Apoptosis
As one of the cellular death mechanisms, apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, can be defined as the process of a proper death of any cell under certain or necessary conditions. Apoptosis is controlled by the interactions between several molecules and responsible for the elimination of unwanted cells from the body.
Many biochemical events and a series of morphological changes occur at the early stage and increasingly continue till the end of apoptosis process. Morphological event cascade including cytoplasmic filament aggregation, nuclear condensation, cellular fragmentation, and plasma membrane blebbing finally results in the formation of apoptotic bodies. Several biochemical changes such as protein modifications/degradations, DNA and chromatin deteriorations, and synthesis of cell surface markers form morphological process during apoptosis.
Apoptosis can be stimulated by two different pathways: (1) intrinsic pathway (or mitochondria pathway) that mainly occurs via release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria and (2) extrinsic pathway when Fas death receptor is activated by a signal coming from the outside of the cell.
Different gene families such as caspases, inhibitor of apoptosis proteins, B cell lymphoma (Bcl)-2 family, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor gene superfamily, or p53 gene are involved and/or collaborate in the process of apoptosis.
Caspase family comprises conserved cysteine aspartic-specific proteases, and members of caspase family are considerably crucial in the regulation of apoptosis. There are 14 different caspases in mammals, and they are basically classified as the initiators including caspase-2, -8, -9, and -10; and the effectors including caspase-3, -6, -7, and -14; and also the cytokine activators including caspase-1, -4, -5, -11, -12, and -13. In vertebrates, caspase-dependent apoptosis occurs through two main interconnected pathways which are intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. The intrinsic or mitochondrial apoptosis pathway can be activated through various cellular stresses that lead to cytochrome c release from the mitochondria and the formation of the apoptosome, comprised of APAF1, cytochrome c, ATP, and caspase-9, resulting in the activation of caspase-9. Active caspase-9 then initiates apoptosis by cleaving and thereby activating executioner caspases. The extrinsic apoptosis pathway is activated through the binding of a ligand to a death receptor, which in turn leads, with the help of the adapter proteins (FADD/TRADD), to recruitment, dimerization, and activation of caspase-8 (or 10). Active caspase-8 (or 10) then either initiates apoptosis directly by cleaving and thereby activating executioner caspase (-3, -6, -7), or activates the intrinsic apoptotic pathway through cleavage of BID to induce efficient cell death. In a heat shock-induced death, caspase-2 induces apoptosis via cleavage of Bid.
Bcl-2 family members are divided into three subfamilies including (i) pro-survival subfamily members (Bcl-2, Bcl-xl, Bcl-W, MCL1, and BFL1/A1), (ii) BH3-only subfamily members (Bad, Bim, Noxa, and Puma9), and (iii) pro-apoptotic mediator subfamily members (Bax and Bak). Following activation of the intrinsic pathway by cellular stress, pro‑apoptotic BCL‑2 homology 3 (BH3)‑only proteins inhibit the anti‑apoptotic proteins Bcl‑2, Bcl-xl, Bcl‑W and MCL1. The subsequent activation and oligomerization of the Bak and Bax result in mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). This results in the release of cytochrome c and SMAC from the mitochondria. Cytochrome c forms a complex with caspase-9 and APAF1, which leads to the activation of caspase-9. Caspase-9 then activates caspase-3 and caspase-7, resulting in cell death. Inhibition of this process by anti‑apoptotic Bcl‑2 proteins occurs via sequestration of pro‑apoptotic proteins through binding to their BH3 motifs.
One of the most important ways of triggering apoptosis is mediated through death receptors (DRs), which are classified in TNF superfamily. There exist six DRs: DR1 (also called TNFR1); DR2 (also called Fas); DR3, to which VEGI binds; DR4 and DR5, to which TRAIL binds; and DR6, no ligand has yet been identified that binds to DR6. The induction of apoptosis by TNF ligands is initiated by binding to their specific DRs, such as TNFα/TNFR1, FasL /Fas (CD95, DR2), TRAIL (Apo2L)/DR4 (TRAIL-R1) or DR5 (TRAIL-R2). When TNF-α binds to TNFR1, it recruits a protein called TNFR-associated death domain (TRADD) through its death domain (DD). TRADD then recruits a protein called Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD), which then sequentially activates caspase-8 and caspase-3, and thus apoptosis. Alternatively, TNF-α can activate mitochondria to sequentially release ROS, cytochrome c, and Bax, leading to activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 and thus apoptosis. Some of the miRNAs can inhibit apoptosis by targeting the death-receptor pathway including miR-21, miR-24, and miR-200c.
p53 has the ability to activate intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis by inducing transcription of several proteins like Puma, Bid, Bax, TRAIL-R2, and CD95.
Some inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) can inhibit apoptosis indirectly (such as cIAP1/BIRC2, cIAP2/BIRC3) or inhibit caspase directly, such as XIAP/BIRC4 (inhibits caspase-3, -7, -9), and Bruce/BIRC6 (inhibits caspase-3, -6, -7, -8, -9).
Any alterations or abnormalities occurring in apoptotic processes contribute to development of human diseases and malignancies especially cancer.
References:
1.Yağmur Kiraz, Aysun Adan, Melis Kartal Yandim, et al. Major apoptotic mechanisms and genes involved in apoptosis[J]. Tumor Biology, 2016, 37(7):8471.
2.Aggarwal B B, Gupta S C, Kim J H. Historical perspectives on tumor necrosis factor and its superfamily: 25 years later, a golden journey.[J]. Blood, 2012, 119(3):651.
3.Ashkenazi A, Fairbrother W J, Leverson J D, et al. From basic apoptosis discoveries to advanced selective BCL-2 family inhibitors[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2017.
4.McIlwain D R, Berger T, Mak T W. Caspase functions in cell death and disease[J]. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology, 2013, 5(4): a008656.
5.Ola M S, Nawaz M, Ahsan H. Role of Bcl-2 family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis[J]. Molecular and cellular biochemistry, 2011, 351(1-2): 41-58.
対象は Apoptosis
- Pyroptosis(31)
- Caspase(54)
- 14.3.3 Proteins(1)
- Apoptosis Inducers(41)
- Bax(8)
- Bcl-2 Family(108)
- Bcl-xL(8)
- c-RET(8)
- IAP(26)
- KEAP1-Nrf2(68)
- MDM2(13)
- p53(112)
- PC-PLC(4)
- PKD(7)
- RasGAP (Ras- P21)(1)
- Survivin(6)
- Thymidylate Synthase(10)
- TNF-α(131)
- Other Apoptosis(884)
- Apoptosis Detection(0)
- Caspase Substrate(0)
- APC(5)
- PD-1/PD-L1 interaction(61)
- ASK1(3)
- PAR4(2)
- RIP kinase(50)
- FKBP(19)
- Cuproptosis(0)
製品は Apoptosis
- Cat.No. 商品名 インフォメーション
-
GC11543
Cesium chloride

-
GC68857
Cetrelimab
JNJ 63723283; JNJ 3283
Cetrelimab(JNJ 63723283; JNJ 3283)は、PD-1を標的とする人工合成のIgG4κモノクローナル抗体です。Cetrelimabは、HEK293細胞においてPD-1に結合するKdが1.72 nMであり、PD-1とPD-L1およびPD-L2の相互作用を阻害します(IC50値はそれぞれ111.7 ng/mLおよび138.6 ng/mL)。また、Cetrelimabは末梢T細胞を刺激し、細胞因子(IFN-γ、IL-2、TNF-α)レベルを増加させると同時に腫瘍の成長を抑制します。

-
GC11710
CFM 4
CFM 4 は、CARP-1/APC-2 結合の強力な低分子アンタゴニストです。 CFM 4 は、CARP-1 と APC-2 の結合を防ぎ、G2M 細胞周期停止を引き起こし、10-15 μM の IC50 範囲でアポトーシスを誘導します。 CFM 4 は、薬剤耐性のヒト乳癌細胞の増殖も抑制します。

