PARP
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs) is a large family of proteins with a conserved catalytic domain that catalyze an immediate DNA-damage-dependent post-translational modification of histones and other nuclear proteins leading to the survival of injured proliferating cells. So far, a total number of 18 human PARP proteins encoded by different genes have been identified, including PARP-1 to PARP-4, PARP-5a, PARP-5b, PARP-5c and PARP-6 to PARP-16. The general structural of PARP proteins has been revealed through the extensive study of the founding family member PARP-1, which is characterized by the presence of four functional domains, including a DNA-binding domain, a caspase-cleaved domain, an automodification domain and a catalytic domain.
Products for PARP
- Cat.No. Product Name Information
-
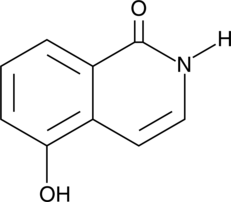
GC40468
1,5-Isoquinolinediol
NSC 65585
The poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs) form a family of enzymes with roles in DNA repair and apoptosis.
-
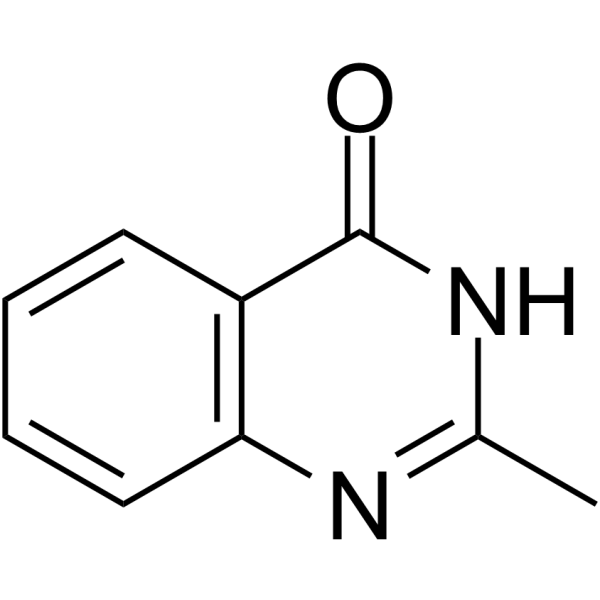
GC62781
2-Methylquinazolin-4-ol
2-Methylquinazolin-4-ol is a potent competitive poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase inhibitor, with a Ki of 1.1 μM.
-
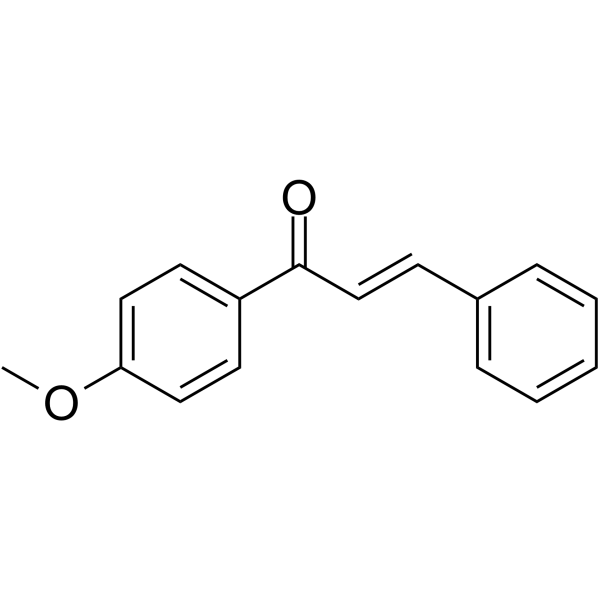
GC62805
4’-Methoxychalcone
4’-Methoxychalcone regulates adipocyte differentiation through PPARγ activation.
-
GC11761
4-amino-1,8-Naphthalimide
4-Aminonaphthalimide,4-ANI
4-amino-1,8-Naphthalimide is a potent PARP inhibitor and potentiates the cytotoxicity of γ-radiation in cancer cells.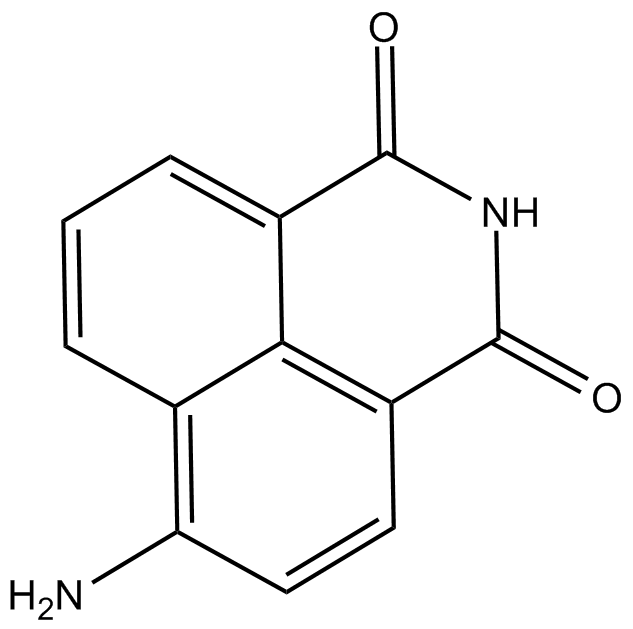
-
GC35150
5,7,4'-Trimethoxyflavone
5,7,4'-Trimethoxyflavone is isolated from Kaempferia parviflora (KP) that is a famous medicinal plant from Thailand. 5,7,4'-Trimethoxyflavone induces apoptosis, as evidenced by increments of sub-G1 phase, DNA fragmentation, annexin-V/PI staining, the Bax/Bcl-xL ratio, proteolytic activation of caspase-3, and degradation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) protein.5,7,4'-Trimethoxyflavone is significantly effective at inhibiting proliferation of SNU-16 human gastric cancer cells in a concentration dependent manner.
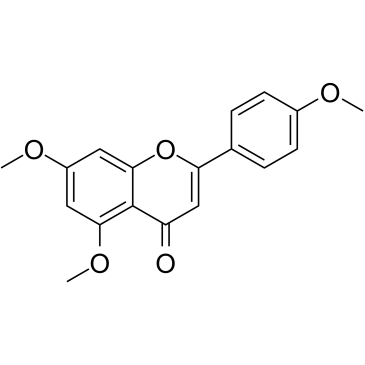
-
GN10629
5,7-dihydroxychromone
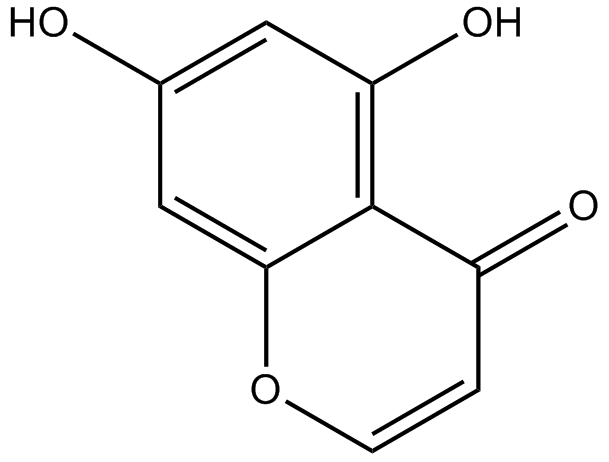
-
GC68161
5-AIQ
5-Aminoisoquinolin-1-one
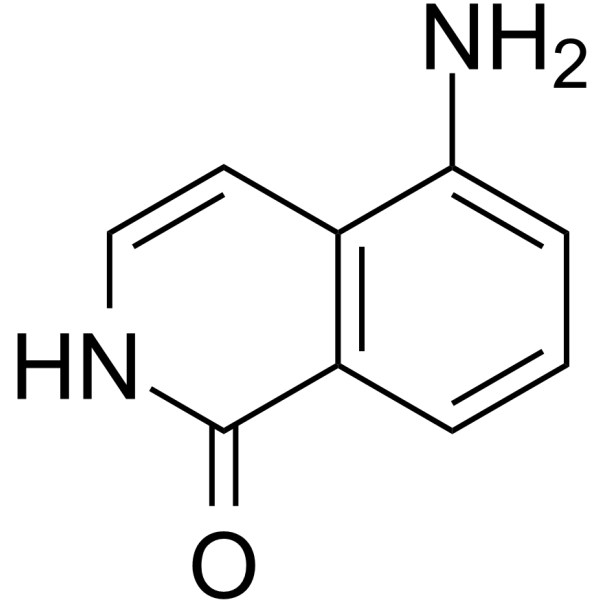
-
GC45772
6(5H)-Phenanthridinone
NSC 11021, NSC 40943, NSC 61083
An inhibitor of PARP1 and 2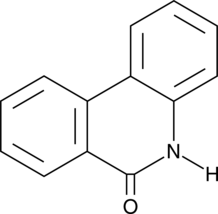
-
GC12390
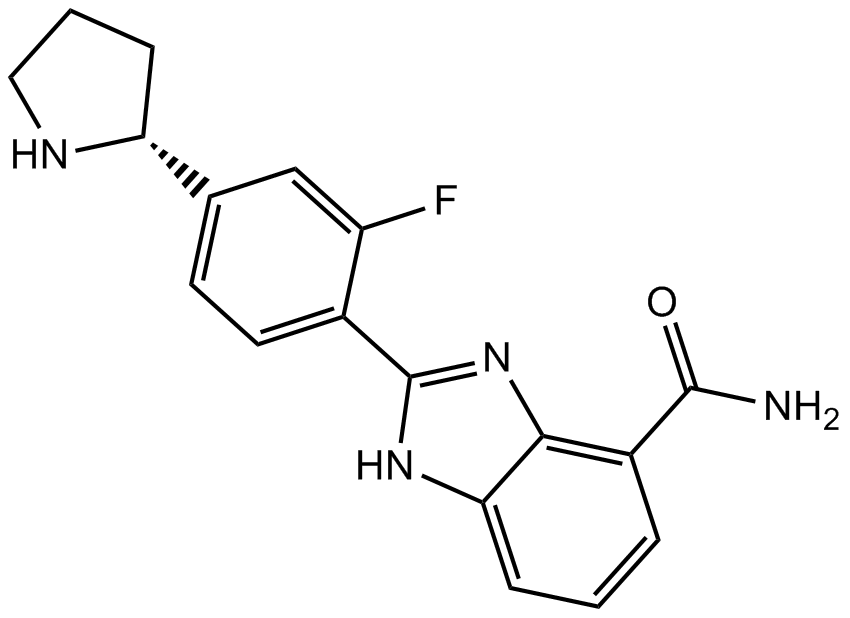
A-966492
A PARP1 and PARP2 inhibitor
-
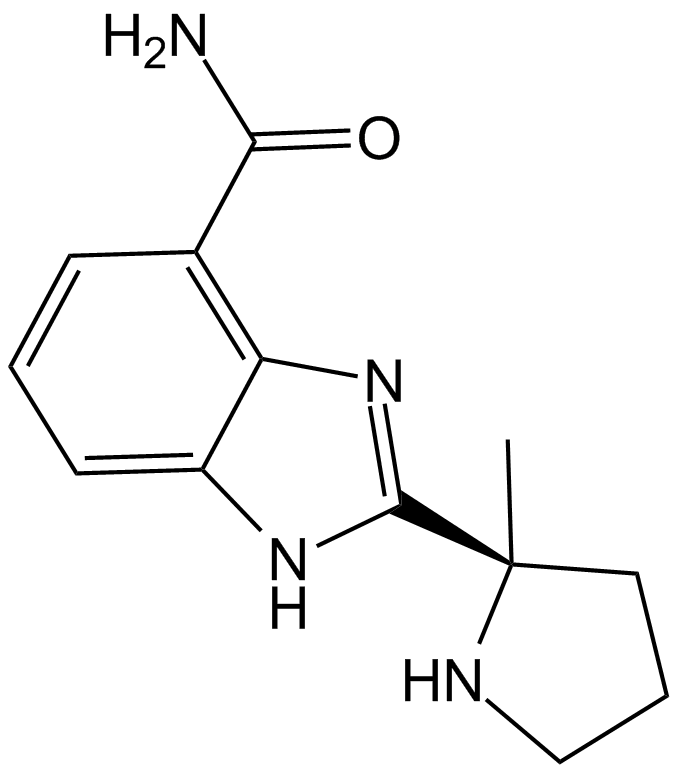
GC12422
ABT-888 (Veliparib)
-
GC16318
AG-14361
A PARP1 inhibitor

