Immunology/Inflammation
The immune and inflammation-related pathway including the Toll-like receptors pathway, the B cell receptor signaling pathway, the T cell receptor signaling pathway, etc.
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a central role in host cell recognition and responses to microbial pathogens. TLR4 initially recruits TIRAP and MyD88. MyD88 then recruits IRAKs, TRAF6, and the TAK1 complex, leading to early-stage activation of NF-κB and MAP kinases [1]. TLR4 is endocytosed and delivered to intracellular vesicles and forms a complex with TRAM and TRIF, which then recruits TRAF3 and the protein kinases TBK1 and IKKi. TBK1 and IKKi catalyze the phosphorylation of IRF3, leading to the expression of type I IFN [2].
BCR signaling is initiated through ligation of mIg under conditions that induce phosphorylation of the ITAMs in CD79, leading to the activation of Syk. Once Syk is activated, the BCR signal is transmitted via a series of proteins associated with the adaptor protein B-cell linker (Blnk, SLP-65). Blnk binds CD79a via non-ITAM tyrosines and is phosphorylated by Syk. Phospho-Blnk acts as a scaffold for the assembly of the other components, including Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk), Vav 1, and phospholipase C-gamma 2 (PLCγ2) [3]. Following the assembly of the BCR-signalosome, GRB2 binds and activates the Ras-guanine exchange factor SOS, which in turn activates the small GTPase RAS. The original RAS signal is transmitted and amplified through the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, which including the serine/threonine-specific protein kinase RAF followed by MEK and extracellular signal related kinases ERK 1 and 2 [4]. After stimulation of BCR, CD19 is phosphorylated by Lyn. Phosphorylated CD19 activates PI3K by binding to the p85 subunit of PI3K and produce phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) from PIP2, and PIP3 transmits signals downstream [5].
Central process of T cells responding to specific antigens is the binding of the T-cell receptor (TCR) to specific peptides bound to the major histocompatibility complex which expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Once TCR connected with its ligand, the ζ-chain–associated protein kinase 70 molecules (Zap-70) are recruited to the TCR-CD3 site and activated, resulting in an initiation of several signaling cascades. Once stimulation, Zap-70 forms complexes with several molecules including SLP-76; and a sequential protein kinase cascade is initiated, consisting of MAP kinase kinase kinase (MAP3K), MAP kinase kinase (MAPKK), and MAP kinase (MAPK) [6]. Two MAPK kinases, MKK4 and MKK7, have been reported to be the primary activators of JNK. MKK3, MKK4, and MKK6 are activators of P38 MAP kinase [7]. MAP kinase pathways are major pathways induced by TCR stimulation, and they play a key role in T-cell responses.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) binds to the cytosolic domain of CD28, leading to conversion of PIP2 to PIP3, activation of PKB (Akt) and phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1), and subsequent signaling transduction [8].
References
[1] Kawai T, Akira S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors[J]. Nature immunology, 2010, 11(5): 373-384.
[2] Kawai T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity[J]. Immunity, 2011, 34(5): 637-650.
[3] Packard T A, Cambier J C. B lymphocyte antigen receptor signaling: initiation, amplification, and regulation[J]. F1000Prime Rep, 2013, 5(40.10): 12703.
[4] Zhong Y, Byrd J C, Dubovsky J A. The B-cell receptor pathway: a critical component of healthy and malignant immune biology[C]//Seminars in hematology. WB Saunders, 2014, 51(3): 206-218.
[5] Baba Y, Matsumoto M, Kurosaki T. Calcium signaling in B cells: regulation of cytosolic Ca 2+ increase and its sensor molecules, STIM1 and STIM2[J]. Molecular immunology, 2014, 62(2): 339-343.
[6] Adachi K, Davis M M. T-cell receptor ligation induces distinct signaling pathways in naive vs. antigen-experienced T cells[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2011, 108(4): 1549-1554.
[7] Rincón M, Flavell R A, Davis R A. The Jnk and P38 MAP kinase signaling pathways in T cell–mediated immune responses[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2000, 28(9): 1328-1337.
[8] Bashour K T, Gondarenko A, Chen H, et al. CD28 and CD3 have complementary roles in T-cell traction forces[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2014, 111(6): 2241-2246.