-
GC35668
CG-200745
CG-200745
CG-200745 (CG-200745) は、触媒ポケットの底部で亜鉛に結合するヒドロキサム酸部分を有する、経口活性の強力な汎 HDAC 阻害剤です。 CG-200745 は、ヒストン H3 とチューブリンの脱アセチル化を阻害します。 CG-200745 は、p53 の蓄積を誘導し、p53 依存性のトランス活性化を促進し、MDM2 および p21 (Waf1/Cip1) タンパク質の発現を増強します。 CG-200745 は、ゲムシタビンおよび 5-フルオロウラシル (5-FU; ) に対するゲムシタビン耐性細胞の感受性を高めます。 CG-200745 はアポトーシスを誘導し、抗腫瘍効果があります。
-
GC10666
CGP 57380
MNK1 Inhibitor
CGP 57380 は、2.2 μM の IC50 で Mnk1 の選択的阻害剤として作用する細胞透過性ピラゾロ - ピリミジン化合物ですが、p38、JNK1、ERK1/2、PKC、または Src 様キナーゼに対する阻害活性はありません。
-
GC43234
Chaetoglobosin A
ペニシリウム アクアマリニウムの抽出物に含まれる有効成分であるケトグロボシン A は、サイトカラサン ファミリーのメンバーです。
-
GC18536
Chartreusin
Antibiotic X 465A, Lambdamycin, NSC 5159
シャルトリューシンは、元々Sから分離された抗生物質です。
-
GN10463
Chelerythrine

-
GC13065
Chelerythrine Chloride
Broussonpapyrine chloride, NSC 646662
PKCとBcl-xLの強力な阻害剤

-
GC31886
Chelidonic acid
NSC 3979
ケリドン酸はChelidonium majus Lの成分です。
-
GC40878
Chelidonine
ケリドニンはイソキノリン アルカロイドであり、Chelidonium majus L から分離できます。
-
GC43236
Chevalone B
シュヴァロンBは、元々キノコEから分離されたメロテルペノイドです。

-
GC43237
Chevalone C
メロテルペノイド真菌代謝産物であるシュバロン C は、25.00 μg/mL の IC50 値で抗マラリア活性を示します。

-
GC64993
Chicoric acid
L-Chicoric Acid, Dicaffeoyltartaric Acid, NSC 99173
経口活性ジカフェイル酒石酸であるチコリ酸 (Cichoric acid) は、活性酸素種 (ROS) の生成を誘導します。
-
GC15739
CHIR-124
CHIR-124 は、IC50 が 0.3 nM の強力で選択的な Chk1 阻害剤であり、PDGFR と FLT3 を強力に標的とし、IC50 は 6.6 nM と 5.8 nM です。
-
GC43239
Chk2 Inhibitor
SC-203885
Chk2 阻害剤 (化合物 1) は、チェックポイントキナーゼ 2 (Chk2) の強力かつ選択的な阻害剤であり、Chk2 と Chk1 の IC50 はそれぞれ 13.5 nM と 220.4 nM です。 Chk2 阻害剤は、強力な毛細血管拡張性運動失調症変異 (ATM) 依存性 Chk2 を介した放射線防護効果を誘発することができます。
-
GC45717
Chlamydocin
真菌の代謝産物であるクラミドシンは、IC50 が 1.3 nM の非常に強力な HDAC 阻害剤です。クラミドシンは、強力な抗増殖活性と抗癌活性を示します。クラミドシンは、カスパーゼ 3 を活性化することによってアポトーシスを誘導します。

-
GC17969
CHM 1
NSC 656158
チューブリン重合の阻害剤

-
GC35682
CHMFL-ABL/KIT-155
CHMFL-ABL-KIT-155
CHMFL-ABL/KIT-155 (CHMFL-ABL-KIT-155; 化合物 34) は、非常に強力な経口活性型 II ABL/c-KIT デュアル キナーゼ阻害剤 (それぞれ 46 nM および 75 nM の IC50) であり、 BLK (IC50=81 nM)、CSF1R (IC50=227 nM)、DDR1 (IC50=116 nM)、DDR2 (IC50=325 nM)、LCK (IC50=12 nM)、PDGFRβ (IC50= 80 nM) キナーゼ。 CHMFL-ABL/KIT-155 (CHMFL-ABL-KIT-155) は、細胞周期の進行を停止させ、アポトーシスを誘導します。
-
GC64028
Chrysosplenol D
クリソプレノール D は、トリプル ネガティブのヒト乳癌細胞で ERK1/2 を介したアポトーシスを誘導するメトキシ フラボノイドです。

-
GC13408
CI994 (Tacedinaline)
N-Acetyldinaline, Goe 5549, PD 123654, Tacedinaline
HDAC1、-2、および-3の阻害剤

-
GC13589
CID 755673
CID 755673 は、PKD1、PKD2、および PKD3 に対してそれぞれ 182 nM、280 nM、および 227 nM の IC50 を持つ強力な PKD 阻害剤です。

-
GC19436
CID-5721353
CID-5721353 は、147 μM の Ki に対応する 212 μM の IC50 値を持つ BCL6 の阻害剤です。

-
GC32997
Cinchonine ((8R,9S)-Cinchonine)
シンコニン ((8R,9S)-シンコニン) は、キナの樹皮に含まれる天然化合物です。シンコニン ((8R,9S)-シンコニン) は、ヒト肝癌細胞の小胞体ストレス誘導アポトーシスを活性化します。

-
GC60708
Cinchonine hydrochloride
シンコニン塩酸塩 ((8R,9S)-シンコニン塩酸塩) は、キナの樹皮に含まれる天然のアルカロイドで、抗マラリア活性があります。シンコニン塩酸塩は、ヒト肝癌細胞の小胞体 (ER) ストレス誘発性アポトーシスを活性化します。

-
GC52269
Cinnabarinic Acid-d4
シナバリン酸の定量化のための内部標準
-
GC40986
Cinnamamide
NSC 32953
シナミルアミドはトランスシンナム酸のアミド形態であり、ストレプトマイセスの代謝物です。

-
GN10189
Cinobufagin
NSC 90325
-
GC70418
Cipepofol
Cipepofol(Ciprol)は新規な2,6−二置換フェノール誘導体であり、GABAA受容体の陽変性調節剤と直接作動剤である。

-
GC11908
Cisplatin
CDDP
Cisplatinは、最も優れた金属系抗がん剤の一つであり、精巣、卵巣、膀胱、肺、子宮頸部、頭頸部、胃、およびその他のいくつかのがんなど、広範囲の固形がんの治療に使用されている。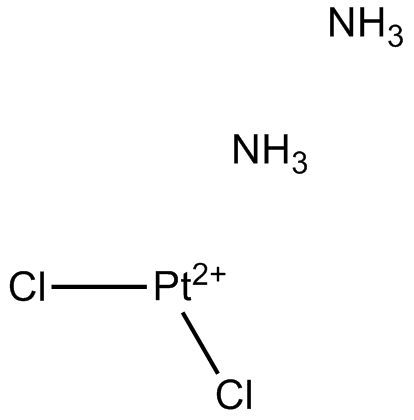
-
GC17491
CITCO
イミダゾチアゾール誘導体である CITCO は、選択的構成アンドロスタン受容体 (CAR) アゴニストです。 CITCO は、脳腫瘍幹細胞 (BTSC) の成長と拡大を阻害し、プレグナン X 受容体 (PXR) に対して 49 nM の EC50 を持ち、他の核内受容体に対する活性はありません。

-
GC35703
Citicoline
シチコリン (シチジン二リン酸-コリン) は、細胞膜の成分であるホスファチジルコリンの合成における中間体です。

-
GC31186
Citicoline sodium salt
Cytidine 5'diphosphocholine, Flussorex, Gerolin, Logan, Neurotron, Sinkron
シチコリンナトリウム塩は、細胞膜の成分であるホスファチジルコリンの合成中間体であり、また神経保護効果も発揮します。

