Pyrintegrin |
| Catalog No.GC17607 |
enhances the survival of hESC
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
Cas No.: 1228445-38-2
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
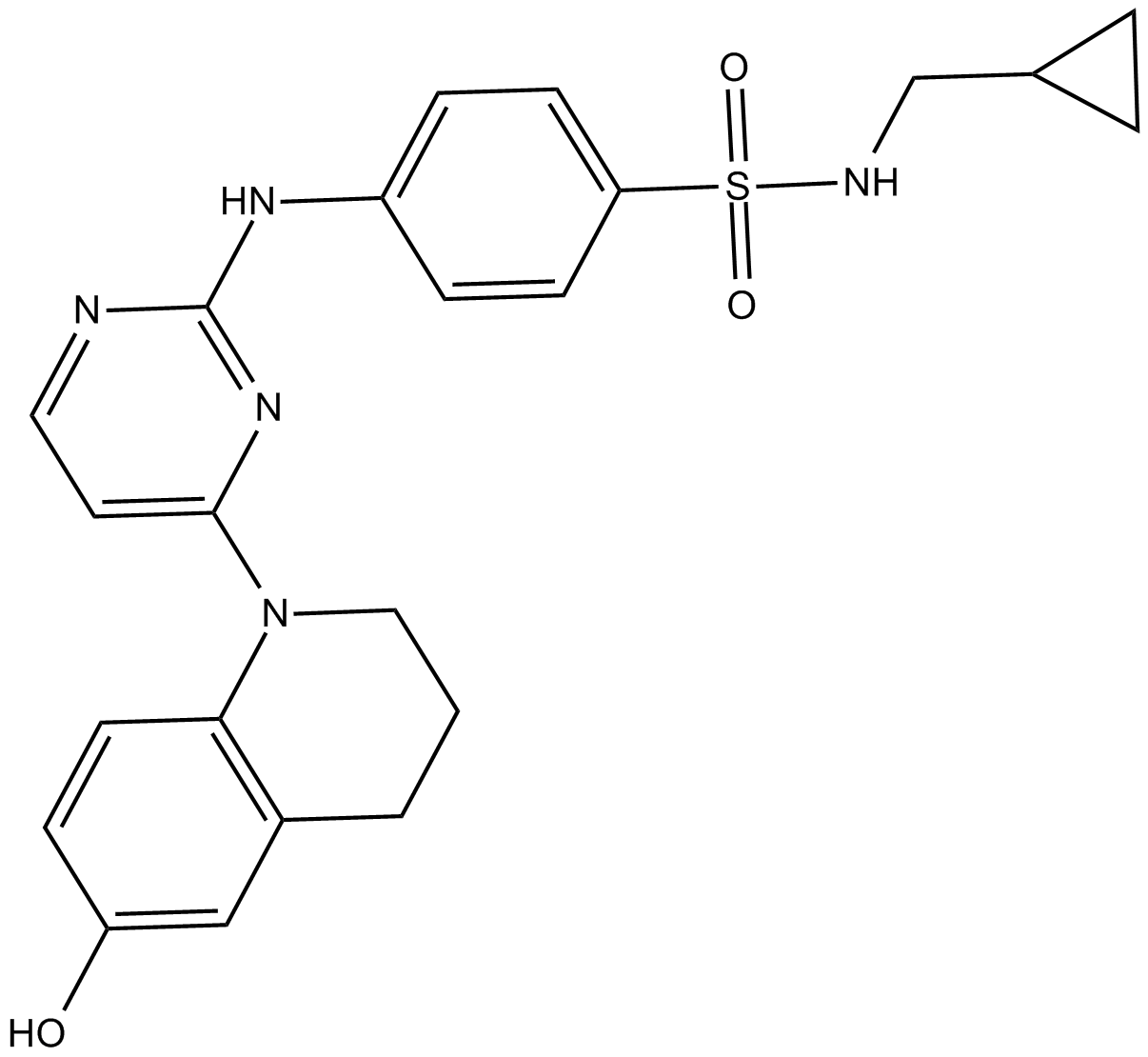
Pyrintegrin, a 2,4-disubstituted pyrimidine, is a novel small-molecule inhibitor of BMP signaling which previously found to promote human embryonic stem cells survival [1].
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are members of the TGF-β superfamily of secreted signaling molecules with important roles in many biological contexts. BMPs could bind to specificserine/threonine kinase receptors and transduce the signal to the nucleus through Smad proteins [2].
In vitro: Pyrintegrin induced differentiation of hADSCs into adipogenic‐like cells in vitro. Pyrintegrin drug treatment can accelerate adipocyte differentiation and augment lipid accumulation, adiponectin and fatty acid secretion in adipogenic medium differentiated human adipose derived stem cells [1]. Pyrimidine (2 μM) enhanced the survival of hESC more than 30-fold after trypsin-mediated dissociation. Pyrimidine increased integrin-dependent attachment of hESC to extracellular matrices without significantly impacting cell proliferation. Pyrintegrin increased the binding of the activated β1 integrin-specific antibody HUTS-21 and enhanced the phosphorylation of multiple growth factor receptors and their downstream kinases, PI3K and MAPK [3].
In vivo: Pyrintegrin promoted proliferation and differentiation of adipose precursor cells depending on their microenvironment. Pyrintegrin increased the number of preadipocytes and the rate of adipocyte differentiation, resulting in enhanced de novo adipogenesis [1].
References:
[1] Shah B S. Pyrintegrin Induced Adipogenesis: Biology[D]. Columbia University, 2012.
[2] von Bubnoff A, Cho K W Y. Intracellular BMP signaling regulation in vertebrates: pathway or network[J]. Developmental biology, 2001, 239(1): 1-14.
[3] Xu Y, Zhu X, Hahm H S, et al. Revealing a core signaling regulatory mechanism for pluripotent stem cell survival and self-renewal by small molecules[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2010, 107(18): 8129-8134.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 33 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