-
GC73642
ALK-IN-26
ALK-IN-26 is an ALK inhibitor with IC50 value of 7.0 μM for ALK tyrosine kinase.

-
GC70420
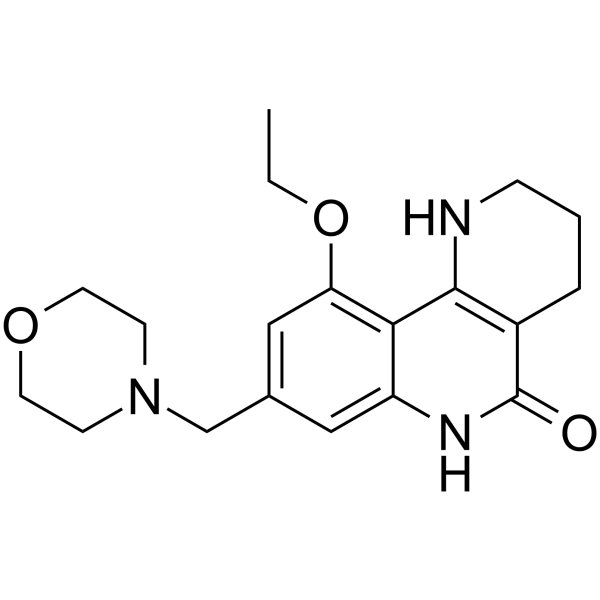
Amelparib
Amelparib is a potent, orally active, and water-soluble inhibitor of PARP-1.
-
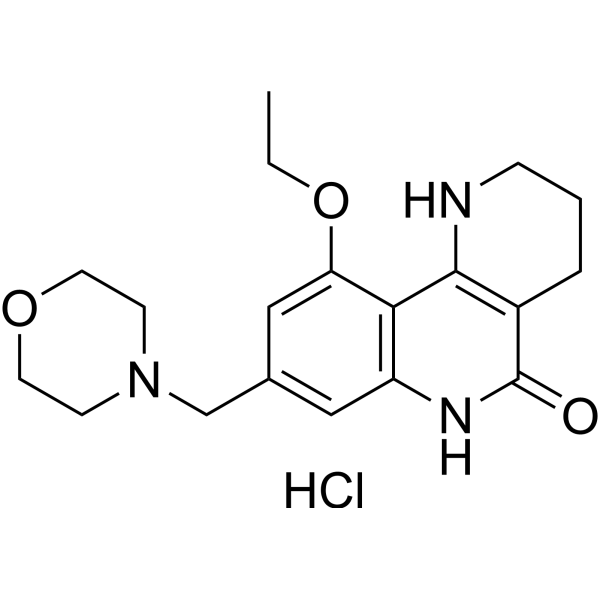
GC70421
Amelparib hydrochloride
Amelparib (JPI-289) hydrochloride is a potent, orally active, and water-soluble inhibitor of PARP-1.
-
GC65899
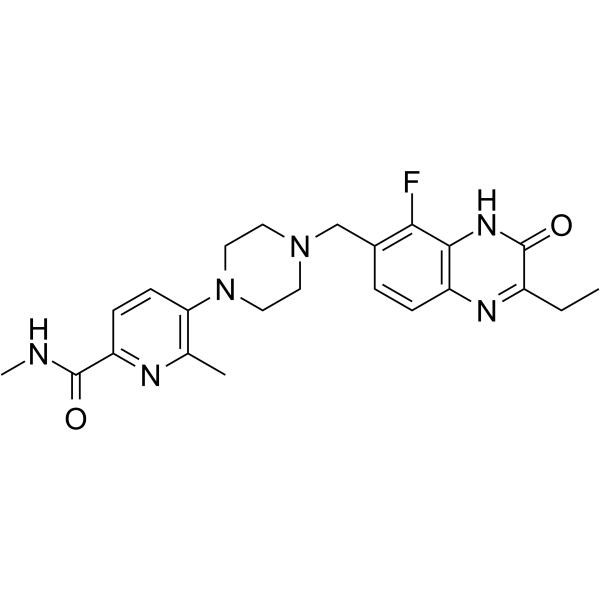
AZ3391
AZ3391 is a potent inhibitor of PARP. AZ3391 is a quinoxaline derivative. PARP family of enzymes play an important role in a number of cellular processes, such as replication, recombination, chromatin remodeling, and DNA damage repair. AZ3391 has the potential for the research of diseases and conditions occurring in tissues in the central nervous system, such as the brain and spinal cord (extracted from patent WO2021260092A1, compound 23).
-
GC16725
AZ6102
TNKS1/2 inhibitor

-
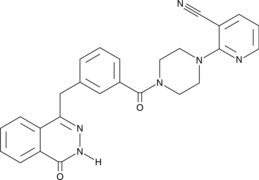
GC46900
AZ9482
A PARP inhibitor
-
GC73919
AZD-9574-acid
AZD-9574-acid (70D), a PPAR-1 inhibitor, can be used for the synthesis of PROTAC (CAS 2923686-70-6).