-
GC43273
Citreoindole
シトレオインドールは、Pの2つの株のハイブリッド細胞融合から分離されたジケトピペラジン代謝物です。

-
GC41514
Citreoviridin
ペニシリウム シトレオビリド NRRL 2579 由来の毒素であるシトレオビリジンは、脳シナプトソームの Na+/K+-ATPase を阻害しますが、ミクロソームでは、Na+/K+-ATPase と Mg2+-ATPase の両方の活性を阻害します。用量依存的に有意に刺激される。

-
GC14203
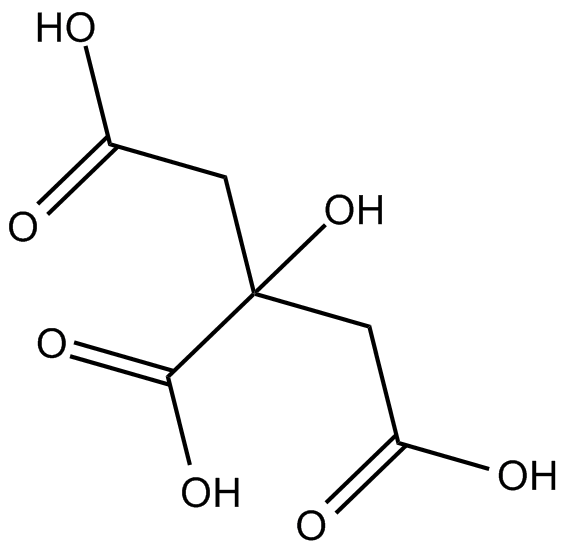
Citric acid
クエン酸は天然の防腐剤であり、食品の酸味増強剤です。
-
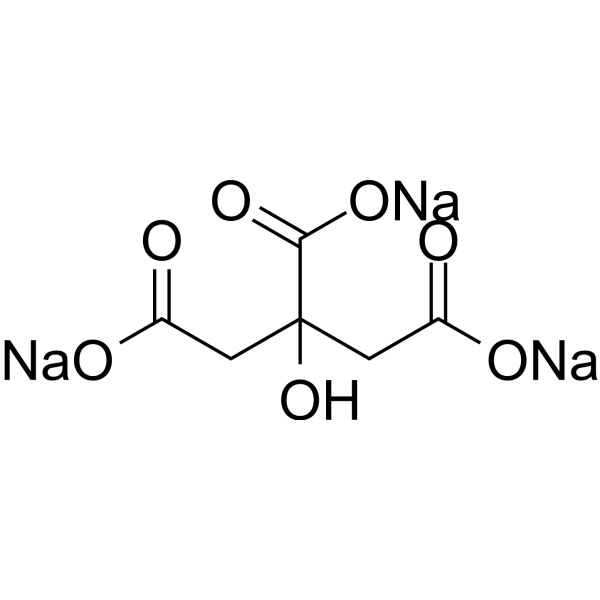
GC68873
Citric acid trisodium
クエン酸トリナトリウムは、天然の防腐剤および食品の酸味増強剤です。クエン酸トリナトリウムは細胞死(アポトーシス)を誘導し、G2/M期およびS期で細胞周期を停止させます。クエン酸トリナトリウムは抗酸化酵素活性を低下させ、肝臓の酸化的損傷を引き起こします。また、クエン酸トリナトリウムはマウスに腎毒性を引き起こします。
-
GC68051
Citric acid-d4
-
GC16661
Citrinin
NSC 186
シトリニン(Citrinin)は、Penicillium、Aspergillus、およびMonascus属のいくつかの真菌株によって産生される多様な生物活性を持つマイコトキシンである。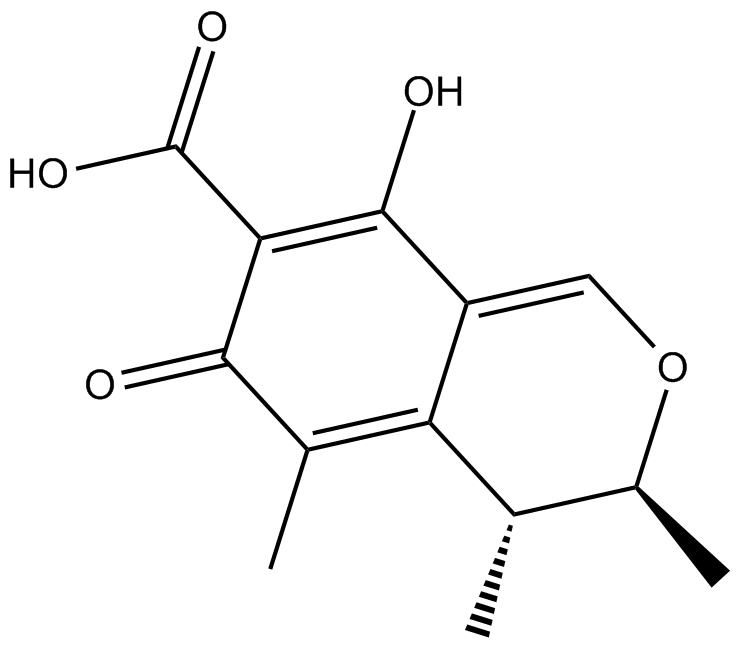
-
GC43274
Citromycetin
NSC 53584
シトロミセチンは、オーストラリアの海洋由来および陸生のペニシリウム種に由来する芳香族ポリケチド化合物です 。
-
GC63393
Citronellyl acetate
酢酸シトロネリルは、植物の二次代謝のモノテルペン生成物であり、抗侵害受容活性があります。

-
GC52367
Citrullinated Vimentin (G146R) (R144 + R146) (139-159)-biotin Peptide
Biotin-GQGKS(Cit)L(Cit)DLYEEEMRELRRQ, Biotin-GQGKSXLXDLYEEEMRELRRQ (X=Citrulline), Citrullinated VIM (G146R) (R144 + R146)-biotin
バイオチニル化されたシトルリン化変異型ビメンチンペプチド

-
GC52370
Citrullinated Vimentin (R144) (139-159)-biotin Peptide
Biotin-GQGKS(Cit)LGDLYEEEMRELRRQ, Biotin-GQGKSXLGDLYEEEMRELRRQ (X=Citrulline), Citrullinated VIM (R144)-biotin
バイオチニル化されたシトルリン化ビメンチンペプチド