Targets for Immunology/Inflammation
- Apoptosis(303)
- 5-Lipoxygenase(18)
- Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase(2)
- TLR(98)
- Papain(1)
- PGDS(1)
- PGE synthase(24)
- SIKs(10)
- IκB/IKK(62)
- AP-1(3)
- KEAP1-Nrf2(42)
- NOD1(1)
- NF-κB(240)
- Interleukin Related(147)
- 15-lipoxygenase(2)
- Others(10)
- Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor(33)
- CD73(16)
- Complement System(52)
- Galectin(31)
- IFNAR(21)
- NO Synthase(75)
- NOD-like Receptor (NLR)(46)
- STING(101)
- Reactive Oxygen Species(446)
- FKBP(11)
- eNOS(5)
- iNOS(28)
- nNOS(20)
- Glutathione(54)
- Adaptive Immunity(216)
- Allergy(161)
- Arthritis(32)
- Autoimmunity(185)
- Gastric Disease(96)
- Immunosuppressants(37)
- Immunotherapeutics(5)
- Innate Immunity(579)
- Pulmonary Diseases(119)
- Reactive Nitrogen Species(54)
- Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators(50)
- Reactive Sulfur Species(26)
- BCL6(0)
- CD20(0)
- CD22(0)
- CD28(0)
- PSMA(0)
- FAP(0)
Products for Immunology/Inflammation
- Cat.No. Product Name Information
-
GC46583
3-Amino-2,6-Piperidinedione
α-Aminoglutarimide, 3-Aminoglutarimide, Glutamimide
An active metabolite of (±)-thalidomide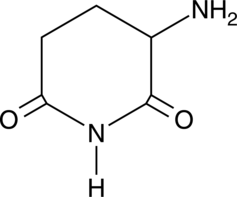
-
GC52129
3-Amino-5-hydroxybenzoic Acid
AHBA
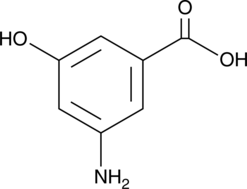
-
GC49849
3-Aminosalicylic Acid
3-ASA, NSC 285111
A salicylic acid derivative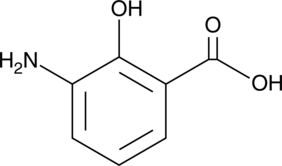
-
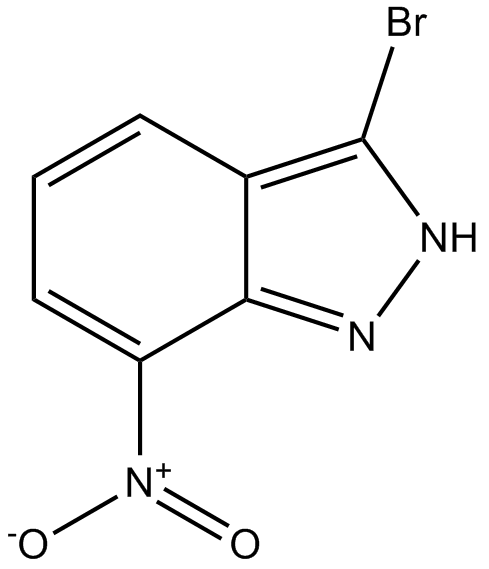
GC38208
3-Bromo-7-nitroindazole
A potent inhibitor of nNOS

-
GC10385
3-Bromo-7-nitroindazole
nNOS inhibitor
-
GC42259
3-Deaza-2'-deoxyadenosine
c3dA
3-Deaza-2'-deoxyadenosine strongly inhibits lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis with low cytotoxicity when applied at 100 μM.
-
GC62794
3-Demethylcolchicine
(–)-3-Demethylcolchicine
3-Demethylcolchicine, a colchicine metabolite, possesses a hydroxy-group on its carbon ring that could participate in radical scavenging and markedly inhibits the carrageenin edema.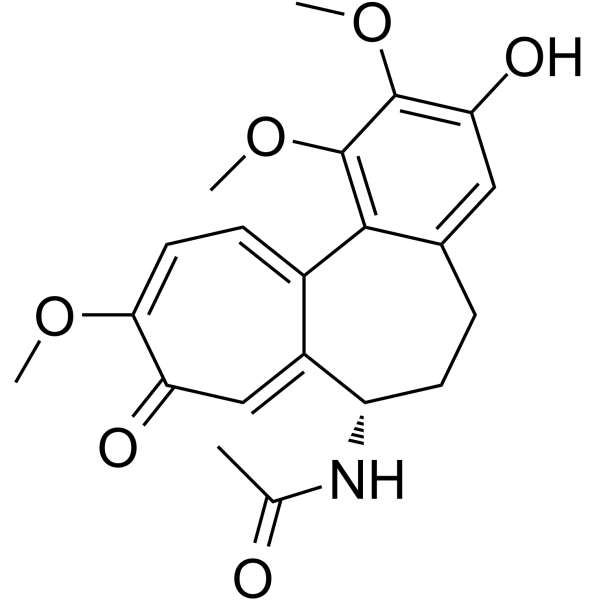
-
GC18655
3-hydroxy Decanoic Acid methyl ester
methyl 3-hydroxy Decanoate, 3-Hydroxy C10:0 methyl ester
3-hydroxy Decanoic acid methyl ester is a hydroxylated fatty acid methyl ester that has been found in methyl-branched poly(3-hydroxyalkanoate) (PHA) polymers produced by P.
-
GC42275
3-hydroxy Desloratidine
SCH 45581
3-hydroxy Desloratidine is a major metabolite of desloratadine , a tricyclic antagonist of the histamine H1 receptor.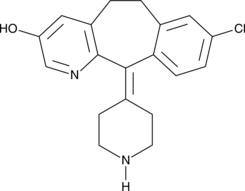
-
GC42276
3-hydroxy Docosanoic Acid
3-hydroxy Behenic Acid, β-hydroxy Docosanoic Acid, 3-hydroxy DCA, β-hydroxy DCA
3-hydroxy Docosanoic acid is a hydroxylated form of the 22-carbon saturated docosanoic acid.
