Immunology/Inflammation
The immune and inflammation-related pathway including the Toll-like receptors pathway, the B cell receptor signaling pathway, the T cell receptor signaling pathway, etc.
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a central role in host cell recognition and responses to microbial pathogens. TLR4 initially recruits TIRAP and MyD88. MyD88 then recruits IRAKs, TRAF6, and the TAK1 complex, leading to early-stage activation of NF-κB and MAP kinases [1]. TLR4 is endocytosed and delivered to intracellular vesicles and forms a complex with TRAM and TRIF, which then recruits TRAF3 and the protein kinases TBK1 and IKKi. TBK1 and IKKi catalyze the phosphorylation of IRF3, leading to the expression of type I IFN [2].
BCR signaling is initiated through ligation of mIg under conditions that induce phosphorylation of the ITAMs in CD79, leading to the activation of Syk. Once Syk is activated, the BCR signal is transmitted via a series of proteins associated with the adaptor protein B-cell linker (Blnk, SLP-65). Blnk binds CD79a via non-ITAM tyrosines and is phosphorylated by Syk. Phospho-Blnk acts as a scaffold for the assembly of the other components, including Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk), Vav 1, and phospholipase C-gamma 2 (PLCγ2) [3]. Following the assembly of the BCR-signalosome, GRB2 binds and activates the Ras-guanine exchange factor SOS, which in turn activates the small GTPase RAS. The original RAS signal is transmitted and amplified through the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, which including the serine/threonine-specific protein kinase RAF followed by MEK and extracellular signal related kinases ERK 1 and 2 [4]. After stimulation of BCR, CD19 is phosphorylated by Lyn. Phosphorylated CD19 activates PI3K by binding to the p85 subunit of PI3K and produce phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) from PIP2, and PIP3 transmits signals downstream [5].
Central process of T cells responding to specific antigens is the binding of the T-cell receptor (TCR) to specific peptides bound to the major histocompatibility complex which expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Once TCR connected with its ligand, the ζ-chain–associated protein kinase 70 molecules (Zap-70) are recruited to the TCR-CD3 site and activated, resulting in an initiation of several signaling cascades. Once stimulation, Zap-70 forms complexes with several molecules including SLP-76; and a sequential protein kinase cascade is initiated, consisting of MAP kinase kinase kinase (MAP3K), MAP kinase kinase (MAPKK), and MAP kinase (MAPK) [6]. Two MAPK kinases, MKK4 and MKK7, have been reported to be the primary activators of JNK. MKK3, MKK4, and MKK6 are activators of P38 MAP kinase [7]. MAP kinase pathways are major pathways induced by TCR stimulation, and they play a key role in T-cell responses.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) binds to the cytosolic domain of CD28, leading to conversion of PIP2 to PIP3, activation of PKB (Akt) and phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1), and subsequent signaling transduction [8].
References
[1] Kawai T, Akira S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors[J]. Nature immunology, 2010, 11(5): 373-384.
[2] Kawai T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity[J]. Immunity, 2011, 34(5): 637-650.
[3] Packard T A, Cambier J C. B lymphocyte antigen receptor signaling: initiation, amplification, and regulation[J]. F1000Prime Rep, 2013, 5(40.10): 12703.
[4] Zhong Y, Byrd J C, Dubovsky J A. The B-cell receptor pathway: a critical component of healthy and malignant immune biology[C]//Seminars in hematology. WB Saunders, 2014, 51(3): 206-218.
[5] Baba Y, Matsumoto M, Kurosaki T. Calcium signaling in B cells: regulation of cytosolic Ca 2+ increase and its sensor molecules, STIM1 and STIM2[J]. Molecular immunology, 2014, 62(2): 339-343.
[6] Adachi K, Davis M M. T-cell receptor ligation induces distinct signaling pathways in naive vs. antigen-experienced T cells[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2011, 108(4): 1549-1554.
[7] Rincón M, Flavell R A, Davis R A. The Jnk and P38 MAP kinase signaling pathways in T cell–mediated immune responses[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2000, 28(9): 1328-1337.
[8] Bashour K T, Gondarenko A, Chen H, et al. CD28 and CD3 have complementary roles in T-cell traction forces[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2014, 111(6): 2241-2246.
Targets for Immunology/Inflammation
- Apoptosis(303)
- 5-Lipoxygenase(18)
- Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase(2)
- TLR(98)
- Papain(1)
- PGDS(1)
- PGE synthase(24)
- SIKs(10)
- IκB/IKK(62)
- AP-1(3)
- KEAP1-Nrf2(42)
- NOD1(1)
- NF-κB(240)
- Interleukin Related(147)
- 15-lipoxygenase(2)
- Others(10)
- Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor(33)
- CD73(16)
- Complement System(52)
- Galectin(31)
- IFNAR(21)
- NO Synthase(75)
- NOD-like Receptor (NLR)(46)
- STING(101)
- Reactive Oxygen Species(446)
- FKBP(11)
- eNOS(5)
- iNOS(28)
- nNOS(20)
- Glutathione(54)
- Adaptive Immunity(216)
- Allergy(161)
- Arthritis(32)
- Autoimmunity(185)
- Gastric Disease(96)
- Immunosuppressants(37)
- Immunotherapeutics(5)
- Innate Immunity(579)
- Pulmonary Diseases(119)
- Reactive Nitrogen Species(54)
- Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators(50)
- Reactive Sulfur Species(26)
- BCL6(0)
- CD20(0)
- CD22(0)
- CD28(0)
- PSMA(0)
- FAP(0)
Products for Immunology/Inflammation
- Cat.No. Product Name Information
-
GC46869
Arachidic Acid-d3
Arachic Acid-d3, Arachidate-d3, Eicosanoate-d3, Icosanoic Acid-d3
An internal standard for the quantification of arachidic acid
-
GC42837
Arachidonic Acid-biotin
Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.