-
GN10219
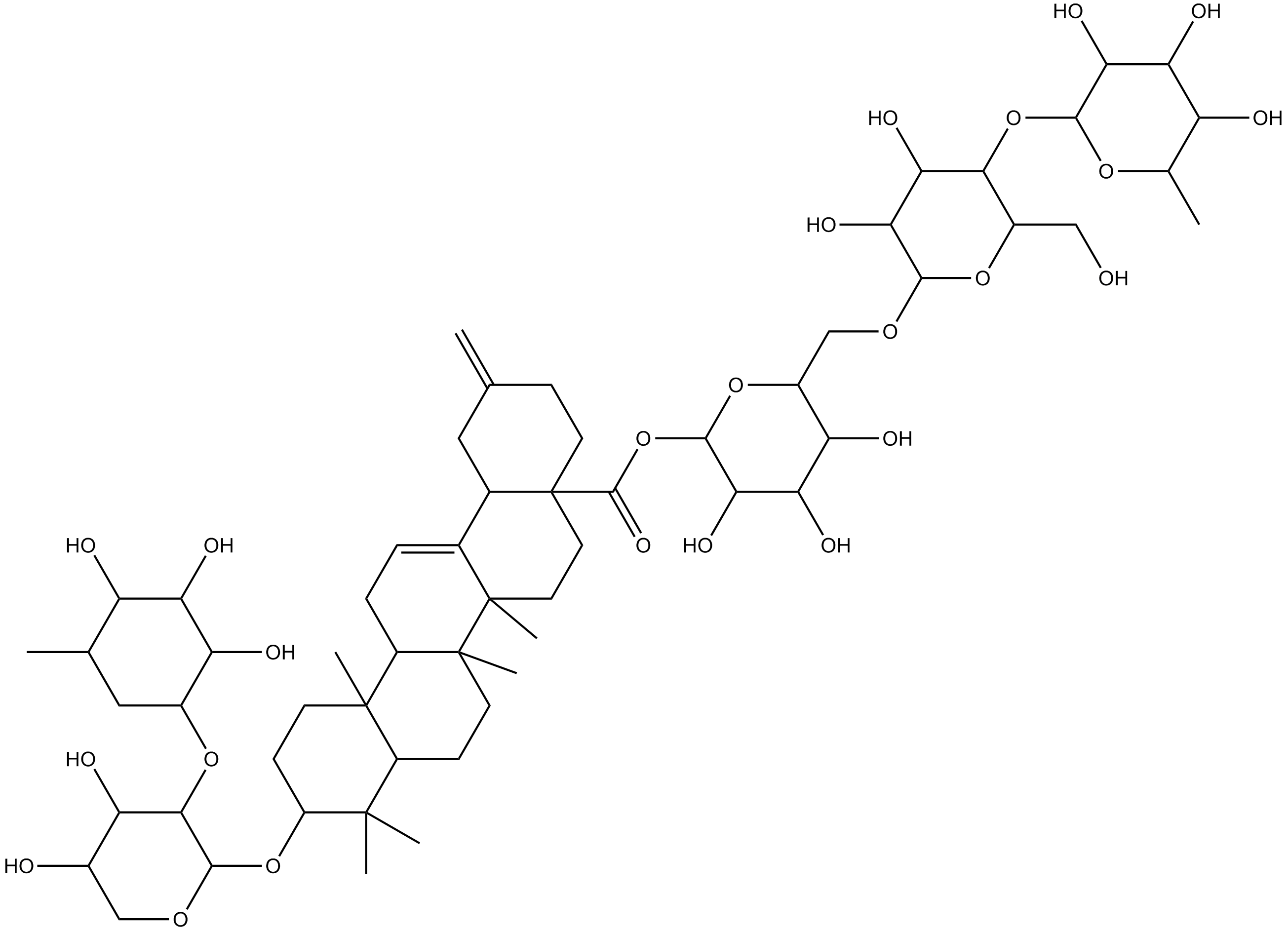
Ciwujianoside-B
-
GC64649
Cjoc42
Cjoc42はガンキリンに結合する化合物です。 Cjoc42 は用量依存的にガンキリン活性を阻害します。 Cjoc42 は、通常大量のガンキリンに関連する p53 タンパク質レベルの低下を防ぎます。 Cjoc42 は、p53 依存性の転写と DNA 損傷に対する感受性を回復します。
-
GC39485
CK2/ERK8-IN-1
CK2/ERK8-IN-1 は、デュアル カゼイン キナーゼ 2 (CK2) (Ki 0.25 μM) および ERK8 (MAPK15、ERK7) 阻害剤であり、IC50 は 0.50 μM です。 CK2/ERK8-IN-1 は、PIM1、HIPK2 (ホメオドメイン相互作用タンパク質キナーゼ 2)、DYRK1A にもそれぞれ 8.65 μM、15.25 μM、11.9 μM の Kis で結合します。 CK2/ERK8-IN-1 にはアポトーシス促進効果があります。
-
GC49556
Cl-Necrostatin-1
7-Cl-Nec-1, 7-Cl-Necrostatin-1, Nec-1f
RIPK1阻害剤

-
GC47098
CL2-SN-38 (dichloroacetic acid salt)
SN-38を含む抗体薬物複合体
-
GC60714
CL2A-SN-38
CL2A-SN-38 は、強力な DNA トポイソメラーゼ I 阻害剤である SN-38 と、抗体薬物複合体 (ADC) を作成するためのリンカー CL2A で構成される薬物-リンカー複合体です。
-
GC52469
CL2A-SN-38 (dichloroacetic acid salt)
SN-38を含む抗体薬物複合体

-
GC10509
Cladribine
2-Chlorodeoxyadenosine, Jk 6251, NSC 105014, RWJ 26251
プリンヌクレオシド類似体であるクラドリビン(2-クロロ-2'-デオキシアデノシン)は、経口活性アデノシンデアミナーゼ阻害剤です。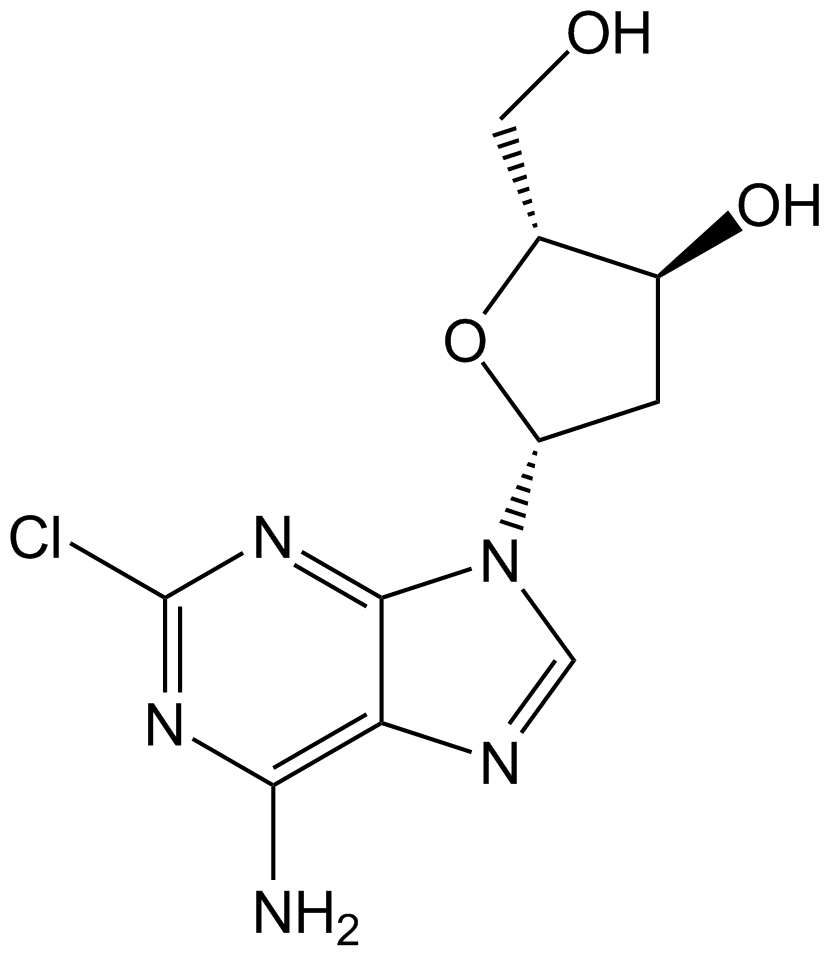
-
GC68882
Cleomiscosin A
Cleomiscosin Aは、Macaranga adenanthaから産生されるクマリン類の木質素です。 Cleomiscosin Aは、マウス腹腔巨噬細胞がTNF-alphaを分泌するのに活性があります。
-
GC60111
Clitocine
キノコから分離されたアデノシン ヌクレオシド アナログであるクリトシンは、強力で効果的なリードスルー エージェントです。クリトシンはナンセンス変異の抑制因子として作用し、p53 ナンセンス変異対立遺伝子を保有する細胞で p53 タンパク質の産生を誘導することができます。クリトシンは、Mcl-1 を標的とすることにより、多剤耐性ヒト癌細胞のアポトーシスを誘導できます。抗がん作用。

