Diphenyleneiodonium chloride (Synonyms: DPI) |
| Catalog No.GC12520 |
Diphenyleneiodonium (DPI) chloride (DPIC), as a NADH/NADPH oxidase inhibitor, has possessing potent antimicrobial activity against Mtb and S.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
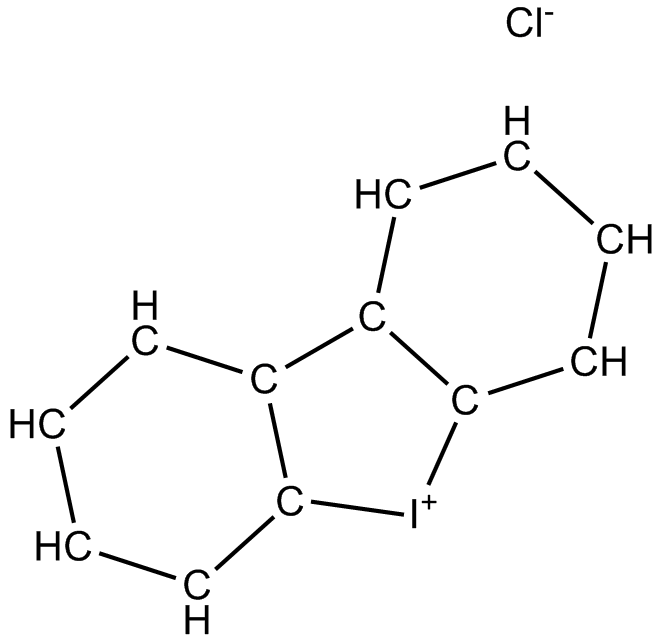
Cas No.: 4673-26-1
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Diphenyleneiodonium (DPI) chloride (DPIC), as a NADH/NADPH oxidase inhibitor, has possessing potent antimicrobial activity against Mtb and S. aureus[1].
In vitro efficacy test it shown that DPIC was equi-potently effective against drug-resistant clinical isolates of S. aureus with MIC of 0.5-1 mg/L as compared to S. aureus ATCC 29213. DPIC has no obvious potency against gram-negative bacteria with MIC ranging from 4-32 mg/L. DPIC also has potent antimicrobial activity against H37Rv with MIC of 0.39 µM or 0.12 mg/L[1]. In vitro, with 0.1 mM DPIC inhibits fungal spore germination and bacterial cell proliferation[2]. In vitro, treatment with 10 µM Diphenyleneiodonium chloride, DPI has strongest inhibition against neutrophil extracellular trap creation[3]. In vitro test it exhibited that treatment with 0.5-4 µM DPI in HCT116 cells decrease in G1 and increase in S phase cells. In addition, DPI treatment (0.5 µM DPI for 3 days) induces senescence of MCF-7 cells[4].
In vivo test it demonstrated that rat were administrated with 1 mg/kg DPI subcutaneously maybe protect against the functional and neurohistological damage of bupivacaine-blocked sciatic nerves in a high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced DN model[5]. In vivo, treatment with 5 mg/kg DPI intraperitoneally in Sprague-Dawley rats, there was obvious reduction in the intracellular ROS, the number of inflammatory cells, and cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) in BALF compared with LPS-treated rats[6].
References:
[1] Pandey M, et al. Diphenyleneiodonium chloride (DPIC) displays broad-spectrum bactericidal activity. Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 14;7(1):11521.
[2] Jung B, et al. Efficacy of Diphenyleneiodonium Chloride (DPIC) Against Diverse Plant Pathogens. Mycobiology. 2019 Jan 14;47(1):105-111.
[3] Ostafin M, et al. Different procedures of diphenyleneiodonium chloride addition affect neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Anal Biochem. 2016 Sep 15;509:60-66.
[4] Piszczatowska K, et al. Inhibition of NADPH Oxidases Activity by Diphenyleneiodonium Chloride as a Mechanism of Senescence Induction in Human Cancer Cells. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Dec 8;9(12):1248.
[5] Ji ZH, et al. Diphenyleneiodonium Mitigates Bupivacaine-Induced Sciatic Nerve Damage in a Diabetic Neuropathy Rat Model by Attenuating Oxidative Stress. Anesth Analg. 2017 Aug;125(2):653-661.
[6] Kim SK, et al. Protective effects of diphenyleneiodonium, an NADPH oxidase inhibitor, on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2019 Feb;46(2):153-162.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 32 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