-
GC17965
AZD2461
A PARP inhibitor

-
GC62310
AZD5305
AZD5305
AZD5305 is a potent, selective and oral active PARP inhibitor. AZD5305 is potent and efficacious in animal xenografts and PDX models.
-
GC73130
Basroparib
STP1002
Basroparib is a potent poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor, with antineoplastic activity.
-
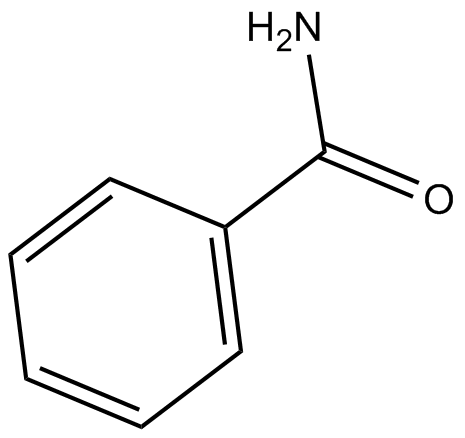
GC12844
Benzamide
poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase inhibitor
-
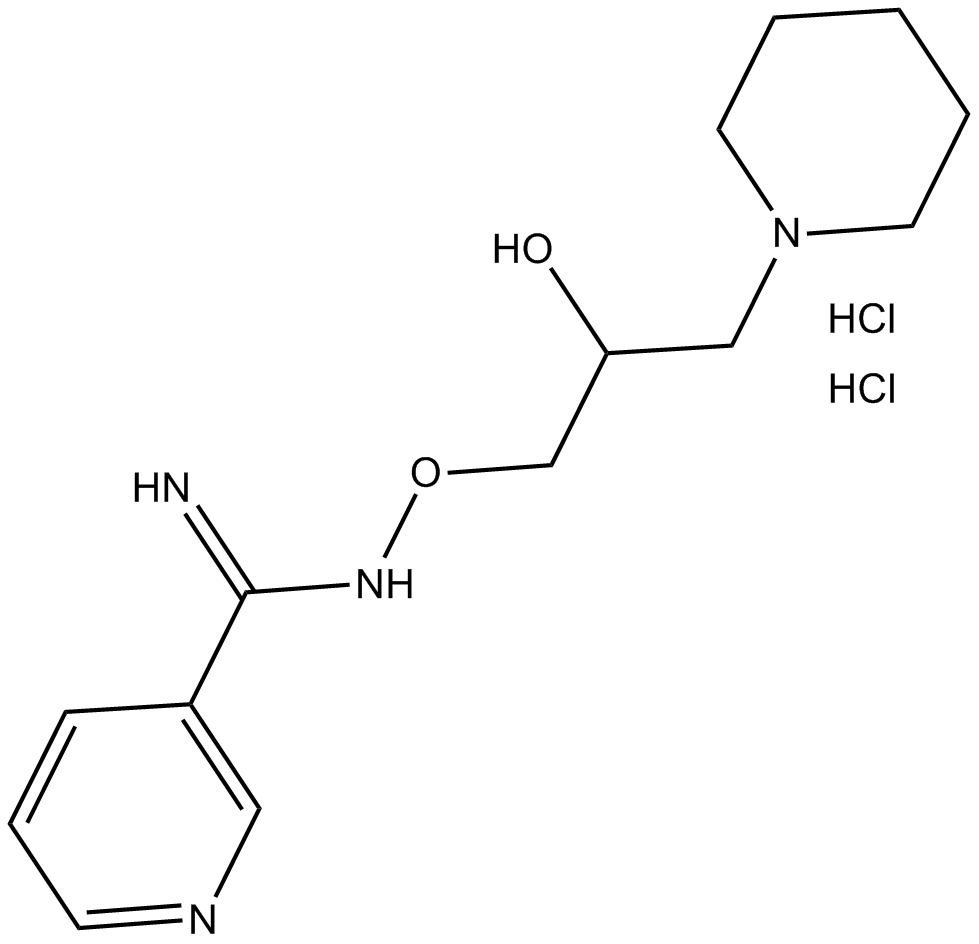
GC14380
BGP-15
PARP inhibitor
-
GC15932
BMN 673
Talazoparib
A PARP inhibitor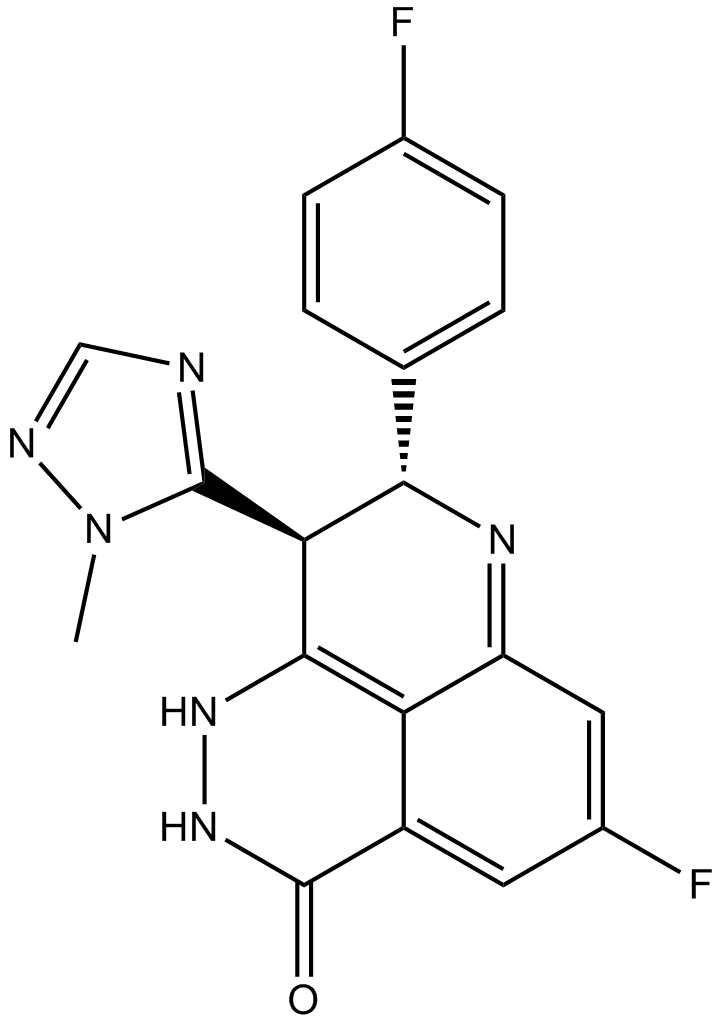
-
GC10920
BMN-673 8R,9S

-
GC35547
BR102375
BR102375 is a non-TZD peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPAR γ) full agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, reveals EC50 value of 0.28?μM and Amax ratio?of 98%.

-
GC33223
BRCA1-IN-1
BRCA1-IN-1 is a novel small-molecule-like BRCA1 inhibitor with IC50 and Ki of 0.53 μM and 0.71 μM, respecrively.

-
GC35550
BRCA1-IN-2
BRCA1-IN-2 (compound 15) is a cell-permeable protein-protein interaction (PPI) inhibitor for BRCA1 with an IC50 of 0.31 μM and a Kd of 0.3 μM, which shows antitumor activities via the disruption of BRCA1 (BRCT)2/protein interactions.
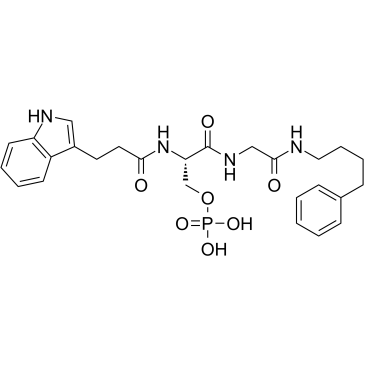
-
GC10690
BYK 204165
PARP Inhibitor XIV
A selective inhibitor of PARP1
-
GC14434
BYK 49187
Potent PARP-1/PARP-2 inhibitor

-
GC47055
CAY10749
CAY10749 (compound 15) is a potent PARP/PI3K inhibitor with pIC50 values of 8.22, 8.44, 8.25, 6.54, 8.13, 6.08 for PARP-1, PARP-2, PI3Kα, PI3Kβ, PI3Kδ, and PI3Kγ, respectively. CAY10749 is a highly effective anticancer compound targeted against a wide range of oncologic diseases.
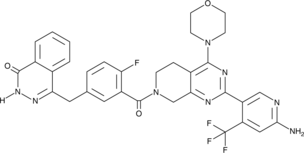
-
GC47056
CAY10753
A TNKS2 inhibitor

-
GC68940
DB008
DB008 is an effective selective inhibitor of PARP16 with an IC50 value of 0.27 μM and contains acrylamide electrophile. DB008 has membrane permeability and can selectively label PARP16.
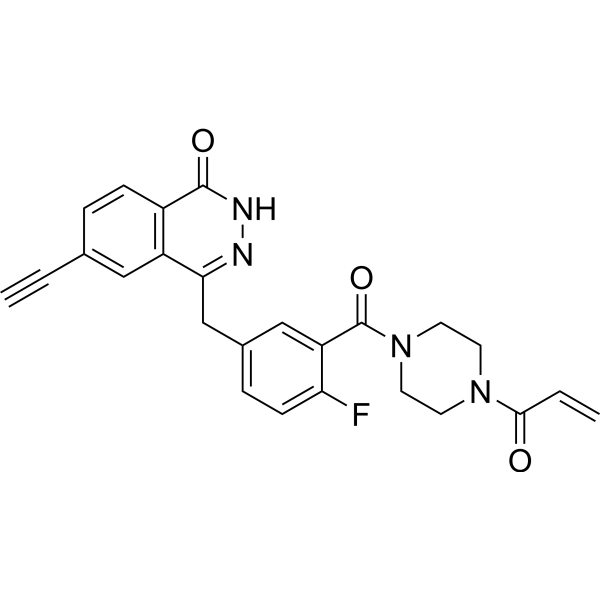
-
GN10040
Dehydrocorydaline