-
GC45774
3-hydroxy Heptadecanoic Acid
β-hydroxy Heptadecanoic Acid, 3-hydroxy Heptadecylic Acid, 3-hydroxy Margaric Acid
A hydroxy fatty acid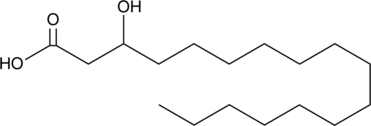
-
GC40474
3-hydroxy Lignoceric Acid
3-hydroxy Lignoceric acid is a hydroxylated form of the 24-carbon saturated lignoceric acid.
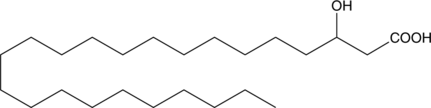
-
GC49847
3-hydroxy methyl Cefuroxime
Descarbamoyl Cefuroxime
3-hydroxy methyl Cefuroxime is a degradation product of Cefuroxime.
-
GC42280
3-hydroxy Myristic Acid methyl ester
methyl 3-hydroxy Myristate, (±)-3-hydroxy Myristic Acid methyl ester, methyl 3-hydroxy Tetradecanoate
3-hydroxy Myristic acid methyl ester is a hydroxylated fatty acid methyl ester that has been found in E.

-
GC42281
3-hydroxy Palmitic Acid
β-hydroxy Hexadecanoic Acid, β-hydroxy Palmitic Acid, DL-3-hydroxy Palmitic Acid
3-hydroxy Palmitic acid is a form of the 16:0 lipid palmitic acid.
-
GC42282
3-hydroxy Palmitic Acid methyl ester
3-hydroxy PAME, 3-hydroxy PA methyl ester
3-hydroxy Palmitic acid methyl ester (3-hydroxy PAME) is an esterized long-chain fatty acid involved in quorum sensing in R.
-
GC42286
3-hydroxy Stearic Acid
3-hydroxy Octadecanoic Acid, β-hydroxy Octadecanoic Acid, β-hydroxy Stearic Acid
3-hydroxy Stearic acid is a long-chain saturated fatty acid and intermediate in the production of 3-hydroxy octadecanedioic acid from stearic acid.
-
GC42288
3-hydroxy Tridecanoic Acid
β-hydroxy Tridecanoic Acid
3-hydroxy Tridecanoic acid is a 13-carbon saturated fatty acid found in bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS).
-
GC49819
3-Hydroxy-4-methyl-2(5H)-thiophenone
A degradation product of cefaclor

-
GC45336
3-hydroxy-DL-Kynurenine
DL-3-Hydroxykynurenine
3-hydroxy-DL-Kynurenine, ametabolite of tryptophan, is a potential endogenous neurotoxin whose increased levels have been described in several neurodegenerative disorders.
-
GC49364
3-Hydroxycoumarin
3-Coumarinol, NSC 74691
A coumarin with diverse biological activities
-
GC45337
3-Hydroxyterphenyllin
NSC 299113
3-Hydroxyterphenyllin is a metabolite of Aspergillus candidus.3-Hydroxyterphenyllin suppresses proliferation and causes cytotoxicity against A2780/CP70 and OVCAR-3 cells. 3-Hydroxyterphenyllin induces S phase arrest and apoptosis. 3-Hydroxyterphenyllin has the potential for the research of ovarian cancer.
-
GC31290
3-Indolepropionic acid
3-Indolepropionic Acid, NSC 3252, NSC 47831
A bacterial metabolite with antioxidant and neuroprotective activities
-
GC48457
3-keto Fusidic Acid
3-keto FA, 3-Oxofusidic Acid
An active metabolite of fusidic acid
-
GC64630
3-O-Acetyl-α-boswellic acid
ABA, 3-O-acetyl-α-Boswellic Acid, α-Boswellic Acid Acetate
3-O-Acetyl-α-boswellic acid suppresses T cell function.
-
GC48488
3-Oxobetulin Acetate
28-O-acetyl-3-Oxobetulin, 3-oxo-28-O-Acetylbetulin
A derivative of betulin
-
GC40692
3-Propylxanthine
D 4028, Enprofylline
3-Propylxanthine acts as a selective and competitive A2B receptor antagonist with the Ki of 7 μM.