-
GC52514
Arachidonic Acid-d11 ethyl ester
C20:4 (cis-5,8,11,14)-d11 ethyl ester, Ethyl Arachidonate-d11, Ethyl (cis-5,8,11,14)-eicosatetraenoate-d11
An internal standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid ethyl ester
-
GC46872
Arachidonic Acid-d5
AA-d5
An internal standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid
-
GC46878
Aranciamycin
NSC 369226
A fungal metabolite with diverse biological activities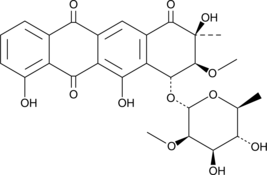
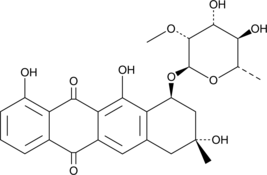
-
GC48472
Aranciamycin A
An antibiotic
-
GC40116
Aranorosin
Aranorosin is a fungal metabolite originally isolated from P.

-
GC69582
ARC186
ARC 186 is a nucleic acid adapter that serves as an efficient complement inhibitor by blocking the activation of C5 catalyzed by convertase.

-
GC65163
Ardisiacrispin B
Ardisiacrispin B displays cytotoxic effects in multi-factorial drug resistant cancer cells via ferroptotic and apoptotic cell death.

-
GC35385
Arglabin
A sesquiterpene lactone

-
GC52332
Arimoclomol
BRX-220
A co-inducer of heat shock proteins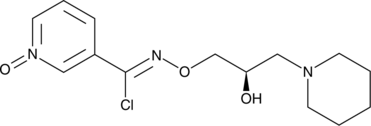
-
GN10579
Aristolochic Acid A
Aristolochic Acid A, Aristolochic Acid I, NSC 11926, NSC 50413, Tardolyt