-
GC12680
DR 2313
A PARP inhibitor
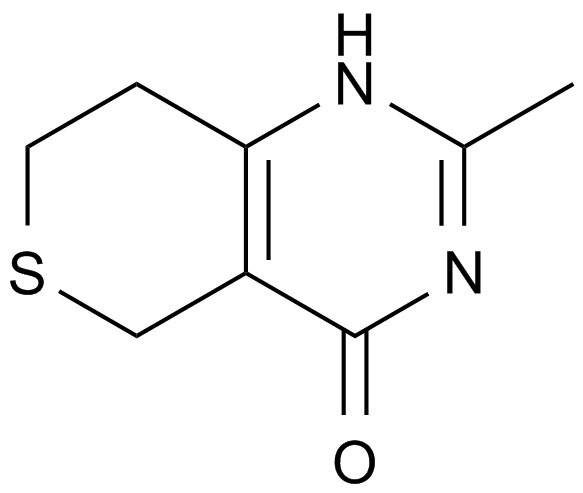
-
GC64209
E7016
GPI 21016
E7016 (GPI 21016) is an orally available PARP inhibitor. E7016 can enhance tumor cell radiosensitivity in vitro and in vivo through the inhibition of DNA repair. E7016 acts as a potential anticancer agent.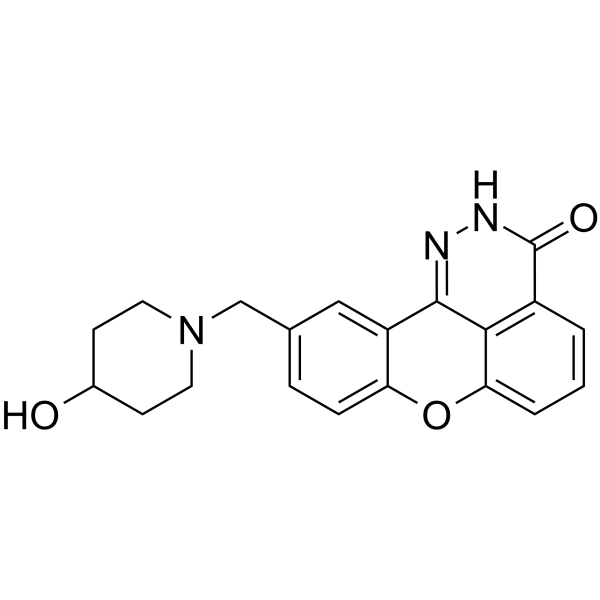
-
GC18172
E7449
E7449; 2X-121
E7449 is an inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) and PARP2 (IC50s = 1 and 1.2 nM, respectively) as well as tankyrase (TNKS) 1/2 (IC50s = 50-100 nM).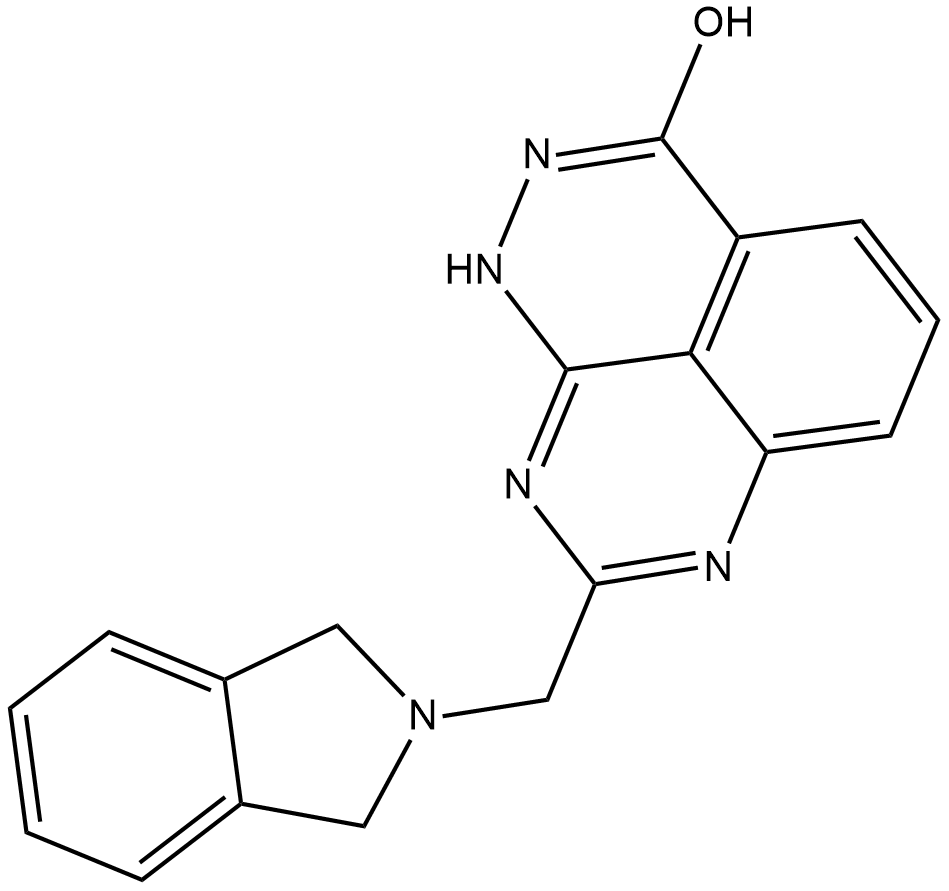
-
GC12991
EB 47
A PARP1 and TNKS2 inhibitor
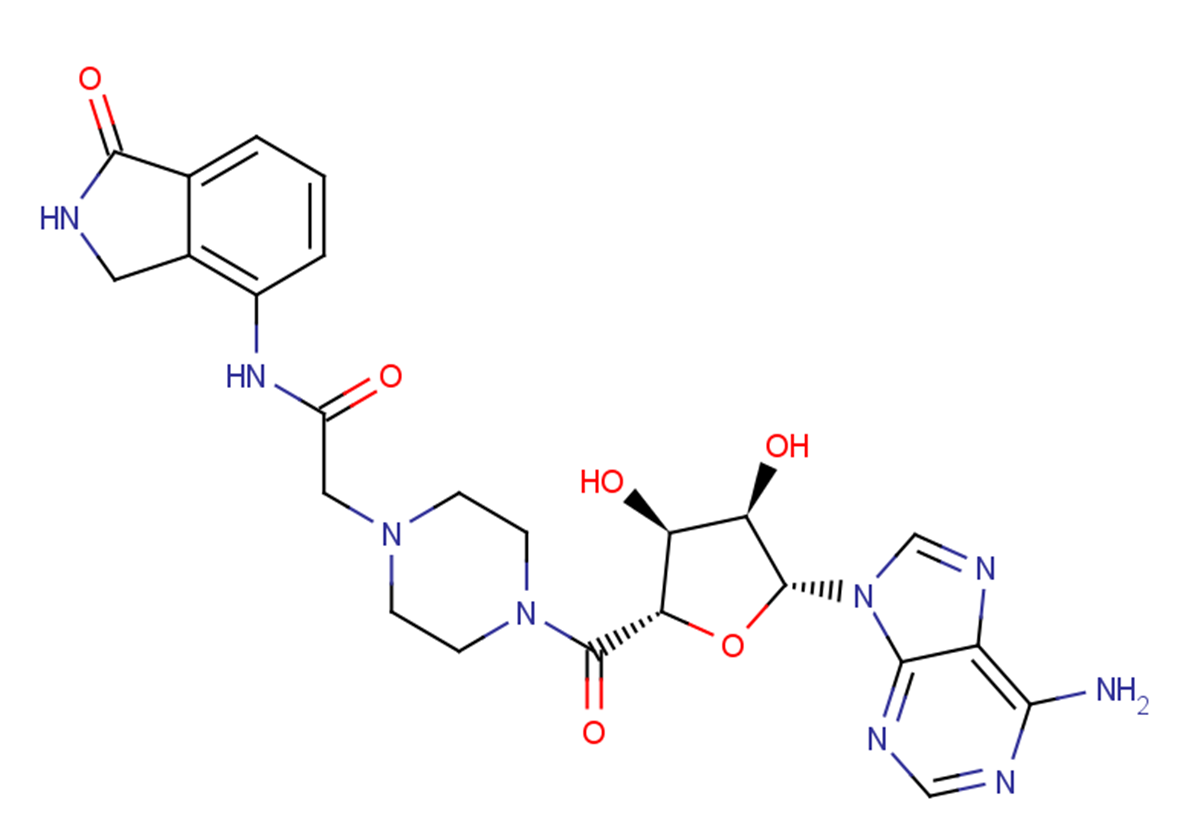
-
GC50506
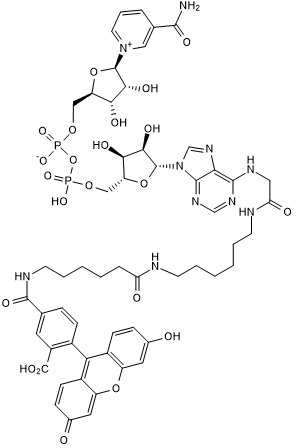
Fluorescein-NAD+
Fluorescent NAD+; substrate for ADP-ribosylation for use in PARP assays
-
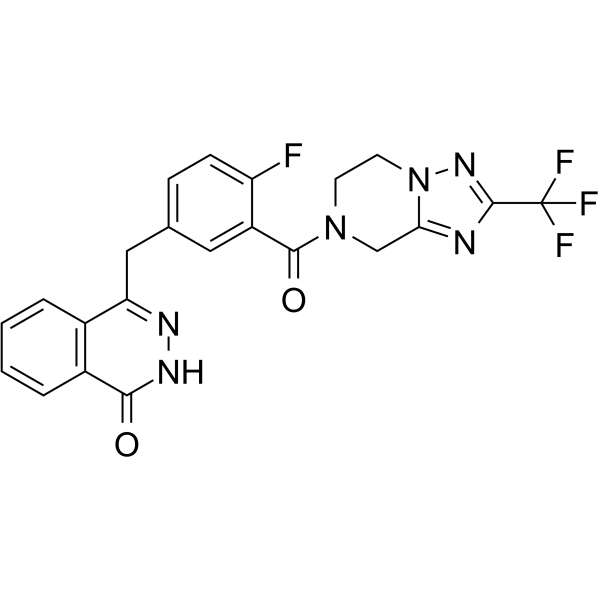
GC62121
Fluzoparib
Fluzoparib (SHR3162) is a potent and orally active PARP1 inhibitor (IC50=1.46±0.72 nM, a cell‐free enzymatic assay) with superior antitumor activity. Fluzoparib selectively inhibits the proliferation of homologous recombination repair (HR)‐deficient cells, and sensitizes both HR‐deficient and HR‐proficient cells to cytotoxic agents. Fluzoparib exhibits good pharmacokinetic properties in vivo and can be used for BRCA1/2-mutant relapsed ovarian cancer research.
-
GC10456
Fucosterol
24-ethylidene Cholesterol
Fucosterol is a plant sterol found in algae
-
GC13541
G007-LK
Tankyrase 1/2 Inhibitor VI
tankyrase 1/2 inhibitor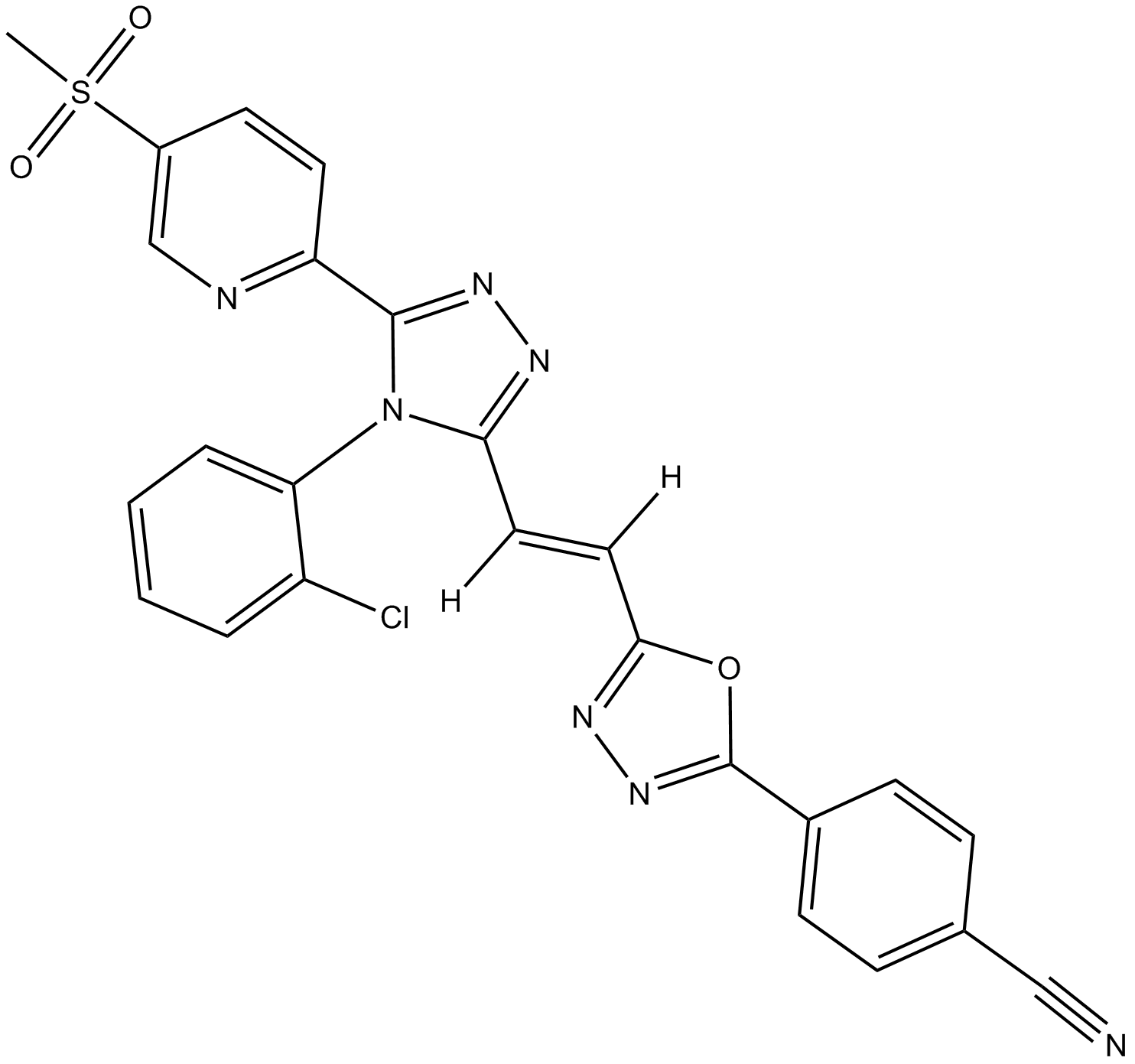
-
GC19542
GeA-69
GeA-69 is a selective, highly cell permeable allosteric inhibitor
-
GC15353
Iniparib (BSI-201)
IND 71677, Iniparib
A PARP1 inhibitor
-
GC12496
INO-1001
m-Aminobenzamide, 3-(Aminocarbonyl) Aniline, 3-Carboxamidoaniline, NSC 36962
A PARP inhibitor
-
GC38385
INO-1001