-
GC45354
4β-Hydroxywithanolide E
NSC 212509
A withanolide with anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities
-
GC48437
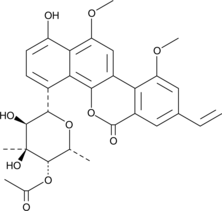
4'-Acetyl Chrysomycin A
A bacterial metabolite with antibacterial and anticancer activities
-
GC42406
4'-hydroxy Chalcone
2-Benzal-4'-hydroxyacetophenone, 2-Benzylidene-4'-hydroxyacetophenone, p-Cinnamoylphenol, NSC 242264
4'-hydroxy Chalcone is a chalcone metabolite with diverse biological activities.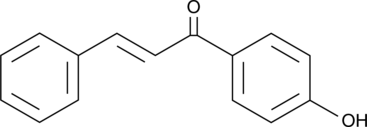
-
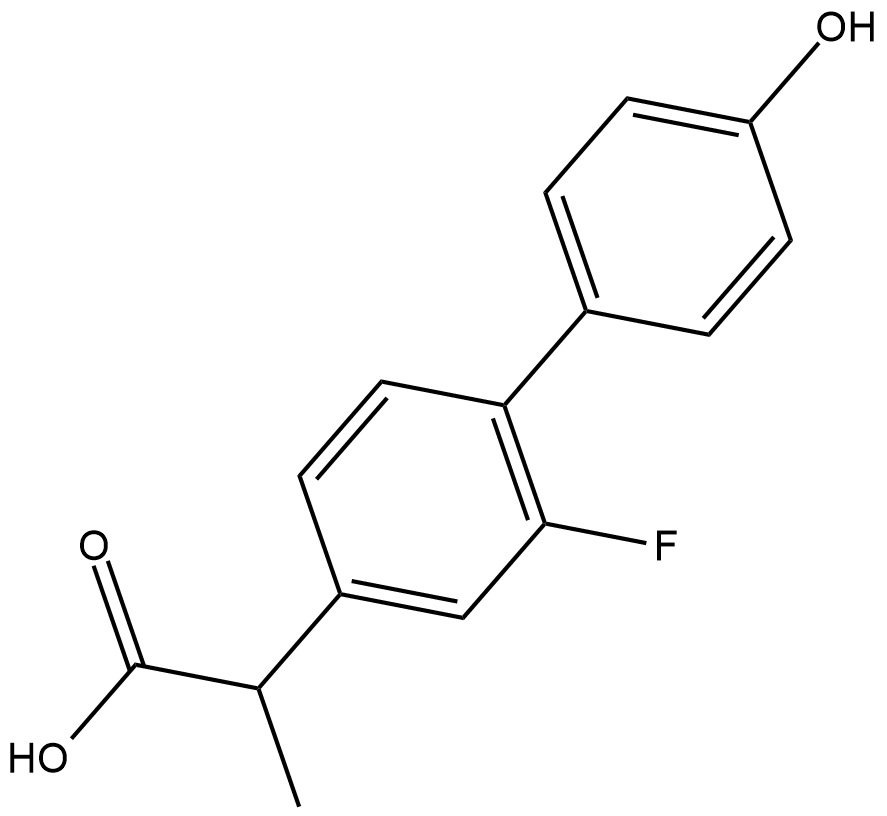
GC18527
4'-hydroxy Flurbiprofen
A major active metabolite of flurbiprofen
-
GC46608
4-(N-Boc-amino)piperidine
4-(t-Butoxycarbonylamino)piperidine, 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)piperidine
An organic building block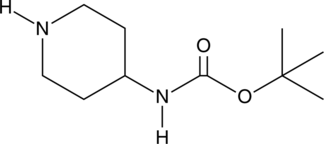
-
GC46609
4-(Phenylcarbonyl)benzoic Acid
4-Benzoylbenzoic Acid, 4-Carboxybenzophenone, NSC 37115, p-Benzoylbenzoic Acid, p-Carboxybenzophenone
A photooxidant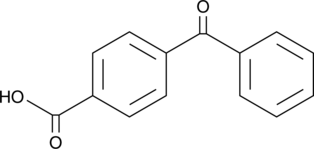
-
GC49337
4-Acetamidobenzenesulfonamide
APAS, N-Acetyl p-Aminobenzene Sulfonamide, N4-Acetyl Sulfanilamide, N-Acetylsulfanilamide, NSC 217, NSC 406839
A metabolite of asulam and sulfanilamide
-
GC42338
4-Aminobenzoic Acid hydrazide
4ABAH, Myeloperoxidase Inhibitor 1, NSC 640
4-Aminobenzoic Acid hydrazide is an irreversible MPO myeloperoxidase inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.3 μM.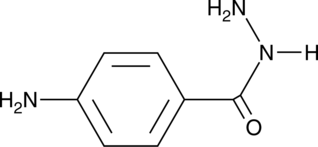
-
GC42351
4-carboxy TEMPO
4-Carboxyl-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-oxyl
4-carboxy TEMPO is a nitroxide and spin label.
-
GC46630
4-CPPC
A MIF-2 inhibitor
-
GC42369
4-Deoxypyridoxine (hydrochloride)
4-Deoxypyridoxine, DOP, 4-DPD
4-Deoxypyridoxine (4-DPD) is a vitamin B6 antimetabolite with diverse biological activities.
-
GC42373
4-epi Minocycline
4-EMC, Minocycline Impurity A
4-epi Minocycline is the main degradation product of and a potential impurity in commercial preparations of minocycline.
