Erlotinib (Synonyms: NSC 718781) |
| Catalog No.GC10627 |
Erlotinib is a potent and orally bioavailable epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor with an IC50 value of 2 nM.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
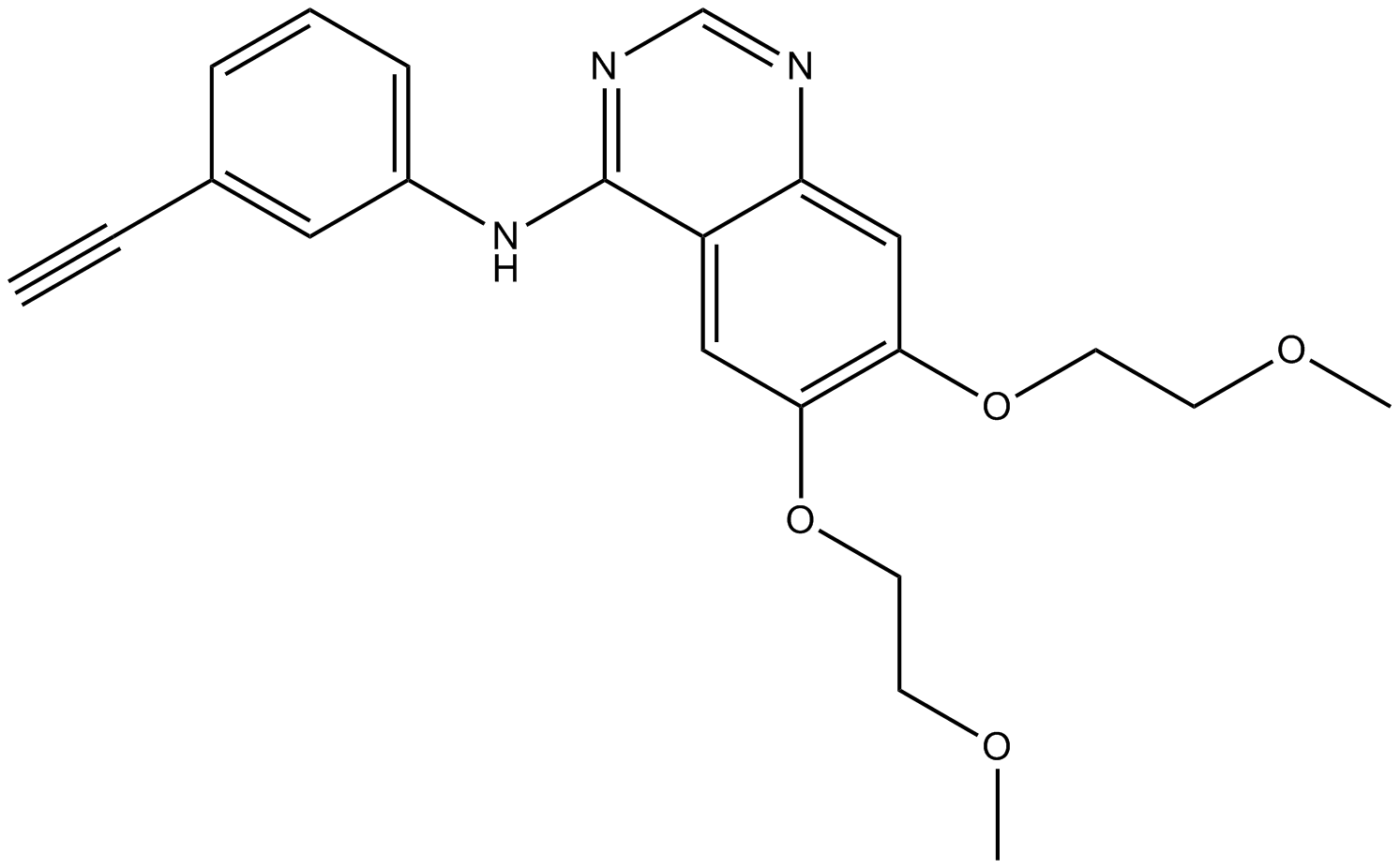
Cas No.: 183321-74-6
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Erlotinib is a potent and orally bioavailable epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor with an IC50 value of 2 nM. Erlotinib competes with ATP for binding sites on tyrosine kinase intracellular domains, inhibiting downstream signaling pathways that induce angiogenesis and cell proliferation[1-3].
Erlotinib selectively and reversibly inhibited intracellular autophosphorylation of EGFR-associated tyrosine kinases with an IC50 value of 20 nM. Erlotinib inhibited the proliferation of DiFi cells (IC50 of 100 nM) and blocks cell cycle progression at the G1 phase[1]. Erlotinib inhibited the growth of BxPC-3 cells, induced apoptosis and suppressed the expression of cellular anti-apoptotic genes, but this effect was not observed in MIAPaCa cells[4].
In HN5 mouse xenograft tumor models, Erlotinib (100 mg/kg) completely blocked EGF-induced EGFR autophosphorylation as well as liver EGFR autophosphorylation in mice[1]. In the mouse BxPC-3 cell orthotopic transplantation model, the Erlotinib group reduced tumor weight by 35% compared with the control group, and Erlotinib downregulated the level of NF-κB in vivo[4].
References:
[1]. Moyer J D, Barbacci E G, Iwata K K, et al. Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by CP-358,774, an inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase[J]. Cancer research, 1997, 57(21): 4838-4848.
[2]. Abdelgalil AA, Al-Kahtani HM, Al-Jenoobi FI. Erlotinib. Profiles Drug Subst Excip Relat Methodol. 2020;45:93-117.
[3]. Janine Smith. Erlotinib: small-molecule targeted therapy in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Clinical Therapeutics 2005; 27(10): 1513-1534.
[4]. Ali S, Banerjee S, Ahmad A, et al. Apoptosis-inducing effect of erlotinib is potentiated by 3, 3′-diindolylmethane in vitro and in vivo using an orthotopic model of pancreatic cancer[J]. Molecular cancer therapeutics, 2008, 7(6): 1708-1719.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 30 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