-
GC15219
Clofarabine
Clolar, Evoltra
がん研究用のヌクレオシド類似体であるクロファラビンは、調節サブユニットのアロステリック部位に結合することにより、リボヌクレオチドレダクターゼの強力な阻害剤 (IC50=65 nM) です 。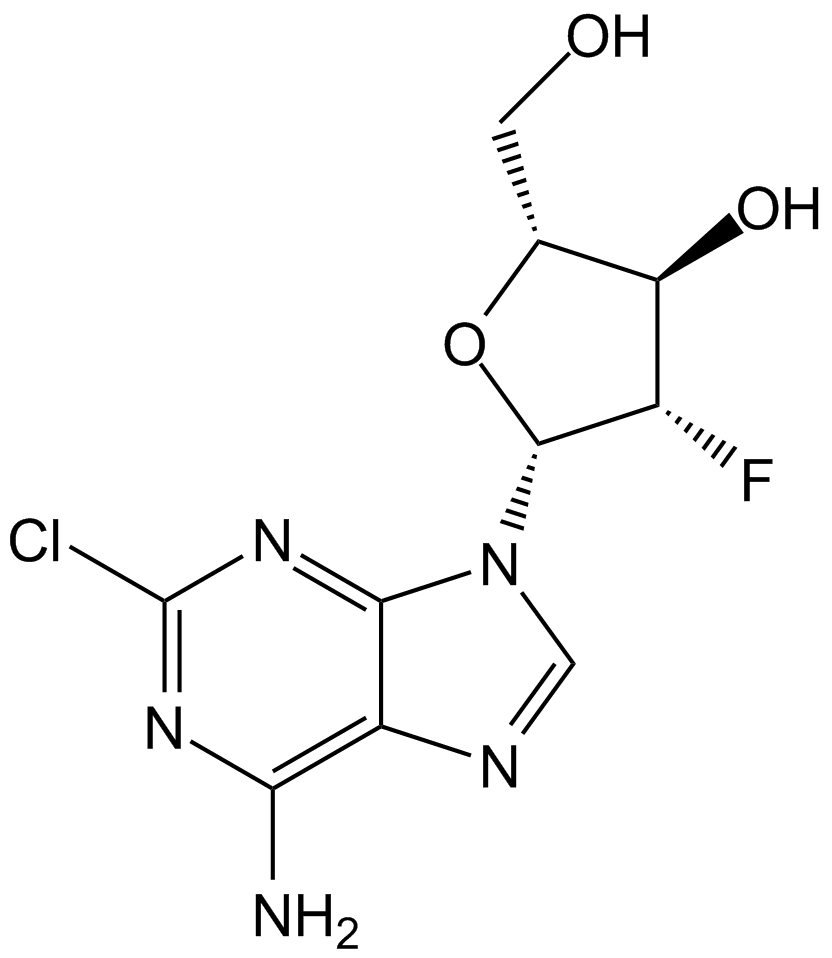
-
GC10813
Clofibric Acid
NSC 1149
クロフィブリン酸 (クロロフィブリン酸) は、脂質調節物質であるクロフィブラート、エトフィブラート、およびエトフィリンクロフィブラートの薬学的に活性な代謝産物であり、脂質低下作用を示す PPARα アゴニストです。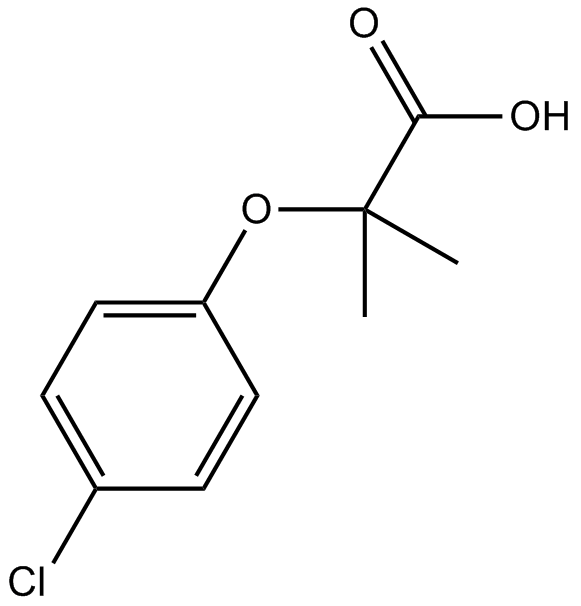
-
GC32587
Clofilium tosylate
カリウム チャネル遮断薬であるトシル酸クロフィリウムは、カスパーゼ 3 の Bcl-2 非感受性活性化を介して、ヒト前骨髄球性白血病 (HL-60) 細胞のアポトーシスを誘導します。

-
GC47105
Clonostachydiol
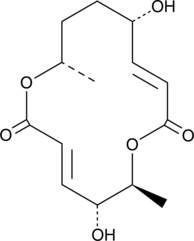
クロノスタキジオールは、真菌 Clonostachys cylindrospora (菌株 FH-A 6607) 由来の駆虫性マクロジオリドです 。
-
GC12367
CM-272
CM-272 は、抗腫瘍活性を備えたクラス初の強力な選択的基質競合性可逆デュアル G9a/DNA メチルトランスフェラーゼ (DNMT) 阻害剤です。 CM-272 は、G9a、DNMT1、DNMT3A、DNMT3B、および GLP を、それぞれ 8 nM、382 nM、85 nM、1200 nM、および 2 nM の IC50 で阻害します。 CM-272 は細胞増殖を阻害し、アポトーシスを促進し、IFN 刺激遺伝子と免疫原性細胞死を誘導します。

-
GC62347
CMC2.24
TRB-N0224
CMC2.24 (TRB-N0224) は、経口で活性なトリカルボニルメタン剤であり、Ras 活性化とその下流のエフェクター ERK1/2 経路を阻害することにより、マウスの膵臓腫瘍に対して効果的です。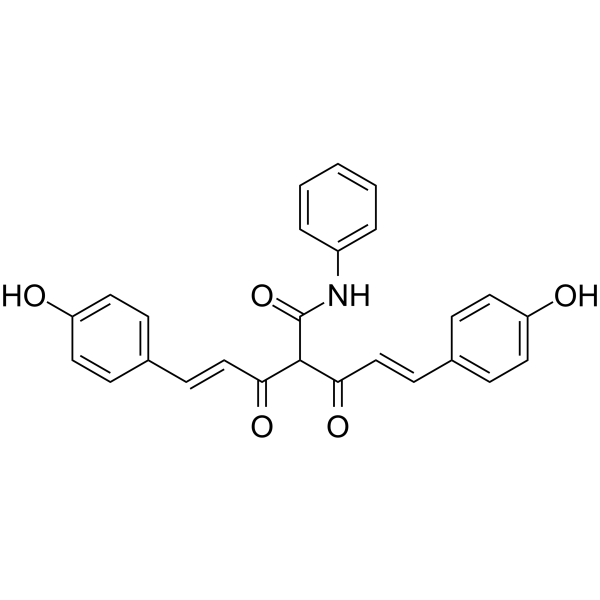
-
GC61567
CMLD-2
HuR-ARE 相互作用の阻害剤である CMLD-2 は、競合的に HuR タンパク質に結合し、アデニン-ウリジン リッチ エレメント (ARE) を含む mRNA (Ki=350 nM) との相互作用を破壊します。 CMLD-2 誘導アポトーシスは、結腸、膵臓、甲状腺、および肺癌細胞株などのさまざまな癌細胞で抗腫瘍活性を示します。 Hu 抗原 R (HuR) は RNA 結合タンパク質であり、標的 mRNA の安定性と翻訳を調節できます。
-
GC49096
Cobaltic Protoporphyrin IX (chloride)
HO-1活性の誘導剤

