Fatty Amides
Products for Fatty Amides
- Cat.No. Product Name Information
-
GC41659
(±)-2-Methyl Arachidonoyl-2'-Fluoroethylamide
2methyl2'fluoro AEA, 2Methyl2'fluoro Anandamide, O689
(±)-2-Methyl arachidonoyl-2'-fluoroethylamide (2-Methyl-2'-fluoro AEA) is an analog of anandamide (AEA) in which the alcohol of the ethanolamide group has been removed and replaced with a fluorine atom.
-
GC46406
11(Z),14(Z)-Eicosadienoic Acid Ethanolamide
An ethanolamide-conjugated form of 11(Z),14(Z)-eicosadienoic acid

-
GC91773
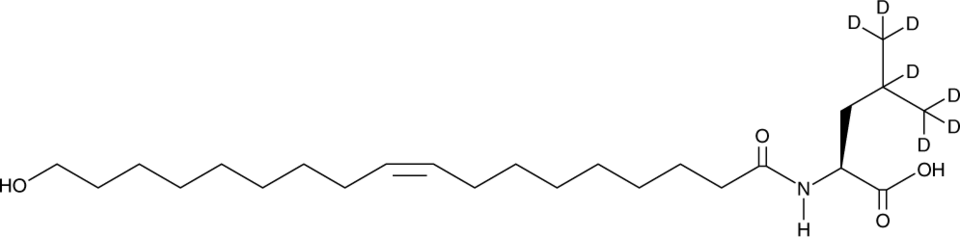
18-hydroxy Oleoyl Leucine-d7
18-hydroxy Oleoyl leucine-d7 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of 18-hydroxy oleoyl leucine by GC- or LC-MS.
-
GC42480
5(Z),8(Z),11(Z)-Eicosatrienoic Acid Ethanolamide
Mead Acid Ethanolamide
5(Z),8(Z),11(Z)-Eicosatrienoic acid ethanolamide is essentially identical to AEA in its agonist binding to CB1 and CB2 receptors.
-
GC18615
Arachidonoyl Cyclopropylamide
ACPA
Arachidonoyl cyclopropylamide (ACPA) is a potent and selective cannabinoid (CB) receptor 1 agonist with Ki values of 2.2 and 715 nM for CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively.
-
GC42839
Arachidonoyl Ethanolamide Phosphate
AEAP, Anandamide Phosphate
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide was the first endogenous cannabinoid (CB) to be isolated and characterized as an agonist acting on the same receptors (CB1 and CB2) as δ9-THC.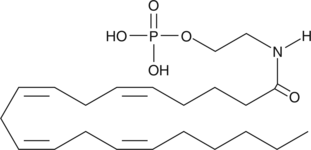
-
GC42845
Arachidonoyl-2'-Fluoroethylamide
2'fluoro AEA, 2'fluoro Anandamide
Arachidonoyl-2'-fluoroethylamide (2-fluoro AEA) is an analog of anandamide in which the alcohol of the ethanolamide group has been removed and replaced with a fluorine atom.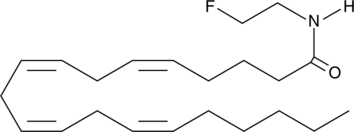
-
GC42847
Arachidonoyl-N,N-dimethyl amide
Arachidonic AcidN,Ndimethyl amide
Anandamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors.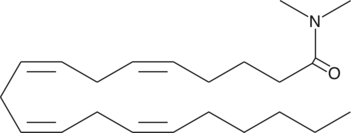
-
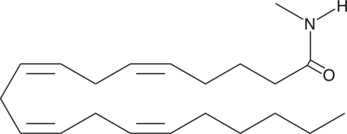
GC42848
Arachidonoyl-N-methyl amide
Anandamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors.
-
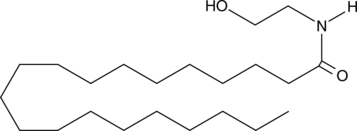
GC42849
Arachidoyl Ethanolamide
N-Arachidoylethanolamine
The endocannabinoids present a rich system of central cannabinoid (CB1), peripheral cannabinoid (CB2), and non-CB receptor-mediated pharmacology that has stimulated research in many fields including memory, weight loss and appetite, neurodegeneration, tumor surveillance, analgesia, and inflammation.
-
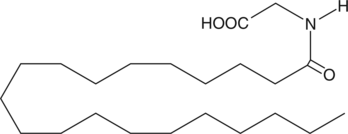
GC42850
Arachidoyl glycine
Arachidoyl glycine consists of the C20:0 fatty acid with glycine attached at its carboxy terminus.
-
GC43301
Commendamide
N-acyl-3-hydroxypalmitoyl-Glycine
Commendamide is a natural bacterial product that was discovered in a screen for commensal bacteria effector genes (Cbegs).
-
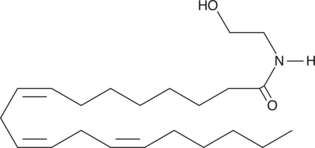
GC43457
Dihomo-γ-Linolenoyl Ethanolamide
Dihomo-γ-linolenoyl ethanolamide is an endocannabinoid containing dihomo-γ-linoleate in place of the arachidonate moiety of AEA.
-
GC91542
Docosahexaenoyl Serinol
Docosahexaenoyl Serinolamide
Docosahexaenoyl serinol is a derivative of 2-docosahexaenoyl glycerol (2-DG).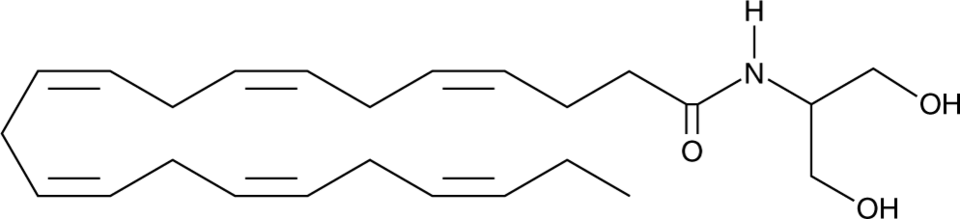
-
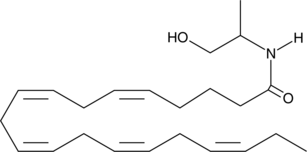
GC43591
Eicosapentaenoyl 1-propanol-2-amide
Monoacylglycerols (MAGs) of ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids have diverse physiological and health effects.
-
GC43593
Eicosapentaenoyl Ethanolamide
EPEA
Eicosapentaenoyl Ethanolamide (EPEA) is an N-acylethanolamide that inhibits dietary-restriction-induced lifespan extension in wild type and TOR pathway mutant nematodes.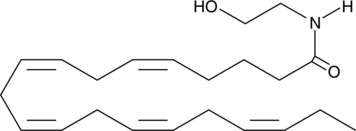
-
GC40408
Glycerophospho-N-Palmitoyl Ethanolamine
GPNAE, GPNPEA
N-Acylated ethanolamines (NAE) are naturally-occurring lipids that have diverse bioactivities.
-
GC41487
Heptadecanoyl Ethanolamide
Palmitoyl ethanolamide (PEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid found in brain, liver, and other mammalian tissues.