-
GC34195
K-756
K-756 is a direct and selective tankyrase (TNKS) inhibitor, which inhibits the ADP-ribosylation activity of TNKS1 and TNKS2 with IC50s of 31 and 36 nM, respectively.

-
GC65907
KSQ-4279
USP1-IN-1
KSQ-4279 (USP1-IN-1, Formula I) is a USP1 and PARP inhibitor (extracted from patent WO2021163530).
-
GC47693
m-Methoxybenzamide
m-Anisamide, meta-Methoxybenzamide, NSC 28589, NSC 209527
m-Methoxybenzamide (3-MBA), an inhibitor of ADP-ribosyltransferase (ADPRTs) and PARP, inhibits cell division in Bacillus subtilis, leading to filamentation and eventually lysis of cells. m-Methoxybenzamide (3-MBA) enhances in vitro plant growth, microtuberization, and transformation efficiency of blue potato (Solanum tuberosum L. subsp. andigenum).
-
GC13419
ME0328
PARP inhibitor,potent and selective

-
GC62252
Mefuparib hydrochloride
MPH
Mefuparib hydrochloride (MPH) is an orally active, substrate-competitive and selective PARP1/2 inhibitor with IC50s of 3.2 nM and 1.9 nM, respectively. Mefuparib hydrochloride induces apoptosis and possesses prominent anticancer activity in vitro and in vivo.
-
GC17802
MK-4827
An orally bioavailable PARP1/2 inhibitor

-
GC12756
MK-4827 hydrochloride
MK-4827 hydrochloride
MK-4827 hydrochloride (MK-4827 hydrochloride) is a highly potent and orally bioavailable PARP1 and PARP2 inhibitor with IC50s of 3.8 and 2.1 nM, respectively. MK-4827 hydrochloride leads to inhibition of repair of DNA damage, activates apoptosis and shows anti-tumor activity.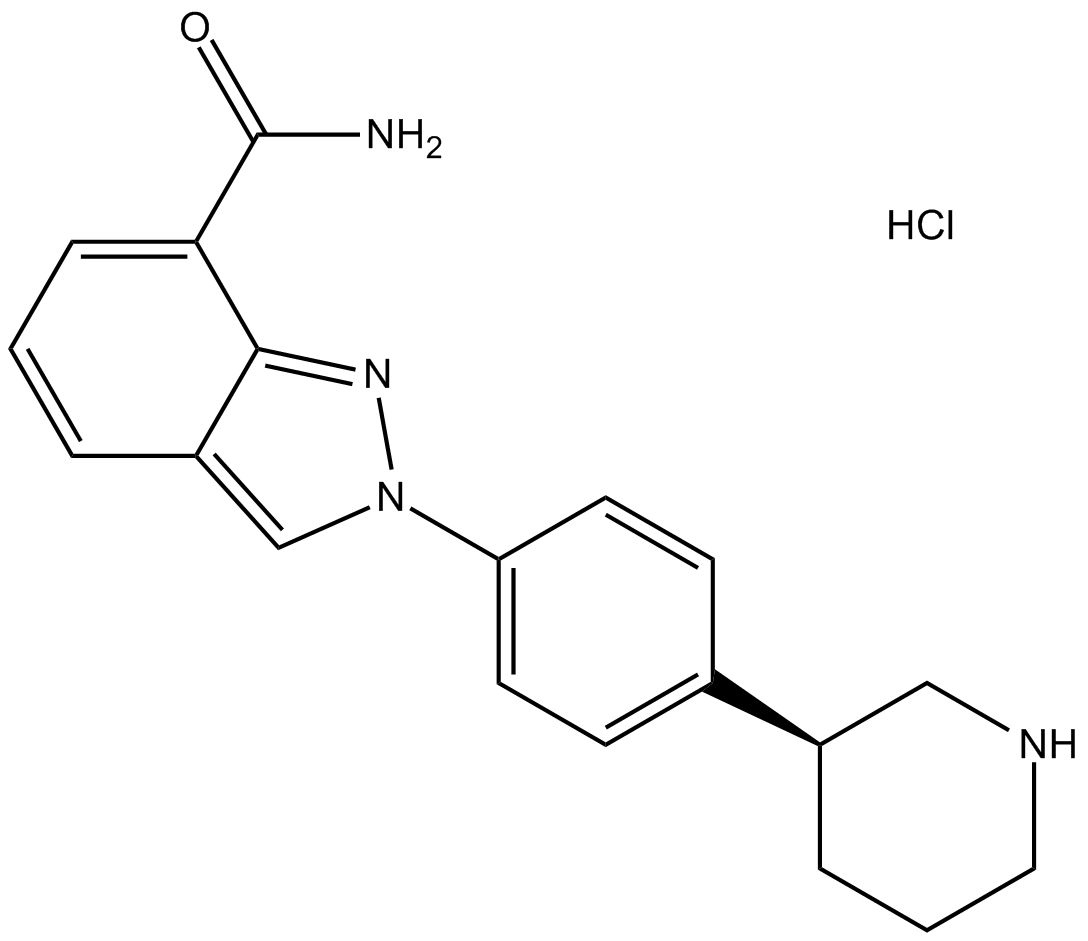
-
GC17052
MK-4827 Racemate
selective inhibitor of PARP1/PARP2