-
GC10033
Cobimetinib
GDC-0973, RG-7420, XL518
口服可能な強力なMEK1阻害剤

-
GC43297
Coenzyme Q2
CoQ2, Ubiquinone-2, Ubiquinone Q2
補酵素Q10は電子伝達系の成分であり、有酸素細胞呼吸に参加し、ATPという形でエネルギーを生成します。

-
GC62192
COG1410
COG1410 は、アポリポタンパク質 E 由来のペプチドです。
-
GC40664
Colcemid
Demecolcine, NSC 3096
Colcemidは、哺乳類の細胞または卵母細胞において、G2/M期の有糸分裂停止または小胞破裂(GVBD)期の減数分裂停止を誘導する細胞骨格阻害剤である。
-
GN10123
Columbianadin
Columbianetin
-
GC49454
Complex 3
抗がん活性を持つ蛍光銅錯体

-
GC18572
Concanavalin A
コンカナマイシンAは、高い活性と選択的なバキュオールプロトン-ATPase(v-[H+]ATPase)阻害剤である、Streptomyces diastatochromogenesから分離されたマクロライド系抗生物質の一種であるコンカナマイシンに属しています。

-
GC18832
Conglobatin
コングロバチンは、元々Sから単離された二量体のマクロライドジラクトンです。
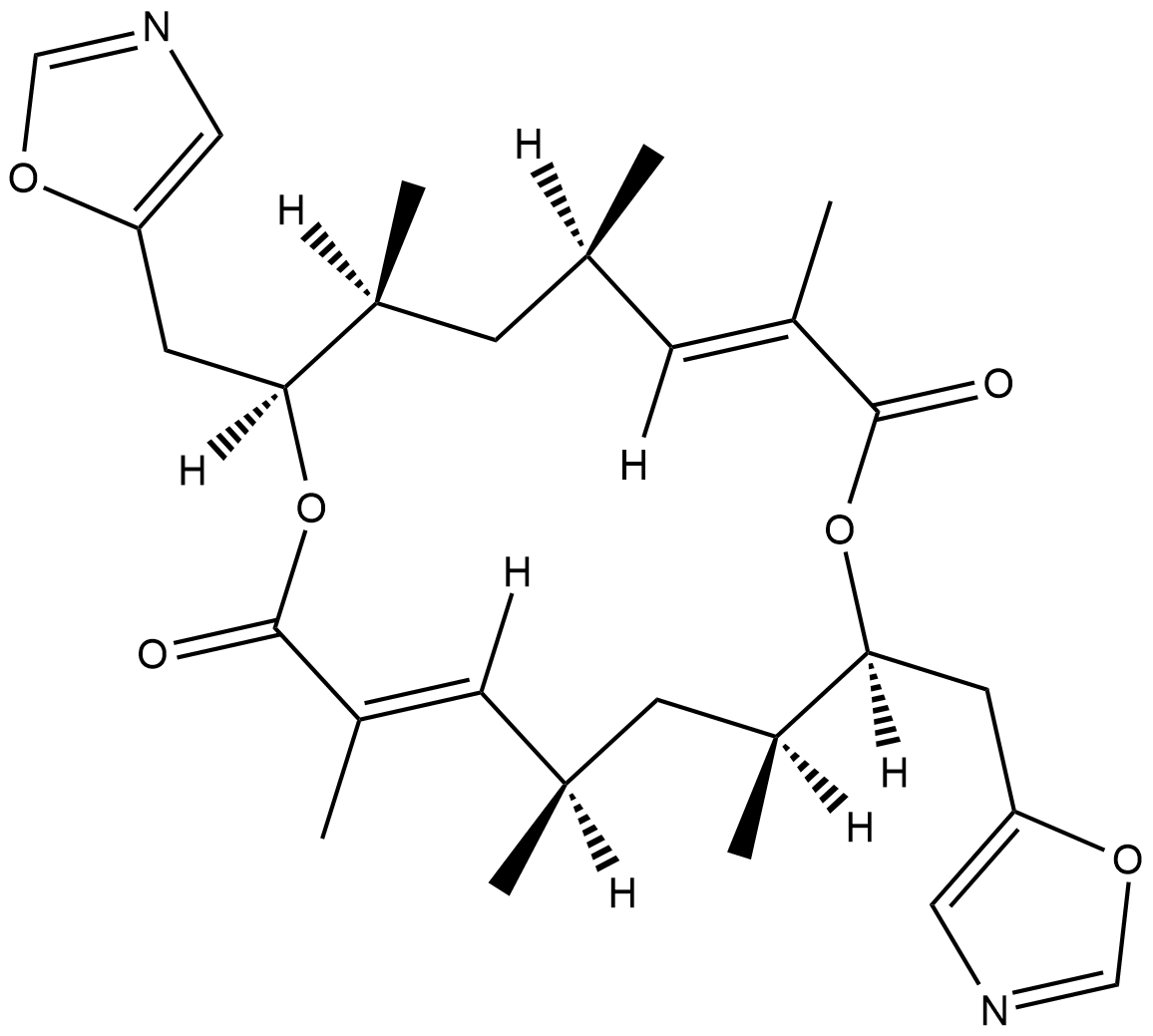
-
GC48483
Conglobatin B
細菌代謝産物

-
GC48497
Conglobatin C1
細菌代謝産物
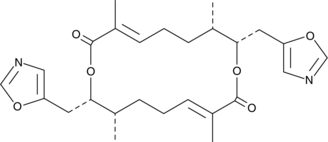
-
GC38376
Coniferaldehyde
コニフェルアルデヒド (フェルルアルデヒド) は、ヘムオキシゲナーゼ-1 (HO-1) の効果的なインデューサーです。
-
GC63379
Conophylline
コノフィリンは、熱帯植物エルバタミア・ミクロフィラの葉から抽出されるビンカアルカロイドです。

-
GC16772
Cortisone acetate
Cortisone 21-acetate, NSC 49420
酢酸コルチゾン (コルチゾン 21-アセテート)、コルチゾール (グルココルチコイド) の酸化代謝産物。
-
GC16116
Costunolide
Costus lactone, Melampolide, NSC 106404
天然セスキテルペンラクトン
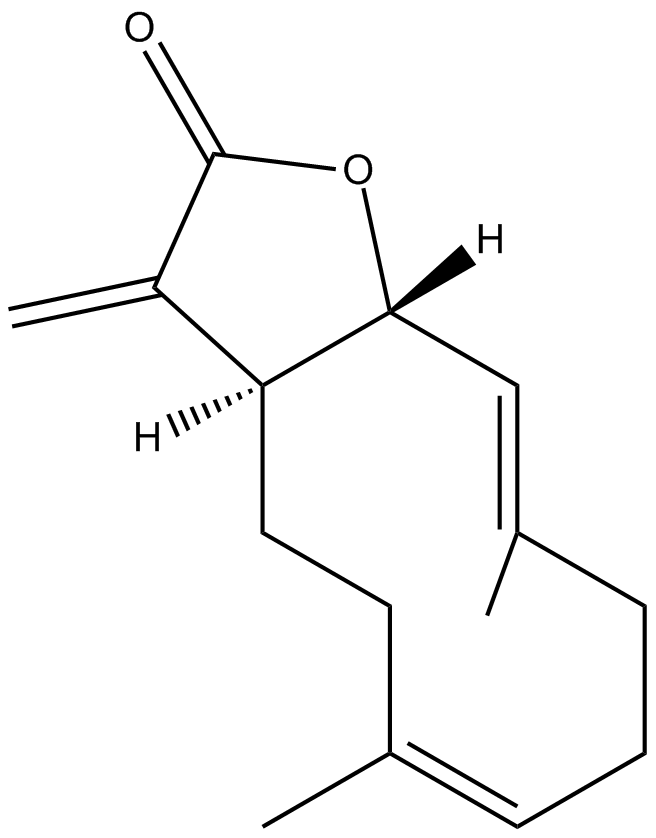
-
GC15225
COTI-2
低毒性の抗がん剤である COTI-2 は、p53 変異型の経口投与可能な第 3 世代活性化剤です。 COTI-2 は、変異 p53 の再活性化と PI3K/AKT/mTOR 経路の阻害の両方によって作用します。 COTI-2 は、複数のヒト腫瘍細胞株でアポトーシスを誘導します。 COTI-2 は、p53 依存性および非依存性メカニズムを介して HNSCC で抗腫瘍活性を示します。 COTI-2 は変異型 p53 を野生型コンフォメーションに変換します。