-
GC43821
Hexadecanamide
NSC 3327, Palmitamide, Palmitic Amide, Palmitoyl Amide
Hexadecanamide is a primary fatty acid amide that is derived from palmitic acid (C16:0) and belongs to a class of important cell signaling lipids.
-
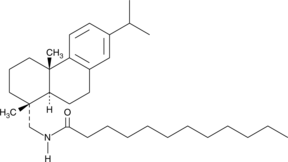
GC44041
Lauric Acid Leelamide
Lauric acid leelamide is the lauric (C-12) amide analog of leelamine.
-
GC49092
Lauroylsarcosine (sodium salt)
Sarkosyl, SDDS, Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate, Sodium N-dodecanoyl Sarcosinate
A fatty acid amide and detergent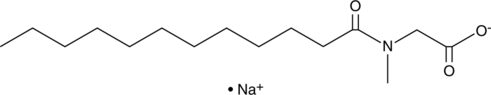
-
GC44065
Lignoceroyl Ethanolamide
Lignoceroyl ethanolamide is a member of the family of fatty N-acyl ethanolamines collectively called endocannabinoids.
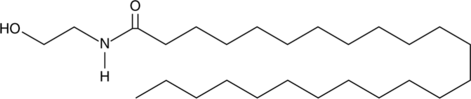
-
GC44261
Myristoyl Ethanolamide
AM3165, Comperlan MM, Schercomid MME
Myristoyl ethanolamide is a member of the family of fatty N-acyl ethanolamines collectively called endocannabinoids.
-
GA23211
Myristoyl-Gly-OH
N-Myristoyl-glycine, Myristoyl-Gly-OH, NSC 622050, N-Tetradecanoyl-glycine
A lipidated amino acid
-
GC18506
N-Arachidonoyl Dopamine
NADA
N-Arachidonoyl Dopamine is a potent and selective endogenous CB1 receptor agonist with a Ki of 250 nM.
-
GC44318
N-Arachidonoyl-3-hydroxy-γ-Aminobutyric Acid
NAG3HABA
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-3-hydroxy-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAG-3H-ABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.
-
GC44319
N-Arachidonoyl-L-Alanine
NALA
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-L-alanine (NALA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.
-
GC44320
N-Arachidonoyl-L-Serine
ARA-S
Arachidonoyl amides of both amino acids and neurotransmitters such as dopamine have been previously reported in the literature.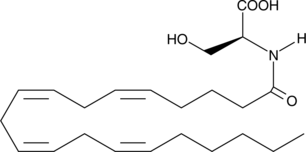
-
GC44410
N-Lignoceroyl Taurine
Several different arachidonoyl amino acid conjugates, including N-arachidonoyl dopamine and N-arachidonoyl-L-serine, have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.