-
GC11537
MK-4827 tosylate
Niraparib tosylate
MK-4827 tosylate (MK-4827 tosylate) is a highly potent and orally bioavailable PARP1 and PARP2 inhibitor with an IC50 of 3.8 and 2.1 nM, respectively. MK-4827 tosylate leads to inhibition of repair of DNA damage, activates apoptosis and shows anti-tumor activity.
-
GC16914
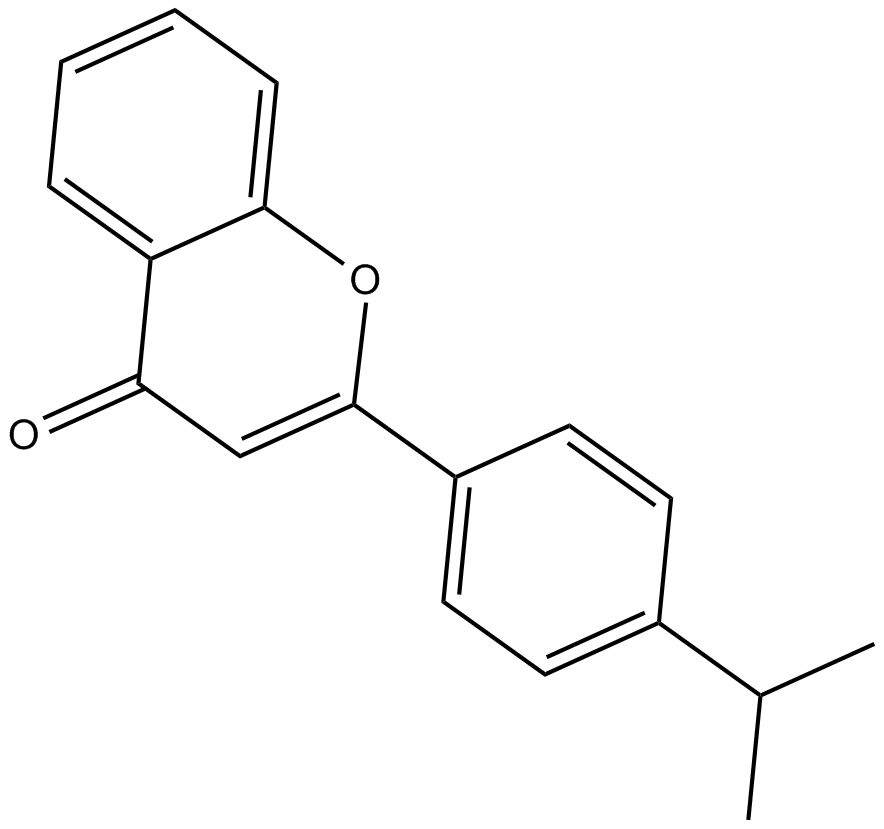
MN 64
tankyrase inhibitor
-
GC62154
N-Descyclopropanecarbaldehyde Olaparib
N-Descyclopropanecarbaldehyde Olaparib is an analogue of Olaparib containing DOTA moiety. N-Descyclopropanecarbaldehyde Olaparib is a CRBN-based ligand for synthesizing novel dual EGFR and PARP PROTAC, DP-C-4. N-Descyclopropanecarbaldehyde Olaparib can be radiolabeled F-18 or fluorophore for positron emission tomography (PET) or optical imaging in several types of tumor.

-
GC65202
Nesuparib
JPI-547/OCN-201
Nesuparib is a potent inhibitor of PARP.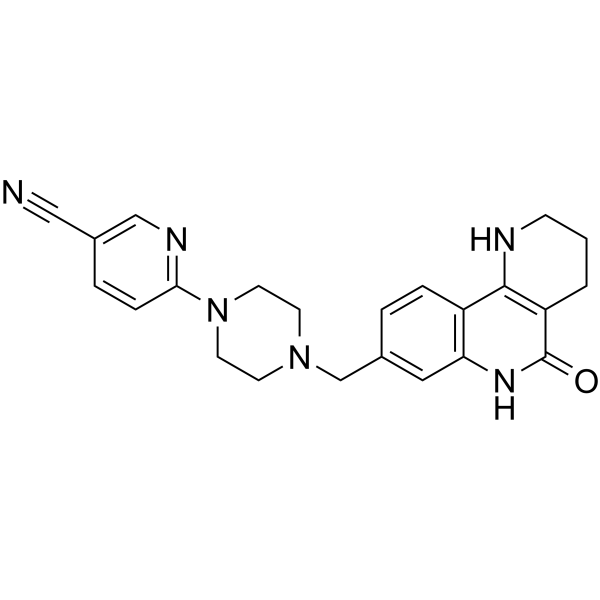
-
GC34120
Niraparib R-enantiomer (MK 4827 (R-enantiomer))
MK 4827 (R-enantiomer)
Niraparib R-enantiomer (MK-4827 R-enantiomer) is an excellent PARP1 inhibitor with IC50 of 2.4 nM.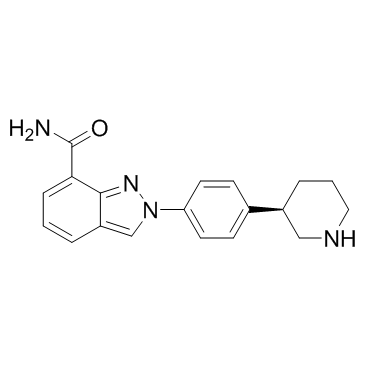
-
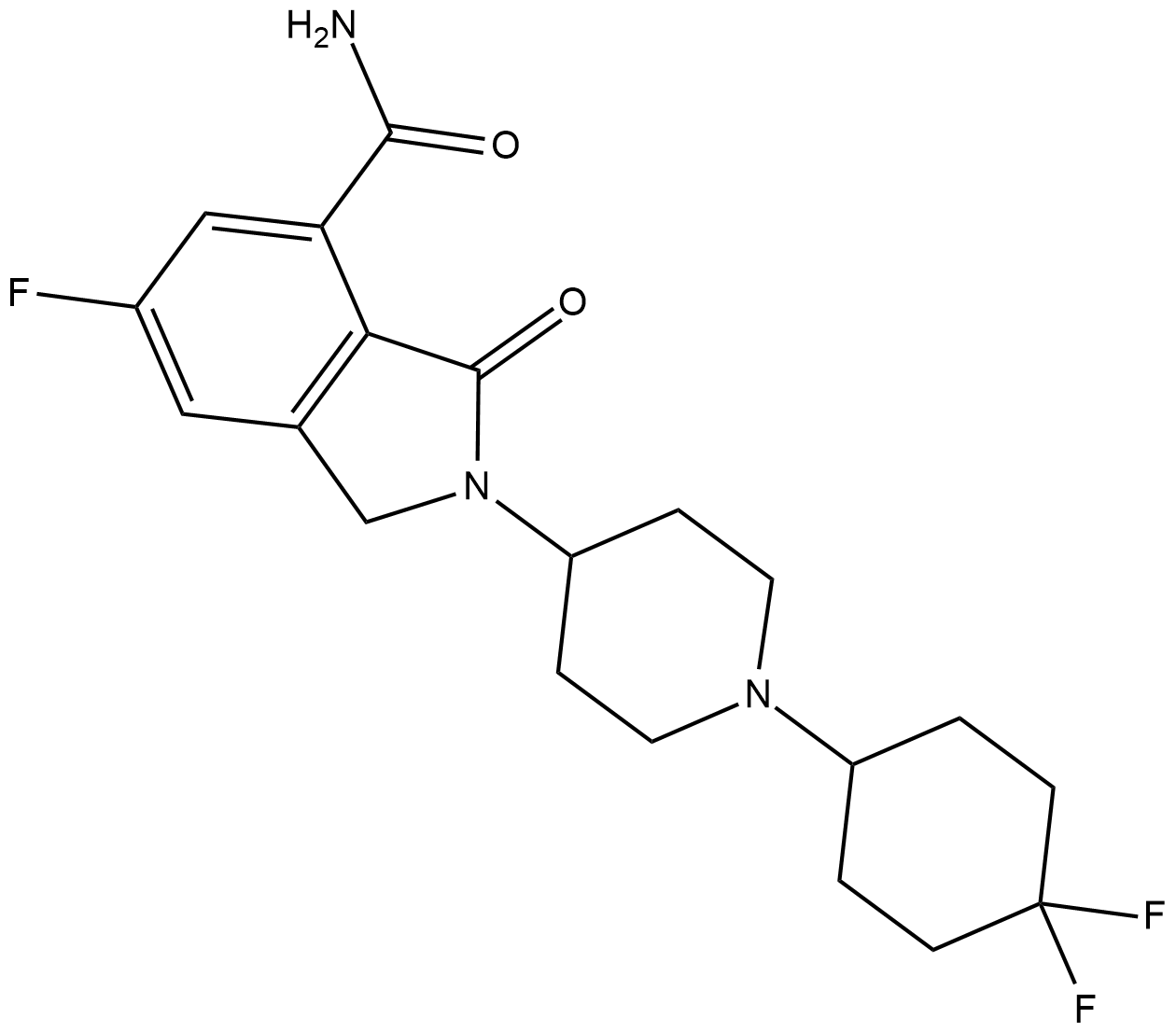
GC19264
NMS-P118
NMS-P118 is a potent, orally available, and highly selective PARP-1 Inhibitor for cancer therapy.
-
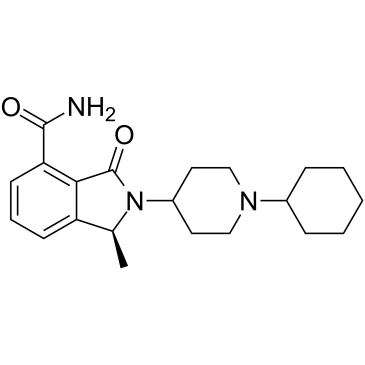
GC36751
NMS-P515
NMS-P515 is a potent, orally active and stereospecific PARP-1 inhibitor, with a Kd of 16 nM and an IC50 of 27 nM (in Hela cells). Anti-tumor activity.
-
GC17775
NU 1025
NSC 696807
An inhibitor of PARP
-
GC17555
NVP-TNKS656
TNKS656
TNKS2 inhibitor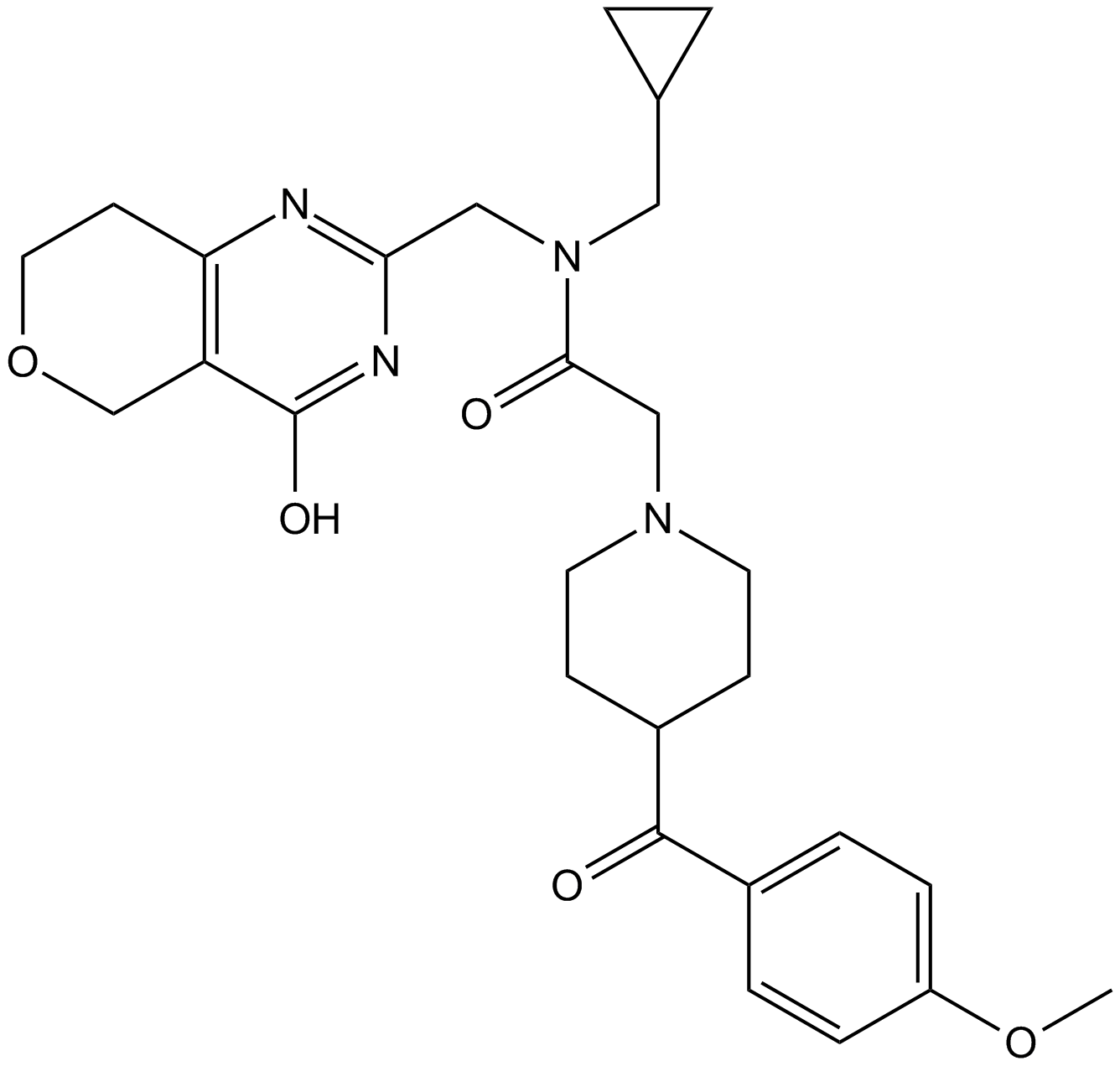
-
GC17580
Olaparib (AZD2281, Ku-0059436)
AZD 2281, Ku0059436
Olaparib (AZD2281, Ku-0059436) is a potent and selective PARP inhibitor that specifically targets PARP1 and PARP2 (IC 50 = 5 nM and 1 nM, respectively).
-
GC69618
Olaparib-d8
AZD2281-d8; KU0059436-d8
Olaparib-d8 is the deuterated form of Olaparib (AZD2281). Olaparib is an orally effective PARP inhibitor that inhibits PARP-1 and PARP-2 with IC50 values of 5 and 1 nM, respectively. Olaparib is also an activator of autophagy and mitophagy.