-
GC42374
4-epi-Chlortetracycline (hydrochloride)
7-chloro-2-Naphthacenecarboxamide
Chlortetracycline is an analog of tetracycline, a broad spectrum antibiotic.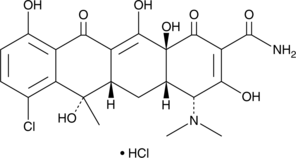
-
GC42401
4-hydroperoxy Cyclophosphamide
4-OOH-CY
4-hydroperoxy Cyclophosphamide, the active metabolite of cyclophosphamide, can cross-link DNA and induce T cell apoptosis independently of caspase receptor activation. It also activates the mitochondrial death pathway through the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS).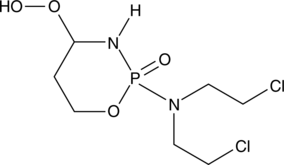
-
GC18858
4-hydroxy Alternariol
4-hydroxy AOH, 4-OH AOH
4-hydroxy Alternariol is a metabolite of the mycotoxin alternariol formed through cytochrome P450 (CYP450) metabolism.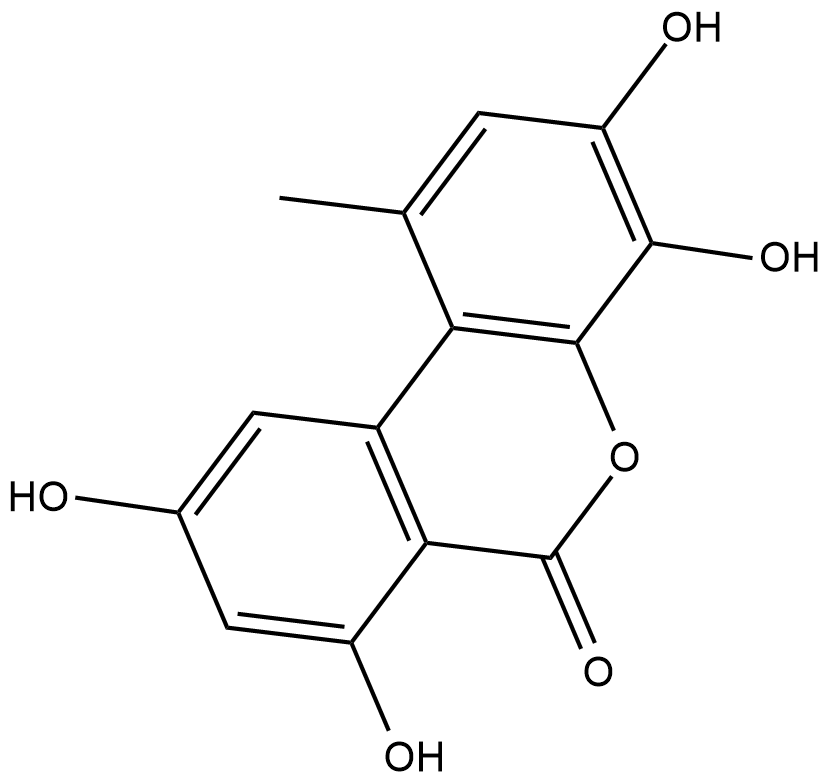
-
GC49575
4-hydroxy Omeprazole sulfide
4-hydroxy OMEP sulfide, 4-hydroxy OMP sulfide, 4-hydroxy OMZ sulfide
A metabolite of omeprazole
-
GA20418
4-Hydroxy-hippuric acid
p-Hydroxyhippuric Acid; para-Hydroxyhippuric Acid
Polyphenol metabolite.
-
GC38663
4-Hydroxychalcone
2-Benzal-4'-hydroxyacetophenone, 2-Benzylidene-4'-hydroxyacetophenone, p-Cinnamoylphenol, NSC 242264
A chalcone metabolite with diverse biological activities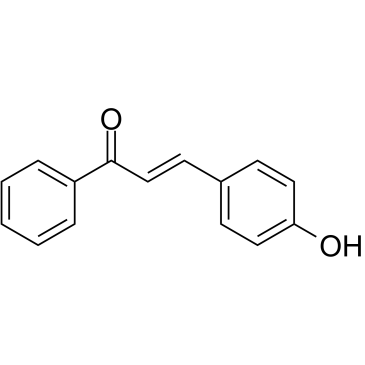
-
GC33815
4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid
4-HPAA, p-HPAA, para-HPAA, p-Hydroxyphenylacetic Acid, para-Hydroxyphenylacetic Acid, NSC 25066, NSC 27460
A phenolic acid with anti-inflammatory activity
-
GC18853
4-isocyanato TEMPO
4-isocyanato TEMPO is a spin labeling reagent used to label the 2'-position in RNA.

-
GC72066
4-Methyl-6-phenyl-2H-pyranone
4-Methyl-6-phenyl-2H-pyranone can be used for the synthesis of N-hydroxypyridone derivatives, which can protect astrocytes against hydrogen peroxide-induced toxicity via improved mitochondrial functionality.
-
GC41299
4-Methylumbelliferyl Caprylate
MUCAP, 4-MU Caprylate
4-Methylumbelliferyl caprylate (MUCAP) is a fluorogenic substrate for C8 esterase.
-
GC42448
4-MUNANA (sodium salt)
4-MUNANA, Neu5Ac-α-4MU, Sodium 2-(4-methylumbelliferyl)-N-acetylneuraminate, 4-Methylumbelliferyl-N-acetyl-α-D-Neuraminic Acid
4-Methylumbelliferyl-N-acetyl-α-D-Neuraminic Acid (sodium salt) is a fluorescent substrate used for neuraminidase activity assay.
