α-Naphthoflavone (Synonyms: 7,8-Benzoflavone,NSC 407011) |
| Catalog No.GC12890 |
α-나프토플라본은 플라보노이드이며 IC50 및 Ki가 각각 0.5 및 0.2 μM인 강력하고 경쟁적인 아로마타제 억제제로 작용합니다.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
Cas No.: 604-59-1
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
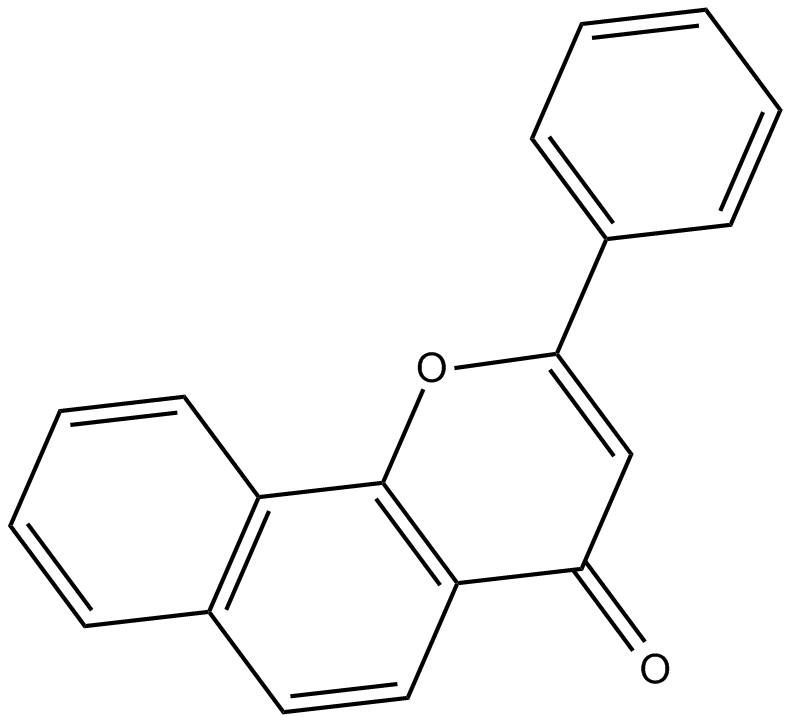
α-Naphthoflavone (α-NF), also known as 7,8-benzoflavone and 2-phenyl-benzo(h)chromen-4-one, is a synthetic flavone derivative. α-Naphthoflavone is a potent inhibitor of the enzyme aromatase, which implicated in converting testosterone to estrogen [1]. It can be prepared from 2-naphthol and cinnamaldehyde [2]. α-naphthoflavone functions as both an Ah receptor antagonist and an inhibitor of cytochrome P450 activity. α-naphthoflavone stimulated P450 3A4 by selectively binding and activating an otherwise inactive subpopulation of this P450 and promoting benzo[a]pyrene binding to the latter [3].
In vitro: α-NF inhibited microsomal rabbit CYP3A6 and human CYP3A4 irreversibly. α-NF and β-NF strongly inhibited CYP1A-mediated ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase (EROD) activity with the Ki value of 9.1 ± 0.8 and 7.6 ± 1.1 nM, respectively. α-NF at 0.5, 5, 50 and 500 μM inhibited liver microsome-catalyzed AFB1-DNA binding by 22, 58, 84 and 91%, respectively [4].
In vivo: α-NF inhibited CYP1A enzymes and caused both synergism and antagonism of retene toxicity to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) [5]. In male Sprague–Dawley rats, treatment with αNF had no significant effects on body mass after 5 days and caused only minor increases of liver, kidney, and heart CYP1A1 mRNA. In contrast, lung CYP1A1 mRNA was increased by αNF treatment to levels comparable to that seen with β-NF treatment [6].
References:
[1]. Campbell D R, Kurzer M S. Flavonoid inhibition of aromatase enzyme activity in human preadipocytes[J]. The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology, 1993, 46(3): 381-388.
[2]. Harvey R G, HAHN J T A I, Bukowska M, et al. A new chromone and flavone synthesis and its utilization for the synthesis of potentially antitumorigenic polycyclic chromones and flavones[J]. Journal of organic chemistry, 1990, 55(25): 6161-6166.
[3]. Koley A P, Buters J T M, Robinson R C, et al. Differential mechanisms of cytochrome P450 inhibition and activation by α-naphthoflavone[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1997, 272(6): 3149-3152.
[4]. Takahashi N, Miranda C L, Henderson M C, et al. Inhibition of in vitro aflatoxin B1-DNA binding in rainbow trout by CYP1A inhibitors: α-naphthoflavone, β-naphthoflavone and trout CYP1A1 peptide antibody[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Pharmacology, Toxicology and Endocrinology, 1995, 110(3): 273-280.
[5]. Hodson P V, Qureshi K, Noble C A J, et al. Inhibition of CYP1A enzymes by α-naphthoflavone causes both synergism and antagonism of retene toxicity to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)[J]. Aquatic toxicology, 2007, 81(3): 275-285.
[6]. Sinal C J, Webb C D, Bend J R. Differential in vivo effects of α‐naphthoflavone and β‐naphthoflavone on CYP1A1 and CYP2E1 in rat liver, lung, heart, and kidney[J]. Journal of biochemical and molecular toxicology, 1999, 13(1): 29-40.
| Cas No. | 604-59-1 | SDF | |
| Synonyms | 7,8-Benzoflavone,NSC 407011 | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-phenyl-4H-naphtho[1,2-b]pyran-4-one | ||
| Canonical SMILES | O=C1C2=C(C(C=CC=C3)=C3C=C2)OC(C4=CC=CC=C4)=C1 | ||
| Formula | C19H12O2 | M.Wt | 272.3 |
| Solubility | ≥ 10mg/mL in DMSO | Storage | 4°C, protect from light |
| General tips | Please select the appropriate solvent to prepare the stock solution according to the
solubility of the product in different solvents; once the solution is prepared, please store it in
separate packages to avoid product failure caused by repeated freezing and thawing.Storage method
and period of the stock solution: When stored at -80°C, please use it within 6 months; when stored
at -20°C, please use it within 1 month. To increase solubility, heat the tube to 37°C and then oscillate in an ultrasonic bath for some time. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Evaluation sample solution: shipped with blue ice. All other sizes available: with RT, or with Blue Ice upon request. | ||
| Prepare stock solution | |||

|
1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg |
| 1 mM | 3.6724 mL | 18.3621 mL | 36.7242 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7345 mL | 3.6724 mL | 7.3448 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3672 mL | 1.8362 mL | 3.6724 mL |
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
 g
g
 μL
μL

Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
3. All of the above co-solvents are available for purchase on the GlpBio website.
Quality Control & SDS
- View current batch:
- Purity: >99.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- SDS (Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 31 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *



