-
GC46005
Arjunolic Acid
A triterpene with diverse biological activities

-
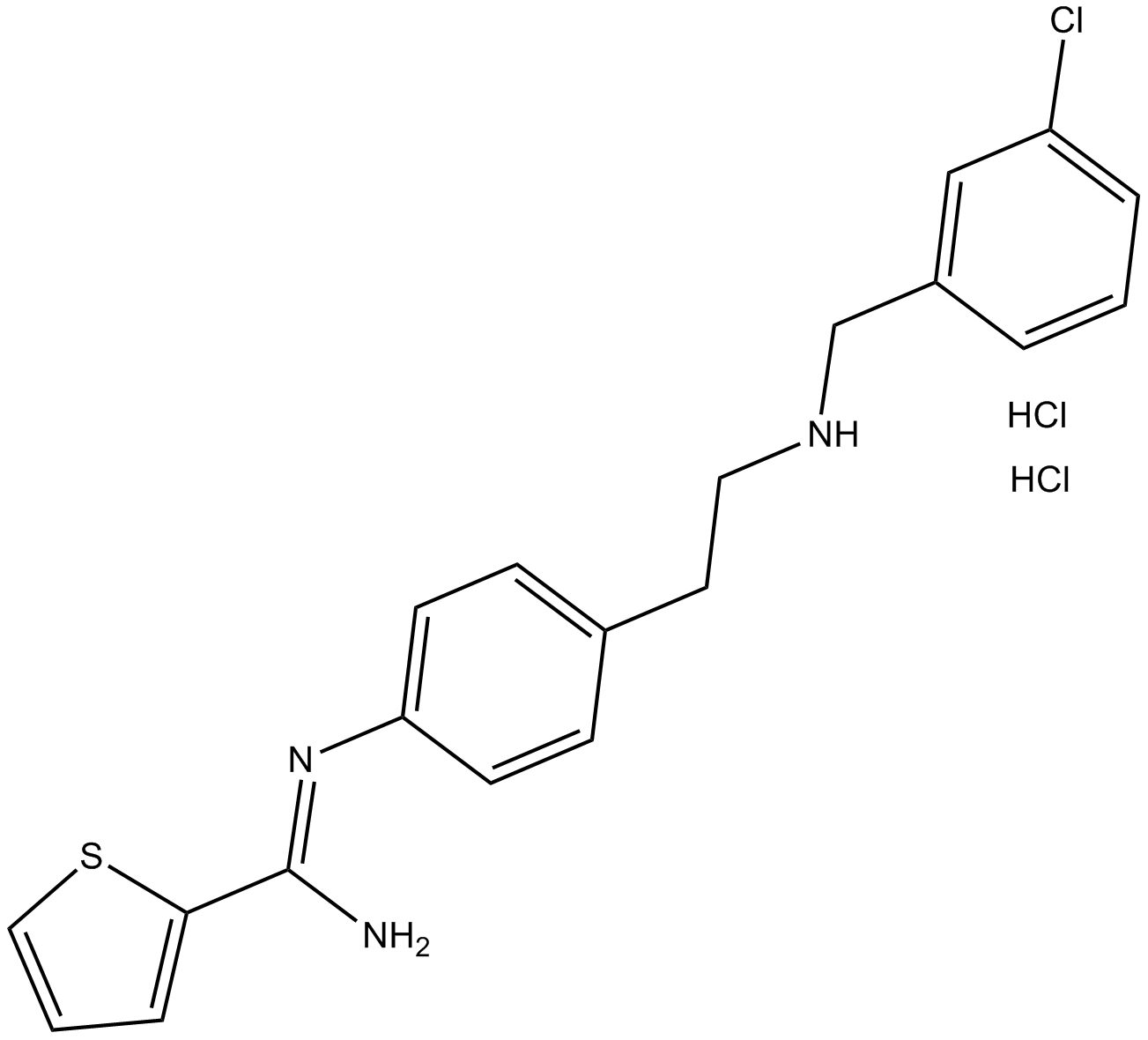
GC14802
ARL 17477 dihydrochloride
Selective nNOS inhibitor
-
GC35394
Armepavine
Armepavine, an active compound from Nelumbo nucifera, exerts not only anti-inflammatory effects on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells, but also immunosuppressive effects on T lymphocytes and on lupus nephritic mice.

-
GC61796
Armillarisin A
Armillarisin A has the potential for the ulcerative colitis (UC) study.

-
GC33070
ARN-3236
An inhibitor of SIK2
-
GC70612
Arochlor 1254
Arochlor 1254 is a polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) mixture with biphenyl and 54% chlorine.

-
GC49103
Aromadendrene
(+)-Aromadendrene, 10(14)-Aromadendrene
A sesquiterpene with diverse biological activities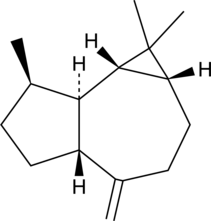
-
GC46881
Artemether-d3
(+)-Artemether-d3
An internal standard for the quantification of artemether
-
GC46882
Artemisinin-d3
Qinghaosu-d3; NSC 369397-d3
An internal standard for the quantification of artemisinin
-
GC45790
Artesunate-d4
Artesunic Acid-d4
An internal standard for the quantification of artesunate
-
GC17659
AS 101
AS101
AS 101 (AS101), an immunomodulatory tellurium compound, is a potent IL-1β inhibitor.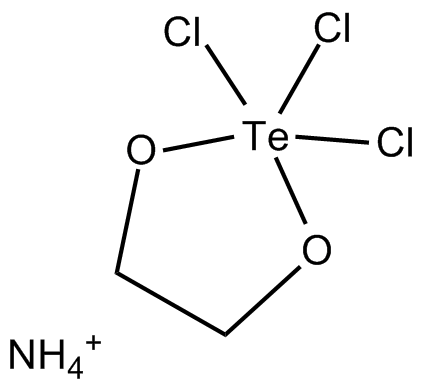
-
GC46883
AS-2077715
An inhibitor of fungal complex III
-
GC35401
Asatone
Asatone is an active component isolated from Radix et Rhizoma Asari, with anti-inflammatory effect via activation of NF-κB and donwn regulation of p-MAPK (ERK, JNK and p38) pathways.
-
GC12070
Ascorbic acid
Ascorbate, NSC 33832, NSC 218455, Vitamin C
An electron donor
-
GN10534
Asiaticoside
Ba 2742, NSC 36002, NSC 166062

-
GC71258
ASK1-IN-4
ASK1-IN-4 (Compound 17) is an ASK1 inhibitor (IC50=0.2 μM).
-
GC18978
Aspartocin D
Aspartocin D is a lipopeptide antibiotic originally isolated from S.