-
GC42461
4-Nitrophenyl β-D-Cellobioside
p-Nitrophenyl β-D-Cellobioside, para-Nitrophenyl β-D-Cellobioside
4-Nitrophenyl β-D-cellobioside is a disaccharide and an enzyme substrate.
-
GC46672
4-Nitrophenyl Palmitate
p-Nitrophenyl Palmitate, para-Nitrophenyl Palmitate, pNpp
A colorimetric lipase and esterase substrate
-
GC35143
4-O-Methyl honokiol
NSC 293101, 4-Methoxyhonokiol
A phenol with diverse biological activities
-
GC31648
4-Octyl Itaconate
4-Octyl Itaconate (4-OI) is a cell-permeable itaconate derivative.
-
GC46673
4-octynyl Itaconate
ITalk
4-octynyl Itaconate (ITalk) is a specific bioorthogonal probe for quantitative and site-specific chemoproteomic profiling of Itaconation in living cells.
-
GC49127
4-oxo Cyclophosphamide
4-keto CP, 4-keto Cyclophosphamide, NSC 139488, 4-oxo CP
An inactive metabolite of cyclophosphamide
-
GC49244
4-oxo Isotretinoin
Ro 22-6595
An active metabolite of isotretinoin
-
GC40477
4-Thiouracil
2-hydroxy-4-Mercaptopyrimidine, NSC 43288, 4-Thiopyrimidin-2-one, 4-TU
4-Thiouracil is a site-specific, photoactivatable probe used to detect RNA structures and nucleic acid-nucleic acid contacts.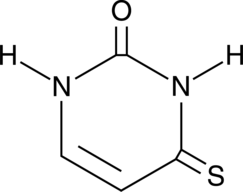
-
GC71507
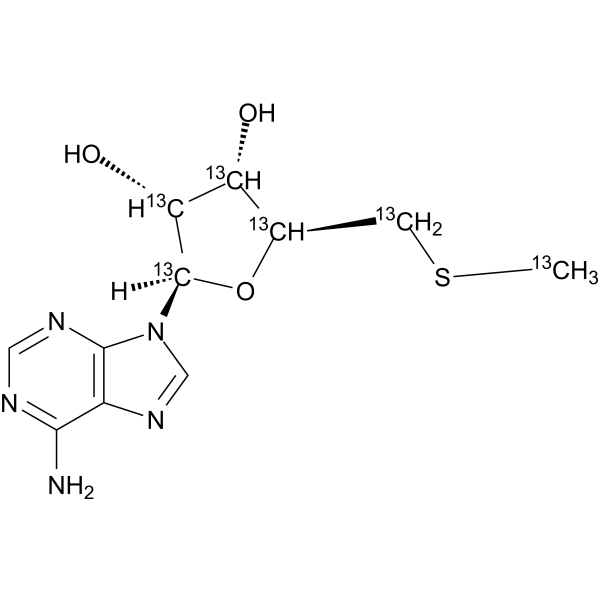
5'-Methylthioadenosine-13C6
5'-Methylthioadenosine-13C6 is the 13C-labeled 5'-Methylthioadenosine.
-
GC18582
5'-hydroxy Meloxicam
A metabolite of meloxicam

-
GC48381
5'-pApA (sodium salt)
c-di-AMP Control, Cyclic di-AMP Negative Control
A linearized form of cyclic di-AMP
-
GC48375
5'-pGpG (sodium salt)
c-di-GMP Control, Cyclic di-GMP Negative Control
A linearized form of cyclic di-GMP
-
GC49339
5(6)-Carboxy-2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate
CDFDA
An oxidant-sensitive fluorescent probe
-
GC41126
5(S),12(S)-DiHETE
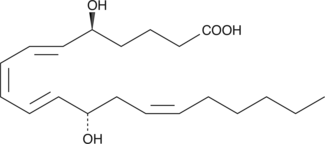
5(S),12(S)-DiHETE is a natural bioactive lipid derived from arachidonic acid.
-
GC41127
5(S),15(S)-DiHETE
5(S),15(S)-DiHETE is synthesized by 15-LO from 5(S)-HETE.

-
GC40782
5(Z),11(Z),14(Z)-Eicosatrienoic Acid
5,11,14,20:3, Sciadonic Acid
5(Z),11(Z),14(Z)-Eicosatrienoic acid is a polyunsaturated fatty acid found in various natural sources including maritime pine (Pinus pinaster) seed oil (MPSO), gymnospermae leaves and seeds, and freshwater gastropods.