-
GC67906
OM-153

-
GN10114
Oroxin A
Baicalein-7-O-Glucoside
-
GC73184
OUL232
OUL232 is a potent inhibitor of mono-ARTs PARP7, PARP10, PARP11, PARP12, PARP14, and PARP15.

-
GC45808
OUL35
NSC 39047
An inhibitor of PARP10
-
GC34071
Pamiparib (BGB-290)
BGB-290
Pamiparib (BGB-290) (BGB-290) is an orally active, potent, highly selective PARP inhibitor, with IC50 values of 0.9 nM and 0.5 nM for PARP1 and PARP2, respectively. Pamiparib (BGB-290) has potent PARP trapping, and capability to penetrate the brain, and can be used for the research of various cancers including the solid tumor.
-
GC36855
Paris saponin VII
Paris saponin VII (Chonglou Saponin VII) is a steroidal saponin isolated from the roots and rhizomes of Trillium tschonoskii Maxim. Paris saponin VII-induced apoptosis in K562/ADR cells is associated with Akt/MAPK and the inhibition of P-gp. Paris saponin VII attenuates mitochondrial membrane potential, increases the expression of apoptosis-related proteins, such as Bax and cytochrome c, and decreases the protein expression levels of Bcl-2, caspase-9, caspase-3, PARP-1, and p-Akt. Paris saponin VII induces a robust autophagy in K562/ADR cells and provides a biochemical basis in the treatment of leukemia.

-
GC64579
PARP-1-IN-2
PARP-1-IN-2 (compound 11g) is a potent and BBB-penetrated PARP1 inhibitor, with an IC50 of 149 nM. PARP1-IN-2 shows significantly potent anti-proliferative activity against Human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cell line A549. PARP1-IN-2 can induce A549 cells apoptosis.
-
GC73272
PARP-1-IN-3
PARP-1-IN-3, a benzamide derivative, is a potent PARP-1 inhibitor with IC50 values of 0.25 nM and 2.34 nM for PARP-1 and PARP-2, respectively.

-
GC65927
PARP-2-IN-1
PARP-2-IN-1 is a potent and selective PARP-2 inhibitor with an IC50 of 11.5 nM.
-
GC68006
PARP1-IN-11

-
GC74078
PARP1-IN-29
PARP1-IN-29 is an orally active PARP-1 inhibitor with an IC50 value of 6.3 nM.

-
GC62275
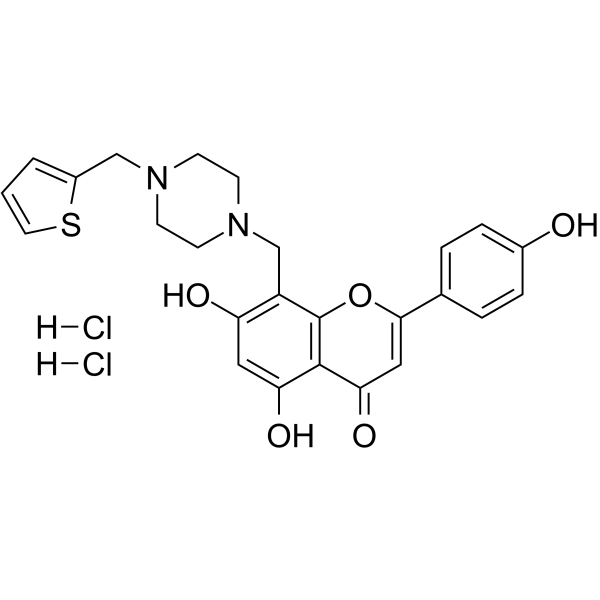
PARP1-IN-5 dihydrochloride
PARP1-IN-5 dihydrochloride is a low toxicity, orally active, potent and selective PARP-1 inhibitor (IC50 =14.7 nM). PARP1-IN-5 dihydrochloride can be used for the research of cancer.
-
GC69660
PARP1-IN-7
PARP1-IN-7 is an inhibitor of poly ADP-ribose polymerase-1 (PARP1), used as an anticancer agent.

-
GC64578
PARP1-IN-8
PARP1-IN-8 (compound 11c) is a potent and BBB-penetrated PARP1 inhibitor, with an IC50 of 97 nM. PARP1-IN-8 shows significantly potent anti-proliferative activity against Human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cell line A549.

-
GC69657
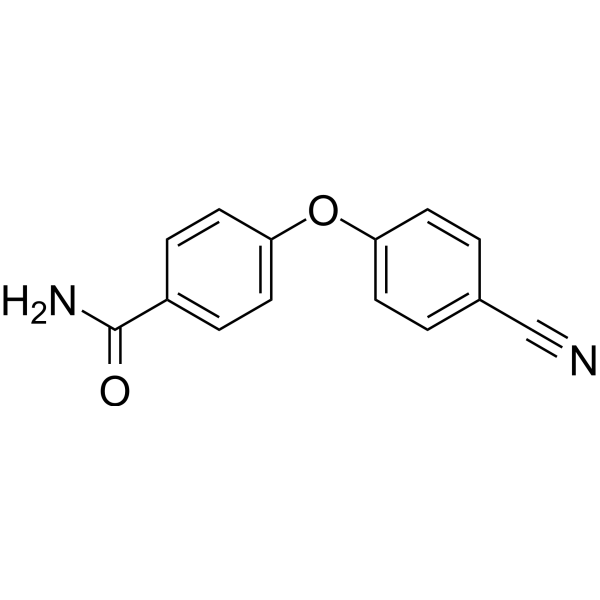
PARP10-IN-2
PARP10-IN-2 is an effective inhibitor of mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase PARP10, with an IC50 of 3.64 μM for human PARP10. It also inhibits PARP2 and PARP15, with IC50 values of 27 μM and 11 μM for human PARP2 and human PARP15, respectively.
-
GC69658
PARP10-IN-3
PARP10-IN-3 is a selective mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase PARP10 inhibitor with an IC50 of 480 nM for human PARP10. It also inhibits PARP2 and PARP15, with IC50 values of 1.7 μM for both human PARP2 and human PARP15.

