2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-Quinolone (Synonyms: PQS, Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal) |
| Catalog No.GC45912 |
A bacterial quorum-sensing signaling molecule
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
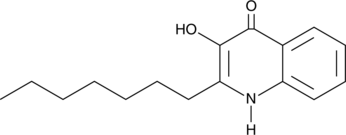
Cas No.: 108985-27-9
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-Quinolone is a quorum-sensing signaling molecule produced by P. aeruginosa in response to increasing cell density.[1] It increases expression of the lasB gene, which encodes the virulence factor elastase, in P. aeruginosa (EC50 = ~30 µM in a reporter cell assay). 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-Quinolone (60 µM) increases secretion of the metabolite pyocyanin and the lectin PA-IL, as well as increases biofilm production in P. aeruginosa populations.[2] It also reduces iron levels in P. aeruginosa growth media when used at a concentration of 40 µM and acts as an iron chelator in a Fe(III)-sulfate solution.[3]
Reference:
[1]. Pesci, E.C., Milbank, J.B.J., Pearson, J.P., et al. Quinolone signaling in the cell-to-cell communication system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96(20), 11229-11234 (1999).
[2]. Diggle, S.P., Winzer, K., Chhabra, S.R., et al. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal molecule overcomes the cell density-dependency of the quorum sensing hierarchy, regulates rhl-dependent genes at the onset of stationary phase and can be produced in the absence of LasR. Mol. Microbiol. 50(1), 29-43 (2003).
[3]. Bredenbruch, F., Geffers, R., Nimtz, M., et al. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal (PQS) has an iron-chelating activity. Environ. Microbiol. 8(8), 1318-1329 (2006).
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 14 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