-
GC46075
5,6-dimethyl-2-Thiouracil
Dimethylthiouracil, NSC 60687
A heterocyclic building block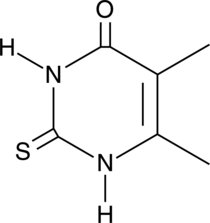
-
GC48815
5,7,8-Trimethoxydictamnine
Acronycidine, NSC 30619
A quinoline alkaloid with antimalarial activity
-
GC52091
5,7-Dichlorothiazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine
A building block
![5,7-Dichlorothiazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine Chemical Structure 5,7-Dichlorothiazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine Chemical Structure](/media/struct/GC5/GC52091.png)
-
GC52227
5-(3',4'-Dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-Valerolactone
(±)-δ-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-Valerolactone, 5-(3',4'-Dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-VL
An active metabolite of various polyphenols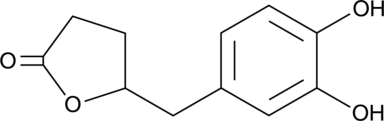
-
GC40527
5-(Hydroxymethyl)-2'-deoxyuridine
5-(Hydroxymethyl)-2'-deoxyuridine is a nucleoside analog with anticancer and antiviral activities.

-
GC68562
5-Aminolevulinic acid-13C-1 hydrochloride
5-ALA-13C-1 hydrochloride; δ-Aminolevulinic acid-13C-1 hydrochloride; 5-Amino-4-oxopentanoic acid-13C-1 hydrochloride
5-Aminolevulinic acid-13C-1 (5-ALA-13C-1) hydrochloride is a 13C-labeled form of 5-Aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride. 5-Aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride (5-ALA hydrochloride) is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of heme in the body and serves as a precursor to porphyrins.
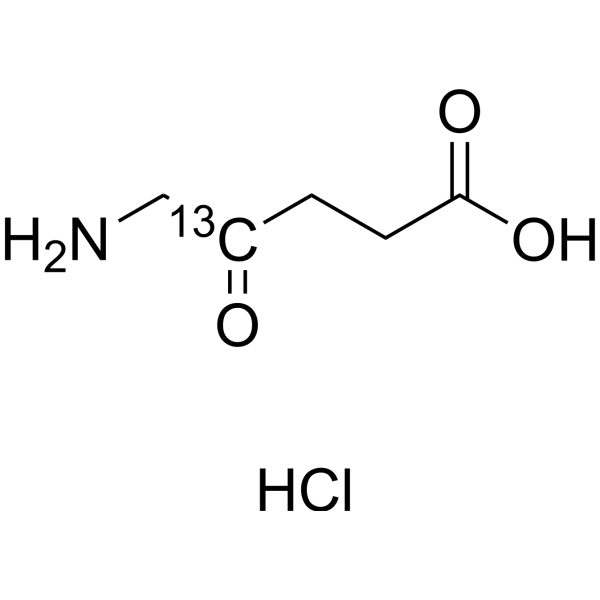
-
GC71833
5-Aminolevulinic acid-d2 hydrochloride
5-Aminolevulinic acid-d2 (hydrochloride) is deuterium labeled 5-Aminolevulinic acid (hydrochloride).
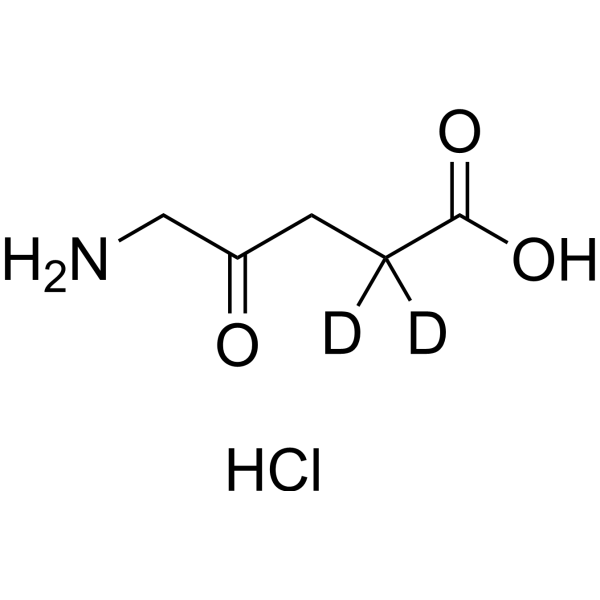
-
GC52413
5-Aminosalicylic Acid-d7
5-ASA-d7, Mesalamine-d7, Mesalazine-d7
An internal standard for the quantification of 5-aminosalicylic acid
-
GC49827
5-Androstenetriol
Δ5-AT
An active metabolite of DHEA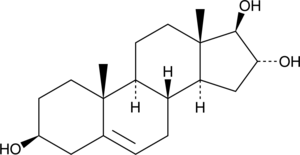
-
GC45357
5-Chlorouracil

-
GC49233
5-Feruloylquinic Acid
5-FQA
A chlorogenic acid with antioxidant activity
-
GC39760
5-Galloylquinic acid
5-Galloylquinic acid, an main scavenger of the reactive oxygen species (ROS) in green tea.