-
GC68035
PARP10/15-IN-1

-
GC69655
PARP10/15-IN-2
PARP10/15-IN-2 (Compound 8h) is an effective dual inhibitor of PARP10 and PARP15, with IC50 values of 0.15 μM and 0.37 μM, respectively. It can enter cells and prevent apoptosis.

-
GC69656
PARP10/15-IN-3
PARP10/15-IN-3 (Compound 8a) is an effective dual inhibitor of PARP10 and PARP15, with IC50 values of 0.14 μM and 0.40 μM, respectively. It can enter cells and prevent apoptosis.

-
GC69659
PARP11 inhibitor ITK7
ITK7
PARP11 inhibitor ITK7 (ITK7) is an effective and selective inhibitor of PARP11. It can effectively inhibit PARP11 with an IC50 value of 14 nM. PARP11 inhibitor ITK7 can be used for research on cellular localization.

-
GC39302
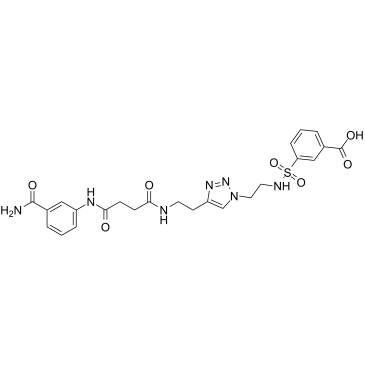
PARP14 inhibitor H10
PARP14 inhibitor H10, compound H 10, is a selective inhibitor against PARP14 (IC50=490 nM), over other PARPs (≈24 fold over PARP1). PARP14 inhibitor H10 induces caspase-3/7-mediated cell apoptosis.
-
GC69661
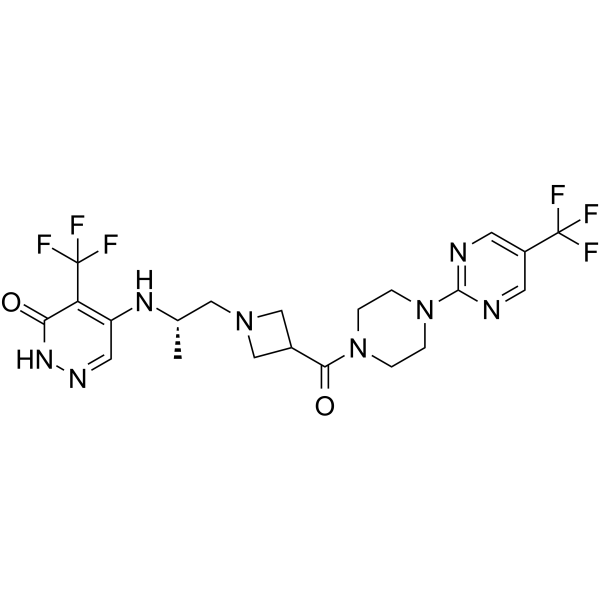
PARP7-IN-14
PARP7-IN-14 (I-1) is an effective selective PARP7 inhibitor with an IC50 value of 7.6 nM. PARP7-IN-14 has anti-cancer activity.
-
GC73566
PARP7-IN-15
PARP7-IN-15 (Compound 18) is a PARP7 inhibitor with IC50 of 0.56 nM, that has antitumor activity.

-
GC73639
PARP7-IN-16
PARP7-IN-16 (compound 36) is a potent, selective and orally active inhibitor of PARP-1/2/7, with IC50s of 0.94, 0.87 and 0.21 nM, respectively.

-
GC73640
PARP7-IN-16 free base
PARP7-IN-16 free base is the free base form of PARP7-IN-16.

-
GC14251
Picolinamide
poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase inhibitor

-
GC10995
PJ34
PJ-34;PJ 34
An inhibitor of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases
-
GC10145
PJ34 hydrochloride
PJ 34 Hydrochloride
An inhibitor of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases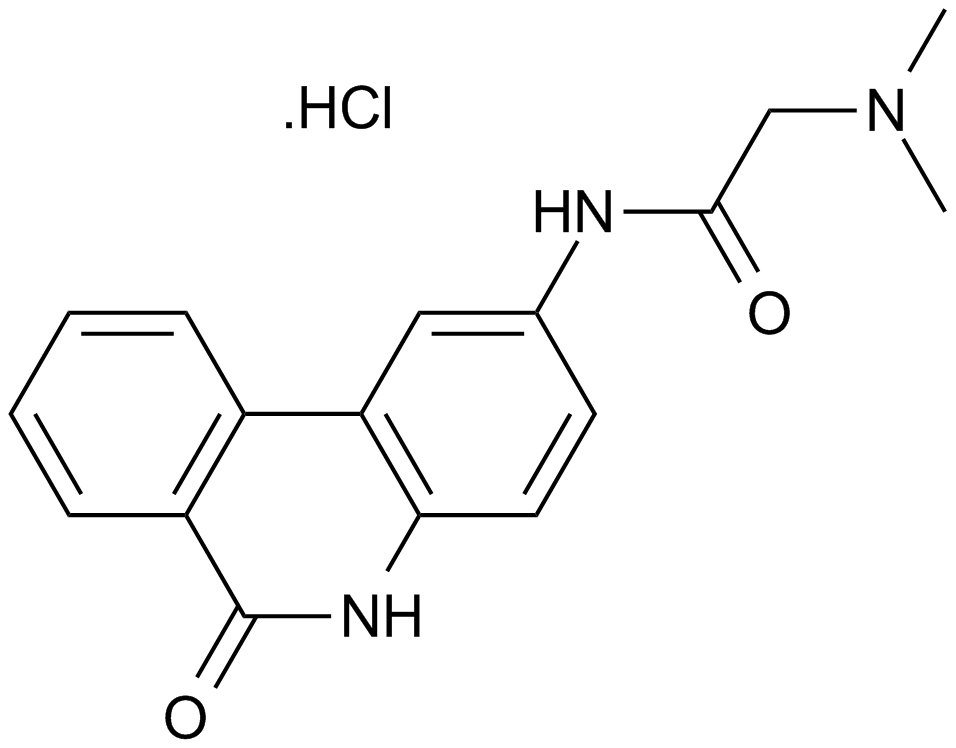
-
GC73943
Polθ/PARP-IN-1
Polθ/PARP-IN-1 (compound 25d) is a potent dual DNA polymerase theta (Polθ) and PARP inhibitor with IC50 values of 45.6, 5.4 nM, respectively.

-
GC65147
PROTAC PARP1 degrader
PROTAC PARP1 degrader is a PARP1 degrader based on MDM2 E3 ligand. It induces significant PARP1 cleavage and programmed cell death. PROTAC PARP1 degrader at 10 μM at 24 h inhibits MDA-MB-231 cell line with an IC50 of 6.12 μM.

-
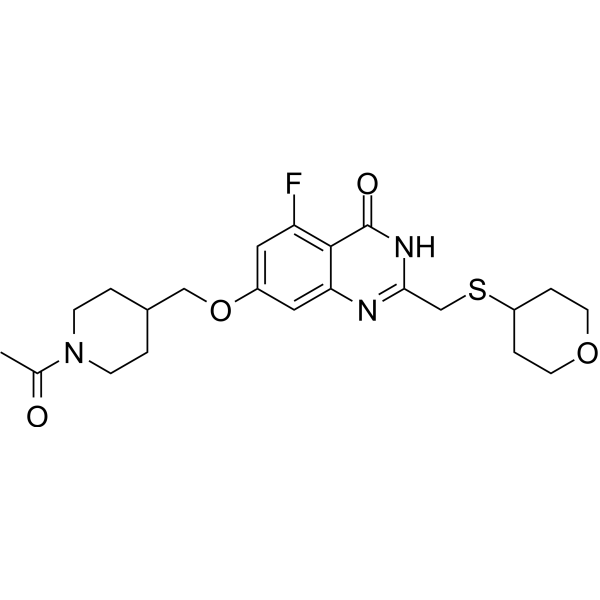
GC69804
RBN-3143
RBN-3143 is an effective NAD+ competitive catalytic PARP14 inhibitor with an IC50 value of 4 nM. RBN-3143 inhibits PARP14-mediated ADP-ribosylation and stabilizes PARP14 in cell lines. RBN-3143 is used for research on lung inflammation.
-
GC62473
RBN012759
RBN012759 is a potent, selective and orally active inhibitor of PARP14, with an IC50 of <3 nM.

-
GC72849
rel-PROTAC PARP1 degrader
rel-PROTAC PARP1 degrader is the relative configuration of ROTAC PARP1 degrader.

-
GC19505
RK-287107
RK-287107 is a potent and specific tankyrase inhibitor with IC50s of 14.3 and 10.6 nM for tankyrase-1 and tankyrase-2, respectively

-
GC13249
Rucaparib (free base)
AG014447
Rucaparib (free base) (AG014699) is an orally active, potent inhibitor of PARP proteins (PARP-1, PARP-2 and PARP-3) with a Ki of 1.4 nM for PARP1. Rucaparib (free base) is a modest hexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (H6PD) inhibitor. Rucaparib (free base) has the potential for castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) research.



