Tosyllysine Chloromethyl Ketone (hydrochloride) (Synonyms: 1-Chloro-3-Toxylamide-7-Amino-L-2-Heptanone,TLCK) |
| カタログ番号GC13967 |
トリプシン様プロテアーゼ阻害剤である N-α-トシル-L-リジン クロロメチル ケトン (TLCK) は、Fas を介した細胞死に対して HeLa 細胞を感作します。
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
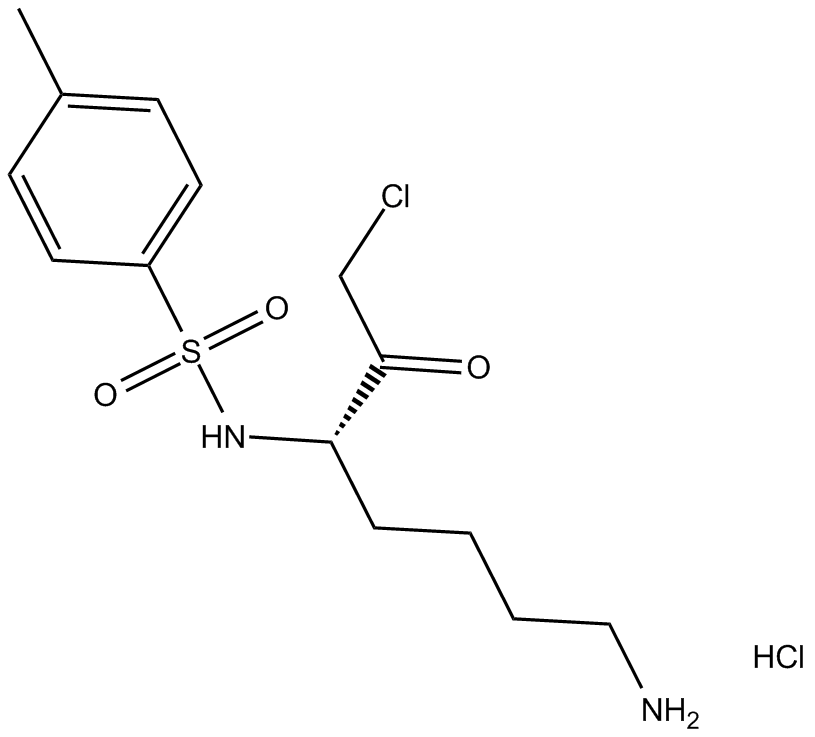
Cas No.: 4272-74-6
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Tosyllysine Chloromethyl Ketone (hydrochloride) is a protease inhibitor [1][2][3].
L-1-chloro-3-[4-tosylamido]-7-amino-2-heptanone-HCl (TLCK) is a protease inhibitor. TLCK is an active site-directed agent that inhibits serine proteinases with trypsin-like activity. TLCK also interacts non-selectively with thiol groups and thereby inhibits cysteine proteinases and other enzymes. In LPS-activated rat alveolar macrophages, TLCK at 1-100 μM inhibited NOx- accumulation and inducible iNOS expression in a concentration-dependent way [1]. To prevent proteolytic degradation, TLCK may be used in protein purification protocols [2]. TLCK significantly increased the cytotoxic activity of C. histolyticum supernatant towards human epithelial HeLa cells probably by hindering natural defence mechanisms of cells. 30 min incubation with bacterial supernatant increased toxicity in both concentrations (200 and 1000 μM) from 18 ± 3% to 39 ± 3% and 57 ± 8%, respectively. TLCK also blocked clostripain enzymatic activity obtained from C. histolyticum. So TLCK might be used to treat diseases complicated by concurrent C. histolyticum infection [3].
References:
[1]. Griscavage JM, Wilk S, Ignarro LJ. Serine and cysteine proteinase inhibitors prevent nitric oxide production by activated macrophages by interfering with transcription of the inducible NO synthase gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Oct 13;215(2):721-9.
[2]. Urban MK, Franklin SG, Zweidler A. Isolation and characterization of the histone variants in chicken erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 4;18(18):3952-60.
[3]. Józwiak, J.,Komar, A.,Jankowska, E., et al. Determination of the cytotoxic effect of Clostridium
histolyticum culture supernatant on HeLa cells in the presence of protease inhibitors. FEMS Immunology & Medical Microbiology 45(2):137-42 (2005).
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 18 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