-
GC15840
CP 31398 dihydrochloride
p53安定剤

-
GC13091
CP-724714
CP-724714 は、強力で選択的な経口活性 ErbB2 (HER2) チロシンキナーゼ阻害剤であり、IC50 は 10 nM です。 CP-724714 は、EGFR キナーゼに対して顕著な選択性を示します (IC50=6400 nM)。 CP-724714 は、無傷の細胞で ErbB2 受容体の自己リン酸化を強力に阻害します。抗腫瘍活動。

-
GC14500
CPI-1189
CPI-1189 は、抗酸化作用と神経保護作用を持つ TNF-α 放出阻害剤です。
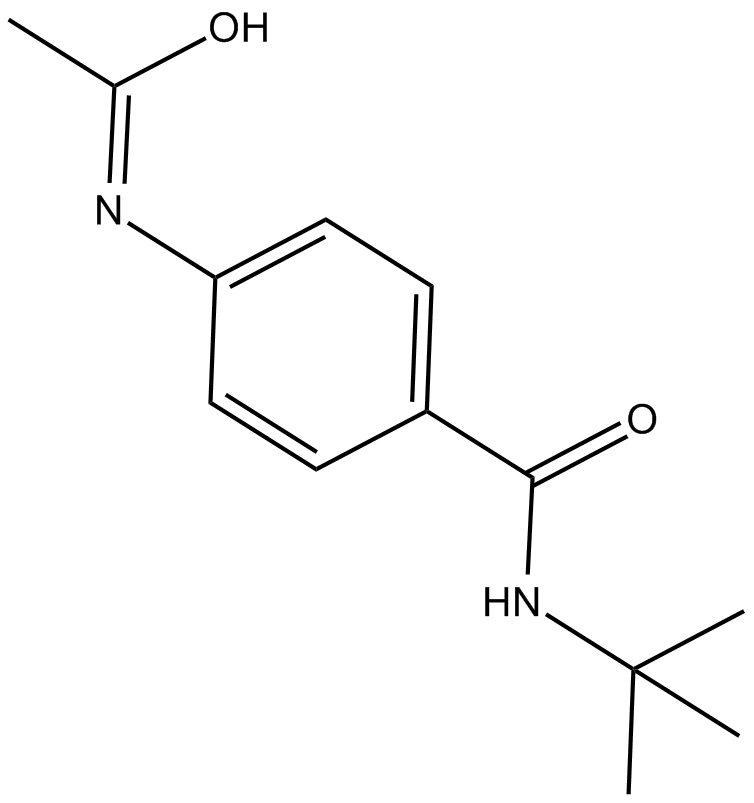
-
GC14699
CPI-203
CPI-203 は、約 37 nM の IC50 値を持つ、BET ブロモドメインの強力で選択的な細胞透過性の新規阻害剤です (BRD4 α-スクリーンアッセイ)。
-
GC10021
CPI-360
EZH2阻害剤

-
GC14921
CPI-613
α-ケトグルタル酸脱水素酵素の阻害剤

-
GC39365
CPTH2
CPTH2 は、強力なヒストン アセチルトランスフェラーゼ (HAT) 阻害剤です。 CPTH2 は、Gcn5 によるヒストン H3 のアセチル化を選択的に阻害します。 CPTH2 はアポトーシスを誘導し、アセチルトランスフェラーゼ p300 (KAT3B) の阻害により明細胞腎癌 (ccRCC) 細胞株の浸潤性を低下させます。

