JGB1741 (Synonyms: ILS-JGB-1741) |
| カタログ番号GC13062 |
JGB1741(ILS-JGB-1741)は、IC50が約15μMの強力で特異的なSIRT1活性阻害剤です。 JGB1741 は弱い SIRT2 および SIRT3 阻害剤であり、すべての IC50 が 100 μM を超えています。 JGB1741は、アセチル化p53レベルを増加させ、Bax / Bcl2比、シトクロムcの放出、およびPARP切断の調節により、p53を介したアポトーシスを引き起こします。 JGB1741は乳がん研究の可能性を秘めています。
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
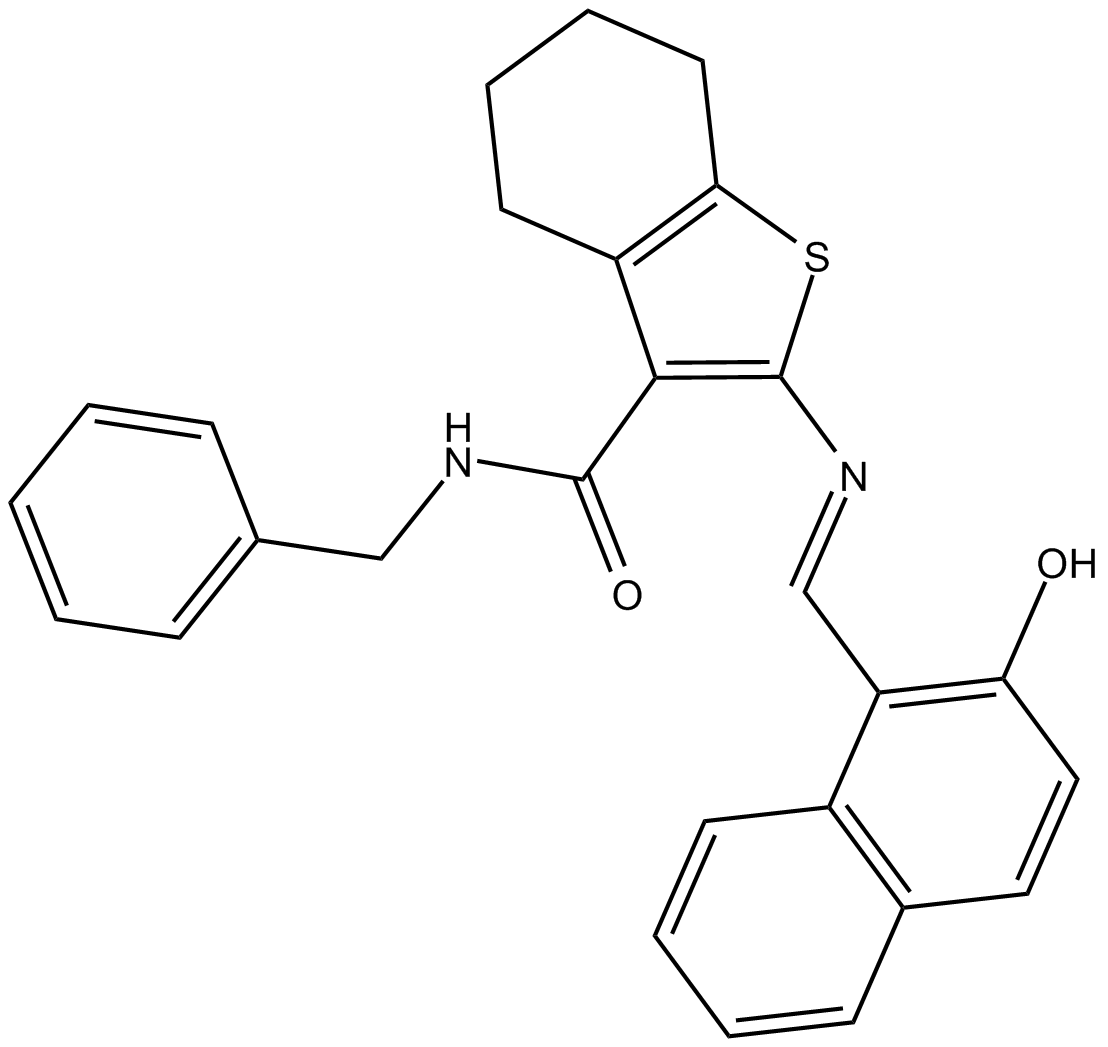
Cas No.: 1256375-38-8
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
JGB1741 is a small molecule SIRT1 inhibitor [1].
Sirtuins or Sir2 (silent information regulator 2)-related enzymes have originally been defined as a family of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent enzymes which are involved in deacetylating lysine residue on multiple proteins. The sirtuins show highly conservation from archaebacteria to eukaryotes. The mammalian sirtuins SIRT1–SIRT7 have been implicated in a variety of cellular functions, such as gene silencing, over the control of the cell cycle and apoptosis, to energy homeostasis [2].
In vitro: JGB1741 potently inhibited the proliferation of human metastatic breast cancer cells, MDA-MB 231. JGB1741 showed antitumor effects on three different cancer cell lines, K562, HepG2 and MDA-MB 231 with an IC50 of 1, 10 and 0.5 μM, respectively. JGB1741-induced apoptosis has been associated with increase in cytochrome c release, modulation in Bax/Bcl2 ratio and cleavage of PARP [1].
References:
[1] Kalle A M, Mallika A, Badiger J, et al. Inhibition of SIRT1 by a small molecule induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells[J]. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 2010, 401(1): 13-19.
[2] Yamamoto H, Schoonjans K, Auwerx J. Sirtuin functions in health and disease[J]. Molecular Endocrinology, 2007, 21(8): 1745-1755.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 10 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















