with an IC50 of 11 nM to inhibit Eph2[1].
ALW-II-41-27(1μM;72 h) inhibited the proliferation of Erlotinib-resistant NSCLC cell lines and increased cell apoptosis. ALW-II-41-27 induced apoptosis was accompanied by an increase in caspase-3 and PARP and a decrease in the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins BCL-xL and MCL-1[3]. ALW-II-41-27(200, 600 or 1,000 nM ALW-II-41-27; 24, 48 or 72 h) inhibited cervical cancer (CC) cell proliferation, migration and invasion by blocking the RhoA/ROCK pathway[4]. ALW-II-41-27 inhibited pY772-EphA2 and EphA2-Y772A decreased the inhibitory effect of ALW-II-41-27 on NPC cell proliferation[6]. Combined treatment with ALW-II-41-27 plus cetuximab reverted primary and acquired resistance to cetuximab, causing cell growth inhibition, inducing apoptosis and cell-cycle G1-G2 arrest[7].
ALW-II-41-27(15 mg/kg;14 days; i.p.) significantly inhibited growth of the erlotinib-resistant tumors[3]. Administration of ALW-II-41-27(15, 30 mg/kg;twice a day; i.p.)significantly inhibited H358 tumor growth in tumor-bearing mice. Histological analysis showed a significant increase in apoptosis in tumors treated with ALW-II-41-27 compared with those treated with NG-25 or the carrier, similar to the effect of genetic ablation of EPHA2[2]. ALW-II-41-27 (12.5, 25, 50, and 100 μg/kg; i.p.) decreased gastrointestinal motility and abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) scores, markedly reduced the levels of oxidative stress markers [4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE), protein carbonyl, and 8-hydroxy-2-de-axyguanine (8-OHdG)] and proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-17, and ICAM-1), and remarkably increased the level of anti-inflammatory cytokine (IL-10) in serum and colon of Trichinella spiralis-infected mice[5].
References:
[1]. Choi Y, Syeda F, et,al. Discovery and structural analysis of Eph receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Aug 1;19(15):4467-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.05.029. Epub 2009 May 13. PMID: 19553108; PMCID: PMC2730633.
[2]. Amato KR, Wang S, et,al. Genetic and pharmacologic inhibition of EPHA2 promotes apoptosis in NSCLC. J Clin Invest. 2014 May;124(5):2037-49. doi: 10.1172/JCI72522. Epub 2014 Apr 8. PMID: 24713656; PMCID: PMC4001547.
[3]. Amato KR, Wang S, et,al. EPHA2 Blockade Overcomes Acquired Resistance to EGFR Kinase Inhibitors in Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016 Jan 15;76(2):305-18. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0717. Epub 2016 Jan 7. PMID: 26744526; PMCID: PMC4715957.
[4]. Li X, Li D, et,al.ALW-II-41-27, an EphA2 inhibitor, inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells via inhibition of the RhoA/ROCK pathway. Oncol Lett. 2022 Apr;23(4):129. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13249. Epub 2022 Feb 18. PMID: 35251349; PMCID: PMC8895465.
[5]. Zeng L, Li K, et,al.A Novel EphA2 Inhibitor Exerts Beneficial Effects in PI-IBS in Vivo and in Vitro Models via Nrf2 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2018 Mar 27;9:272. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00272. PMID: 29662452; PMCID: PMC5890185.
[6]. Xiang YP, Xiao T, et,al. Y772 phosphorylation of EphA2 is responsible for EphA2-dependent NPC nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth by Shp2/Erk-1/2 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 27;11(8):709. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02831-0. PMID: 32848131; PMCID: PMC7449971.
[7]. Martini G, Cardone C, et,al. EPHA2 Is a Predictive Biomarker of Resistance and a Potential Therapeutic Target for Improving Antiepidermal Growth Factor Receptor Therapy in Colorectal Cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019 Apr;18(4):845-855. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0539. Epub 2019 Mar 1. PMID: 30824612.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 30 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