-
GC35747
Crebanine
(–)-Crebanine
Stephania venosa 由来のアルカロイドであるクレバニンは、ヒト癌細胞の G1 停止とアポトーシスを誘導します。
-
GC34543
cRIPGBM
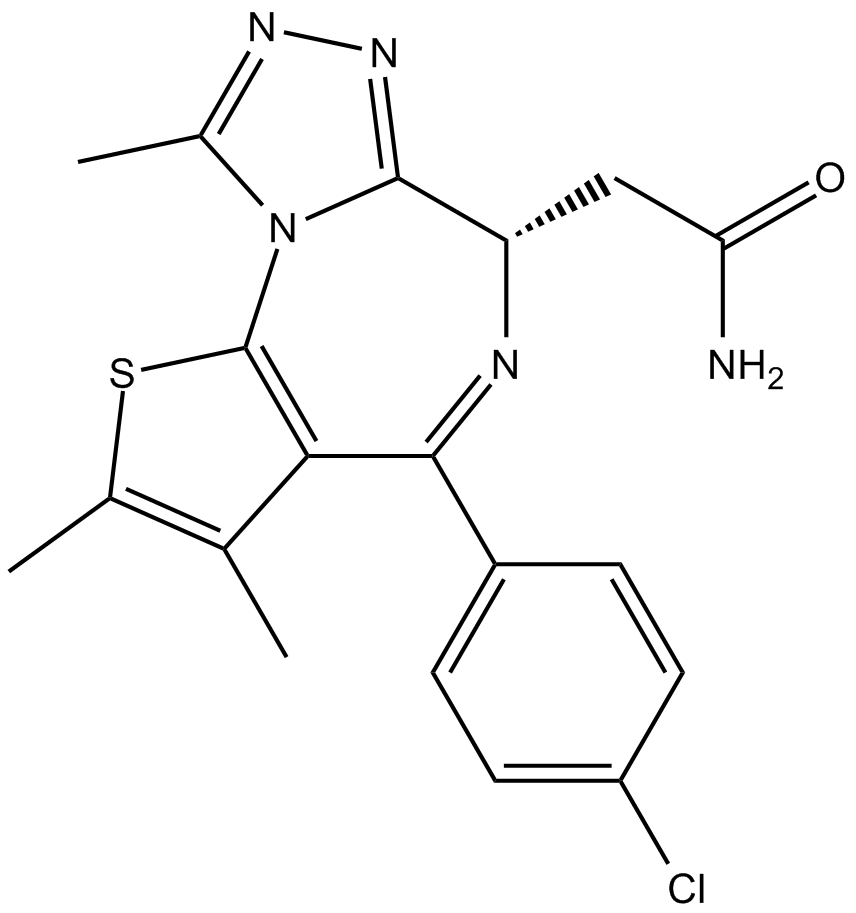
cRIPGBM は、受容体相互作用プロテインキナーゼ 2 (RIPK2) に結合することによる GBM 癌幹細胞 (CSC) のアポトーシスの細胞型選択的インデューサーである RIPGBM のプロアポトーシス誘導体であり、GBM-1 細胞で 68 nM の EC50 を示します。
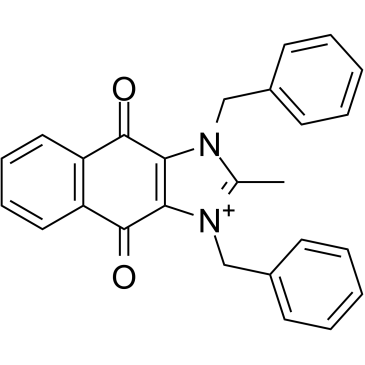
-
GC68903
cRIPGBM chloride
cRIPGBM chlorideは、経口摂取可能な有効なアポトーシス促進物質であり、多形性グリオーマ母細胞腫(GBM)がん幹細胞(CSC)から生成されます。cRIPGBM chlorideは受容体相互作用プロテインキナーゼ2(RIPK2)を標的としており、半システインカスパーゼ1依存性の細胞アポトーシスを誘導します。また、cRIPGBM chlorideはRIPK2/TAK1(生存促進複合体)の形成を抑制し、RIPK2/caspase 1(アポトーシス促進複合体)の形成を増加させます。動物モデルでは、cRIPGBM chlorideが強力な抗腫瘍活性を発揮します。
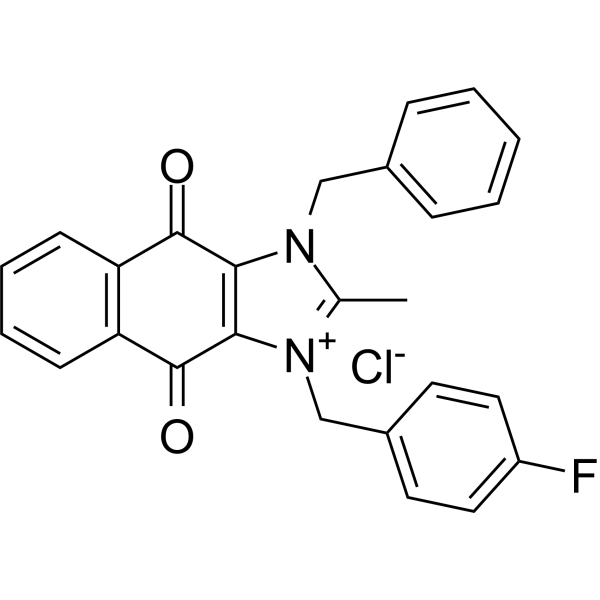
-
GC13838
CRT 0066101
PKD阻害剤
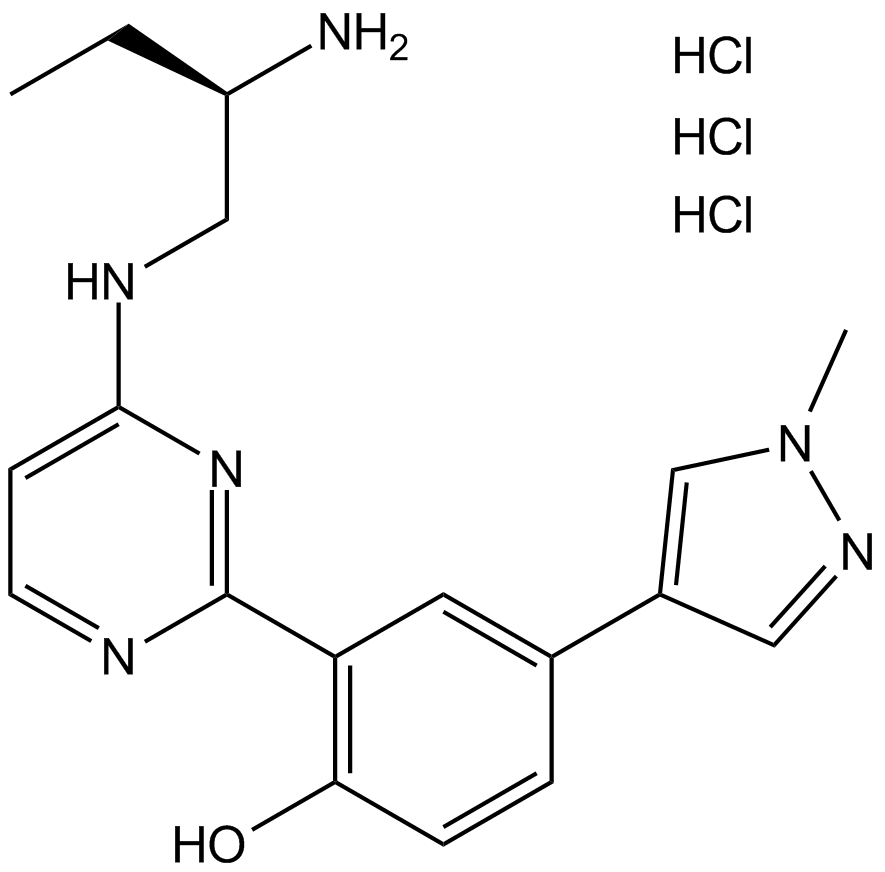
-
GC35750
CRT0066101 dihydrochloride
CRT0066101 二塩酸塩は、PKD1、2、および 3 に対してそれぞれ 1、2.5、および 2 nM の IC50 値を持つ強力で特異的な PKD 阻害剤です。
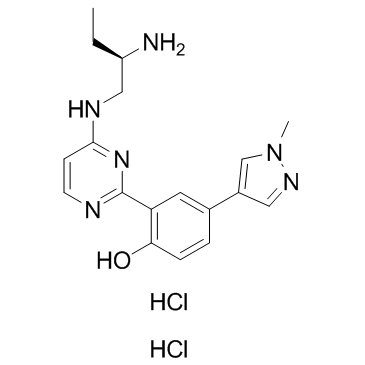
-
GC45414
CRT0066854
CRT0066854 は、強力かつ選択的な非定型 PKC アイソザイム阻害剤です。

-
GC14355
CRT5
CRT0066051
ピラジンベンズアミドである CRT5 は、VEGF で処理された内皮細胞における PKD の 3 つのアイソフォームすべてに対する強力かつ選択的な阻害剤です (IC50 = PKD1、PKD2、および PKD3 に対してそれぞれ 1、2、および 1.5 nM)。
-
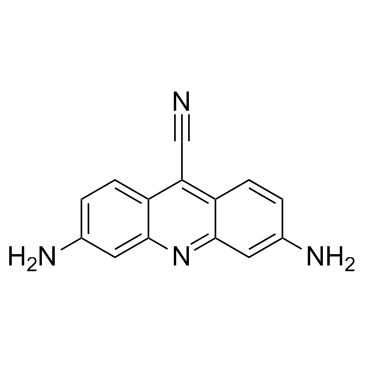
GC32911
CTX1
CTX1 は、HdmX を介した p53 抑制を克服する p53 アクティベーターです。 CTX1 は、マウスの急性骨髄性白血病 (AML) モデル系で強力な抗がん活性を示します。
-
GN10535
Cucurbitacin B
Cuc B, NSC 49451, NSC 144154

-
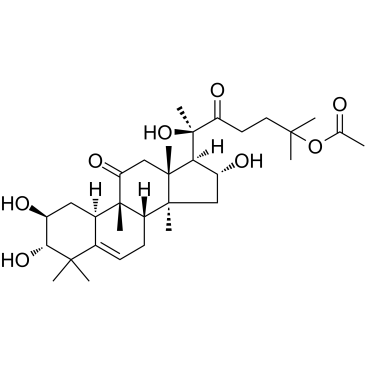
GC35758
Cucurbitacin IIa
ククルビタシン IIa は、Hemsleya amalils Diels から分離されたトリテルペンであり、癌細胞のアポトーシスを誘導し、サバイビンの発現を減少させ、ホスホ ヒストン H3 を減少させ、癌細胞の切断された PARP を増加させます。
-
GN10788
Cucurbitacin IIb
Cuc B, NSC 49451, NSC 144154
-
GC32781
CUDC-427 (GDC-0917)
GDC-0917
CUDC-427 (GDC-0917) は、さまざまながんの治療に使用される強力な第 2 世代の汎選択的 IAP アンタゴニストです。
-
GC12115
CUDC-907
CUDC-907
HDACとPI3Kの二重阻害剤

-
GC11217
CUR 61414
G-856
CUR 61414 は、新規で強力な細胞透過性の Hedgehog シグナル伝達経路阻害剤です (IC50 = 100-200 nM)。
-
GC14787
Curcumin
Indian Saffron, Turmeric yellow
多様な生物学的活性を持つ黄色の色素
-
GC40226
Curcumin-d6
クルクミン D6 (ジフェルロイルメタン D6) は、クルクミン (ターメリック イエロー) とラベル付けされた重水素です。

-
GN10521
Curcumol
(-)-Curcumol