-
GC46089
Asperfuran
(-)-Asperfuran
A fungal metabolite
-
GC42858
Aspergillin PZ
Aspergillin PZ is a fungal metabolite originally isolated from A.
-
GC40682
Asperlactone
Asperlactone is a nematicidal, insecticidal, antibacterial, and antifungal polyketide metabolite produced from A.

-
GC35411
Asperuloside
An iridoid glycoside with diverse biological activities

-
GC35412
Asperulosidic Acid
Asperulosidic Acid (ASPA), a bioactive iridoid glycoside, is extracted from the herbs of Hedyotis diffusa Willd.

-
GC42860
Aspochalasin D
Aspochalasin D is a co-metabolite originally isolated from A.

-
GC46886
Aspyrone
A fungal metabolite with diverse biological activities

-
GC68700
ASR-488
ASR-488 can activate mRNA binding protein CPEB1, induce apoptosis and inhibit the growth of bladder cancer cells.
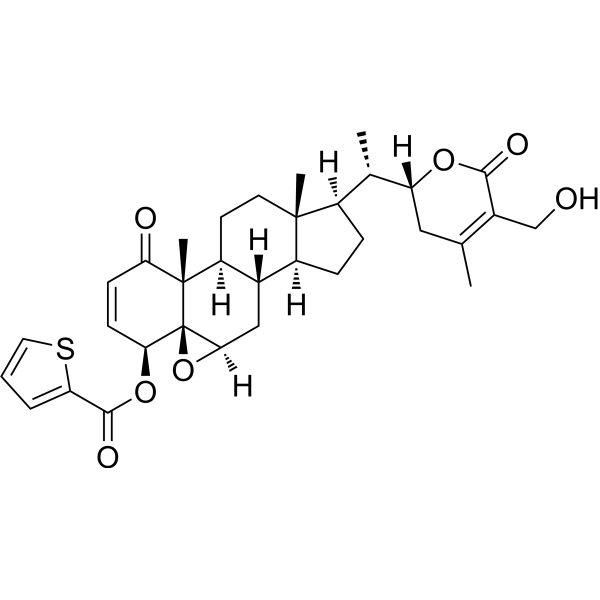
-
GC31350
Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin, the red dietary carotenoid, is an orally effective and potent antioxidant.

-
GC68702
Astegolimab
Astegolimab (MSTT 1041A; RG 6149) is a human IgG2 monoclonal antibody that can block IL-33 signaling by targeting the IL-33 receptor ST2. Astegolimab has potential for use in research on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).

-
GC41640
Asterriquinol D dimethyl ether
Asterriquinol D dimethyl ether is a fungal metabolite that has been found in A.
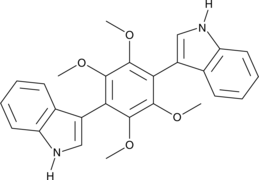
-
GN10415
Astilbin
Taxifolin 3-O-rhamnoside

-
GC42863
Asukamycin
AM1042, Asukamycin A
Asukamycin is polyketide isolated from the S.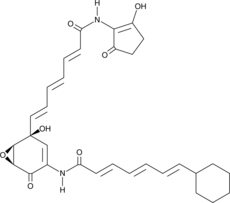
-
GC32457
Asymmetric dimethylarginine
ADMA, Asymmetric dimethylarginine
An endogenous NOS inhibitor
-
GC46091
Aszonapyrone A
A meroditerpene fungal metabolite with diverse biological activities

-
GC39554
AT2 receptor agonist C21
Compound 21
An AT2 receptor agonist
-
GC62334
AT791
AT791 is a potent and orally bioavailable TLR7 and TLR9 inhibitor.