-
GC44456
N-Palmitoyl Glycine
NHexadecanoylGlycine, PalGly
N-Palmitoyl Glycine (N-palmitoyl glycine), an endogenous lipid that acts as a modulator of calcium influx and nitric oxide (NO) production in sensory neurons.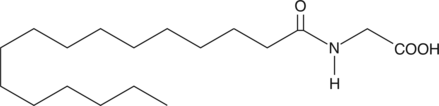
-
GC44457
N-Palmitoyl Taurine
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl dopamine (NADA) and N-arachidonoyl serine (ARA-S), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.

-
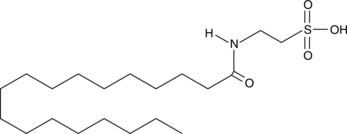
GC44469
N-Stearoyl Taurine
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl dopamine (NADA) and N-arachidonoyl serine (ARA-S), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.
-
GC44309
NAEPA
NAEPA, N-oleoyl ethanolamide phosphoric acid, OEA-P
An LPA mimetic and LPA receptor agonist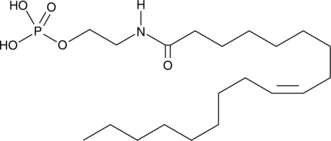
-
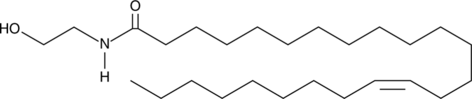
GC44366
Nervonoyl Ethanolamide
Nervonoyl ethanolamide is a member of the family of fatty N-acyl ethanolamines collectively called endocannabinoids.
-
GC44522
oxy-Arachidonoyl Ethanolamide
oxyAEA, oxyAnandamide
AEA acts as an endogenous mimic of δ9-THC, the psychotropic component of marijuana.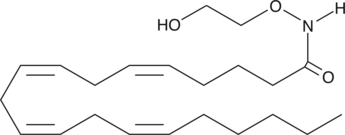
-
GC44548
Palmitoyl Serinol
C16-Serinol, S16
2-Palmitoyl glycerol (2-PG) has been isolated along with the potent endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) from various tissues.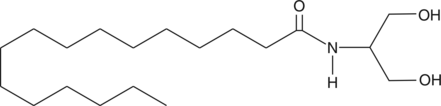
-
GC44593
Pentadecanoyl Ethanolamide
Pentadecanoyl ethanolamide is a member of the family of fatty N-acyl ethanolamines collectively called endocannabinoids.

-
GC40297
R-2 Methanandamide
(R)(-)Arachidonyl2'Hydroxy1'Propylamide
R-2 methanandamide is a cannabinoid analog with a methyl group in the (R) configuration at C-2 of the ethanolamine group.
-
GC45014
Termitomycamide B
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, caused by accumulation of misfolded proteins and a disruption of calcium homeostasis, has been linked to several neuronal diseases including, Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and prion diseases.
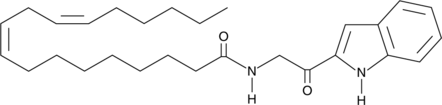
-
GC45015
Termitomycamide E
2'Deoxotermitomycamide A
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, caused by accumulation of misfolded proteins and a disruption of calcium homeostasis, has been linked to several neuronal diseases including, Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and prion diseases.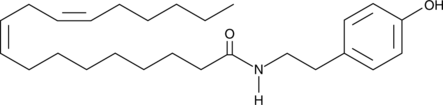
-
GC45083
Tricosanoyl Ethanolamide
Tricosanoyl ethanolamide is a member of the family of fatty N-acyl ethanolamines collectively called endocannabinoids.