-
GC46033
5-Heneicosylresorcinol
An alkylresorcinol

-
GC42549
5-hydroxy Thiabendazole
5-OH TBZ
5-hydroxy Thiabendazole (5-OH TBZ) is a major metabolite of the anthelmintic thiabendazole.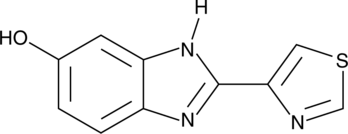
-
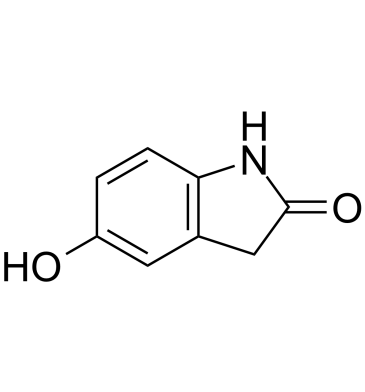
GC61638
5-Hydroxyoxindole
5-Hydroxyoxindole is a structural analog of uric acid.
-
GC46705
5-Methoxycanthinone
5-Methoxycanthin-6-one, NSC 88929
5-Methoxycanthinone is an orally active inhibitor of Leishmania strains.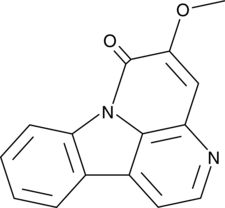
-
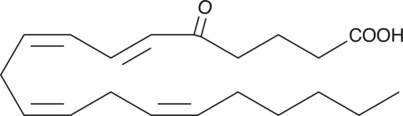
GC40380
5-OxoETE
5-KETE
5-OxoETE is a polyunsaturated keto acid formed by the oxidation of 5-HETE in human neutrophils by a specific dehydrogenase.
-
GC46712
5-Phenyllevulinic Acid
5-Phenyl-4-Oxopentanoic Acid
A fungal metabolite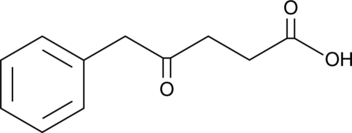
-
GC46079
5-Tricosylresorcinol
5-Tricosylresorcinolthe is the first cyst lipid.

-
GC49676
6β-hydroxy Budesonide
A metabolite of budesonide

-
GC49629
6β-hydroxy Prednisolone
A metabolite of prednisolone

-
GC19536
6'-Sialyllactose Sodium Salt
6'-N-Acetylneuraminyl-D-lactose
6'-Sialyllactose (sodium), a predominant milk oligosaccharide, reduces the internalisation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in human pneumocytes.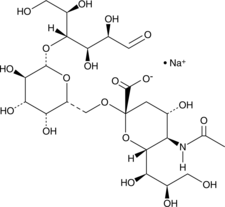
-
GC45772
6(5H)-Phenanthridinone
NSC 11021, NSC 40943, NSC 61083
An inhibitor of PARP1 and 2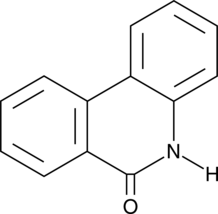
-
GC41424
6(S)-Lipoxin A4
5(S),6(S)-Lipoxin A4, 6-epi-Lipoxin A4, 6(S)-LXA4, 5(S),6(S),15(S)-TriHETE
The lipoxins are trihydroxy fatty acids containing a 7,9,11,13-conjugated tetraene.
-
GC46721
6-Chloro-2-fluoropurine
NSC 37363
A heterocyclic building block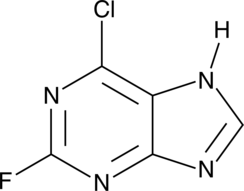
-
GC49551
6-Chloropurine Riboside
NSC 4910
A nucleoside precursor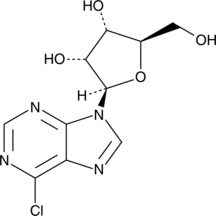
-
GC49749
6-Deoxypenciclovir
BRL 42359
An inactive metabolite of famciclovir
-
GC45955
6-Ethyl-2,7-dimethoxyjuglone
2,7-Dimethoxy-6-ethyljuglone
A fungal metabolite with antimicrobial activity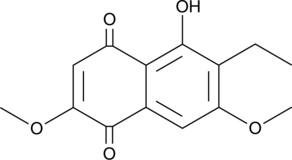
-
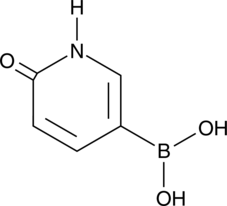
GC46724
6-Hydroxypyridin-3-ylboronic Acid
A heterocyclic building block
-
GC49235
6-Methylmercaptopurine
6-MMP, 6-(Methylthio)purine, NSC 20105, SQ 8,343
A metabolite of 6-mercaptopurine
-
GC49488
6-Methylmercaptopurine-d3
6-MMP-d3, 6-(Methylthio)purine-d3
An internal standard for the quantification of 6-MMP
-
GC49864
6-Methylpterin
6-MPT
A derivative of folic acid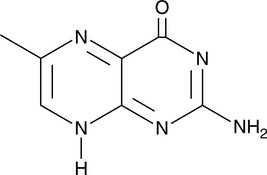
-
GC45715
6-Prenylindole
A bacterial metabolite

-
GC18776
6α-hydroxy Cholesterol
6α-OHC
6α-hydroxy Cholesterol is an oxysterol that increases superoxide anion production in SK-N-BE cells when used at concentrations of 50 and 100 μM.