-
GC46887
Atazanavir-d6
An internal standard for the quantification of atazanavir

-
GC12537
ATB-337
ACS 15,S-Diclofenac
ATB-337 is a hybrid molecule of an H2S donor and the NSAID diclofenac.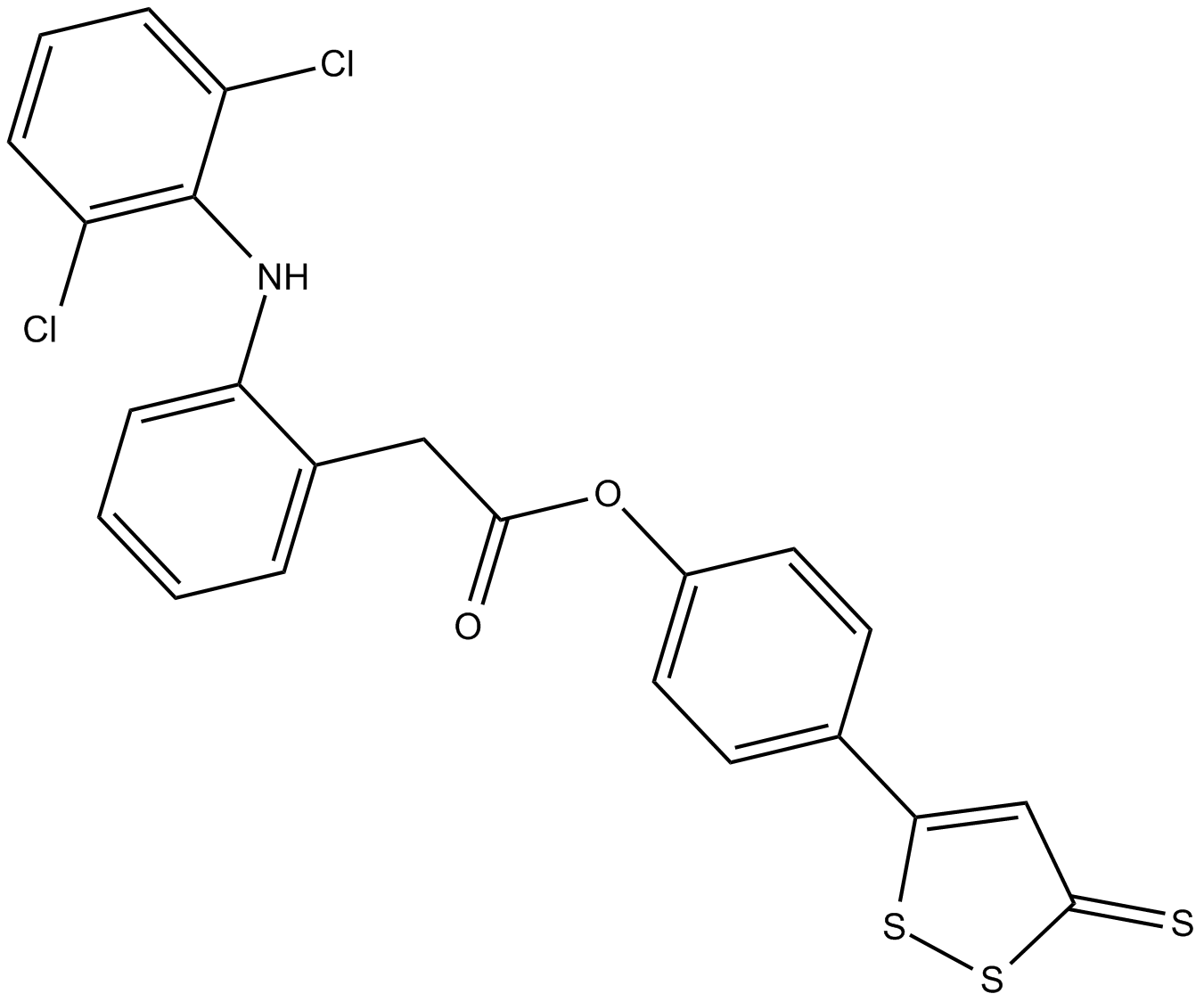
-
GC16245
ATB-343
hybrid molecule of an H2S donor and the NSAID indomethacin

-
GC46892
ATRA-BA Hybrid
A prodrug form of all-trans retinoic acid and butyric acid

-
GN10627
Atractylenolide I

-
GC72319
Atrosab
Atrosab is a humanized IgG1 antagonistic anti-TNFR1 antibody.

