Calicheamicin |
| Catalog No.GC19086 |
항종양 항생제인 칼리케아미신은 이중 가닥 DNA 파손을 일으키는 세포독성제입니다.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
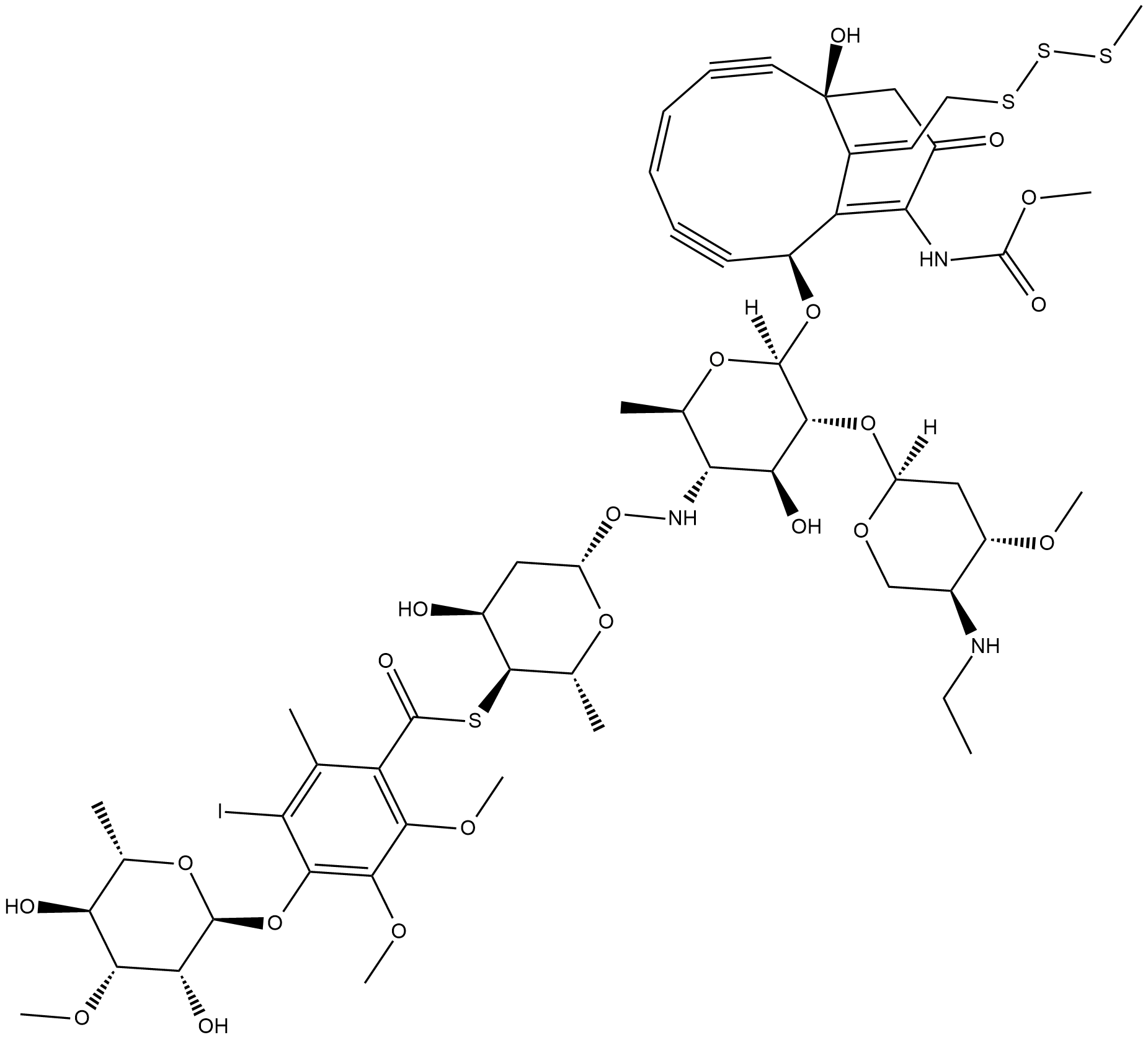
Cas No.: 108212-75-5
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Calicheamicin is a cytotoxic agent that causes double-strand DNA breaks.
PF-06647263 (anti-EFNA4-ADC) is generated via conjugation of hE22 lysine residues to the AcButDMH-N-Ac-calicheamicin-γ1 linker-payload with an average drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) of 4.6. PF-06647263 elicits antigen- and concentration-dependent cytotoxicity, as exposure to PF-06647263 for 96 hours results in cell death (EC50= appr 1 ng/mL)[1]. CMC-544, consisting of a humanized CD22 Ab linked to calicheamicin, is effective in pediatric primary B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL) cells in vitro. CMC-544 induces cell death in various ALL cell lines in a dose- and time-dependent way, with IC50 values ranging from 0.15 to 4.9 ng/mL. CMC-544 (10 ng/mL) is effective and specific in primary BCP-ALL cells[2]. In CMC-544-treated cells, the level of CD22 has decreased relative to that on G5/44-treated cells and continued to decrease[3].
An ADC comprising a humanized anti-EFNA4 monoclonal antibody conjugated to the DNA-damaging agent calicheamicin achieves sustained tumor regressions in both TNBC and ovarian cancer PDX in vivo. PF-06647263 (0.27, 0.36 mg/kg) results in significant tumor regressions in TNBC xenografts[1].
References:
[1]. Damelin M, et al. Anti-EFNA4 Calicheamicin Conjugates Effectively Target Triple-Negative Breast and Ovarian Tumor-Initiating Cells to Result in Sustained Tumor Regressions. Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Sep 15;21(18):4165-73
[2]. de Vries JF, et al. The novel calicheamicin-conjugated CD22 antibody inotuzumab ozogamicin (CMC-544) effectively kills primary pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leukemia. 2012 Feb;26(2):255-64
[3]. Takeshita A, et al. CMC-544 (inotuzumab ozogamicin), an anti-CD22 immuno-conjugate of calicheamicin, alters the levels of target molecules of malignant B-cells. Leukemia. 2009 Jul;23(7):1329-36.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 24 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