-
GC48925
Aureonitol
A fungal metabolite
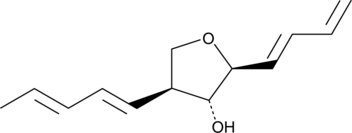
-
GC41490
Aureusimine B
Phevalin
Aureusimine B, also known as phevalin, is a natural pyrazinone produced by certain fungi and by Staphylococcus spp., including S.
-
GC46895
Aurintricarboxylic Acid (ammonium salt)
ATA
A protein synthesis inhibitor with diverse biological activities
-
GC40005
Aurodox
1-methyl-Mocimycin
Aurodox is a polyketide antibiotic originally isolated from S.
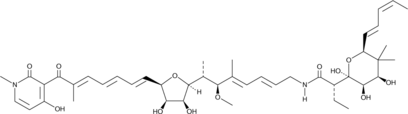
-
GC49646
Aurothioglucose (hydrate)
Gold Thioglucose
A TrxR inhibitor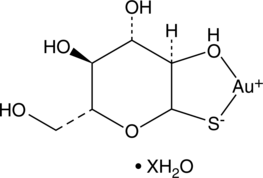
-
GC42877
AUY954
AUY954 is an orally bioavailable and selective agonist of the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1; EC50 = 1.2 nM for stimulating GTPγS binding to S1P1 in CHO cells).
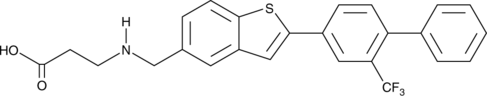
-
GC70987
Avacincaptad pegol sodium
Avacincaptad pegol (ARC1905) is an anti-C5 RNA aptamer that inhibits the cleavage of complement factor 5 (C5) into C5a and C5b.

-
GC72391
Avdoralimab
Avdoralimab (IPH 5401) is a fully human IgGκ monoclonal antibody that targets the complement C5a receptor 1 (C5aR1) that prevents its binding to C5a.
-
GC32486
AVE-3085
AVE-3085 is a potent endothelial nitric oxide synthase enhancer, used for cardiovascular disease treatment.

-
GC42880
Avenanthramide-C methyl ester
Avenanthramide-C methyl ester is an inhibitor of NF-κB activation that acts by blocking the phosphorylation of IKK and IκB (IC50 ~ 40 μM).

-
GC45388
Averantin
(–)-Averantin

-
GC42881
Avermectin B1a aglycone
Avermectin B1a aglycone is an aglycone form of the anthelmintic and insecticide avermectin B1a.

-
GC42882
Avermectin B1a monosaccharide
Avermectin B1a monosaccharide is a macrolide anthelmintic and monosaccharide form of avermectin B1a.

-
GC45984
Avilamycin A
An antibiotic
-
GC68709
Avizakimab
BOS161721
Avizakimab (BOS161721) is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that targets interleukin-21 (IL-21).

-
GC48511
Avrainvillamide
CJ-17,665
A fungal metabolite
-
GC42885
AX 048
The group IVA phospholipase A2 (PLA2), known as calcium-dependent cytosolic PLA2 (cPLA2), selectively releases arachidonic acid from membrane phospholipids, playing a central role in initiating the synthesis of prostaglandins and leukotrienes.

-
GC35440
AX-024
AX-024 is an orally available, first-in-class inhibitor of the TCR-Nck interaction that selectively inhibits TCR-triggered T cell activation with an IC50 ~1 nM.

-
GC19046
AX-024 hydrochloride
AX-024 hydrochloride is an cytokine release inhibitor which can strongly inhibit the production of interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα), interferon-γ (IFN-γ), IL-10 and IL-17A.
-
GC65283
AXC-715 trihydrochloride
T785 trihydrochloride
AXC-715 (T785) trihydrochloride is a TLR7/TLR8 dual agonist, extracted from patent WO2020168017 A1.
-
GC64938
AZD-7648
AZD-7648 is a potent, orally active, selective DNA-PK inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.6 nM. AZD-7648 induces apoptosis and shows antitumor activity.

-
GC10135
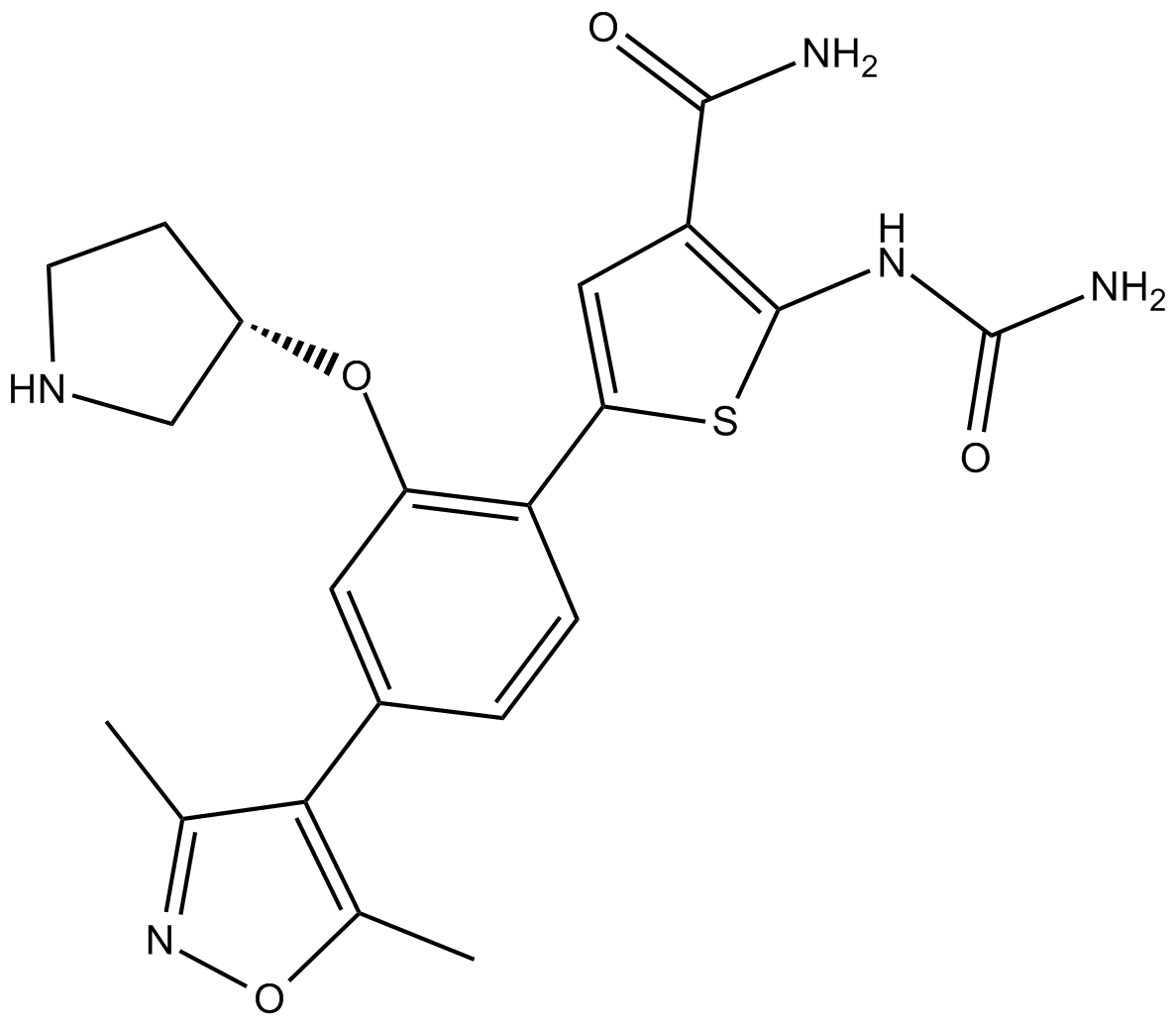
AZD3264
IKK2 inhibitor
-
GC62488
AZD8848
AZD8848 is a selective toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) antedrug agonist which is developed for the research of asthma and allergic rhinitis.

-
GC49057
Azelastine-13C-d3 (hydrochloride)
An internal standard for the quantification of azelastine

-
GC42891
azido-FTY720
FTY720 is a derivative of ISP-1 (myriocin), a fungal metabolite of the Chinese herb Iscaria sinclarii as well as a structural analog of sphingosine.

-
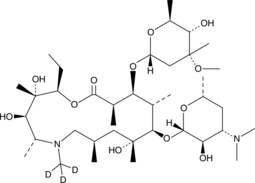
GC46903
Azithromycin-d3
An internal standard for the quantification of azithromycin
-
GC46904
Azoxystrobin
ICI-A 5504
A broad-spectrum fungicide
-
GC60616
AZT triphosphate
3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine-5'-triphosphate
AZT triphosphate (3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine-5'-triphosphate) is a active triphosphate metabolite of Zidovudine (AZT).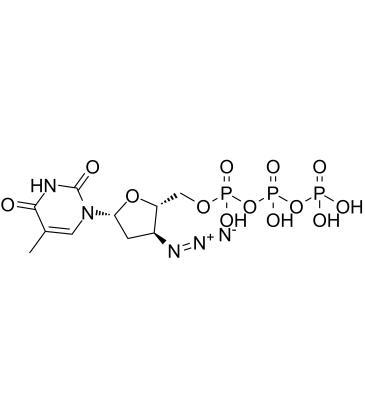
-
GC60617
AZT triphosphate TEA
3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine-5'-triphosphate TEA
AZT triphosphate TEA (3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine-5'-triphosphate TEA) is a active triphosphate metabolite of Zidovudine (AZT).
-
GC45795
Aztreonam-d6
SQ 26,776-d6
An internal standard for the quantification of aztreonam
-
GC39280
B022
B022 is a potent and selective NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) inhibitor (Ki of 4.2 nM; IC50=15.1 nM).

-
GC18580
B355252
A neuroprotective agent

-
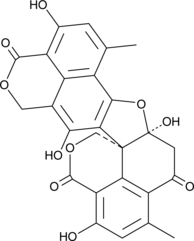
GC42895
Bacillosporin C
Bacillosporin C is an oxaphenalenone dimer originally isolated from T.
-
GC49793
Bacitracin A (technical grade)
NSC 45737
A polypeptide antibiotic
-
GC46905
Bacitracin Complex
A mixture of bacitracin polypeptides in complex with copper

-
GC45938
Bacopaside X
Bacopaside VII, Jujubogenin isomer of Bacopasaponin C
A triterpenoid saponin
-
GC49302
Bactenecin (bovine) (trifluoroacetate salt)
H-Arg-Leu-Cys-Arg-Ile-Val-Val-Ile-Arg-Val-Cys-Arg-OH, RLCRIVVIRVCR-OH
A cationic peptide
-
GN10018
Baicalin
Baicalein 7-glucuronide
Baicalin is a flavonoid glycoside and an allosteric carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) activator.
-
GC52344
Bak BH3 (72-87) (human) (trifluoroacetate salt)
A Bak-derived peptide

-
GC18126
Balsalazide
anti-inflammatory drug
-
GC35466
Balsalazide sodium hydrate
Balsalazide sodium hydrate could suppress colitis-associated carcinogenesis through modulation of IL-6/STAT3 pathway.
-
GC17574
BAPTA
calcium chelator

-
GC18313
BAR501 Impurity
BAR501 impurity is an impurity found in the preparation of BAR501 that acts as an agonist of the G protein-coupled bile acid-activated receptor (GP-BAR1).
-
GC66331
Basiliximab
CHI 621
Basiliximab (CHI 621) is a recombinant chimeric murine/human IgG1 monoclonal anti-interleukin-2 receptor antibody. Basiliximab can be used for the research of renal transplantation.
-
GC52476
Bax Inhibitor Peptide V5 (trifluoroacetate salt)
BIP V5, VPMLK
A Bax inhibitor
-
GC10345
Bay 11-7085
NK-κB activation inhibitor

-
GC13035
Bay 11-7821
BAY 11-7082
Bay 11-7821(BAY 11-7082) is an inhibitor of IκBα phosphorylation and NF-κB, selectively and irreversibly inhibits TNF-α-induced IκB-α phosphorylation (IC50 value is approximately 10μM), and reduces the expression of NF-κB and adhesion molecules. Bay 11-7821 inhibits ubiquitin-specific proteases USP7 and USP21 with IC50 values of 0.19 and 0.96μM, respectively .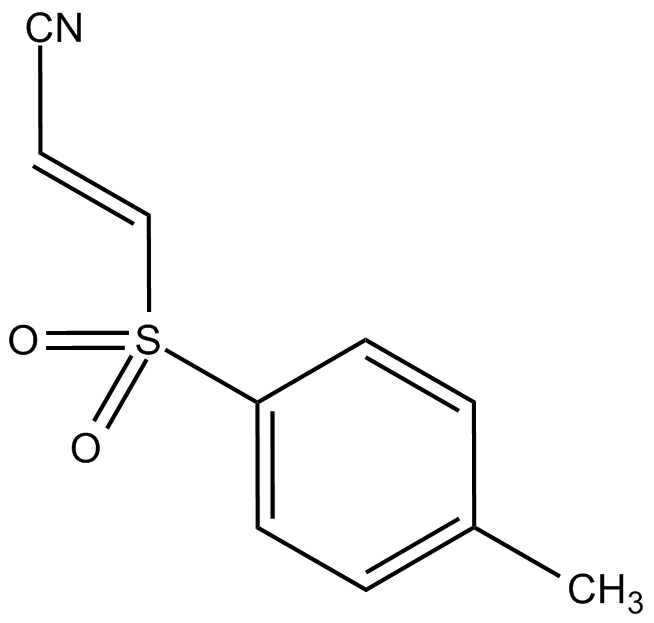
-
GC42897
BAY 61-3606 (hydrochloride)
BAY 61-3606 is a cell-permeable, reversible inhibitor of spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk; Ki = 7.5 nM; IC50 = 10 nM).



