Calcium Channel
Calcium channel is an ion channel that selectively permeable to calcium ions. It serves vital functions in cellular signal transduction.
Products for Calcium Channel
- Cat.No. Product Name Information
-
GC15513
ω-Agatoxin IVA
ω-Agatoxin IVA is a potent, selective P/Q type Ca2+ (Cav2.1) channel blocker with IC50s of 2 nM and 90 nM for P-type and Q-type Ca2+ channels, respectively.
-
GC12608
ω-Agatoxin TK
ω-Agatoxin TK, a peptidyl toxin of the venom of Agelenopsis aperta, is a potent and selective P/Q type Ca2+ channel blocker.

-
GC13886
ω-Conotoxin GVIA
ω-Conotoxin GVIA is a cone snail toxin that selectively blocks N-type channels in neurons .
-
GC18070
ω-Conotoxin MVIIC
wide spectrum blocker of N, P and Q type calcium channels
-
GC31248
β-Amino Acid Imagabalin Hydrochloride (PD-0332334)
PD-0332334
β-Amino Acid Imagabalin Hydrochloride (PD-0332334) (PD-0332334) is a ligand for the α2δ subunit of the voltage-dependent calcium channel.
-
GC70188
ω-Agatoxin IVA TFA
ω-Agatoxin IVA TFA is an effective selective blocker of P/Q-type Ca2+ (Cav2.1) channels, with IC50 values of 2 nM and 90 nM for P-type and Q-type Ca2+ channels, respectively. ω-Agatoxin IVA TFA (IC50, 30-225 nM) inhibits high potassium-induced glutamate release and calcium influx. It also blocks the release of serotonin and adrenaline induced by high potassium, without affecting L-type or N-type calcium channels.

-
GC45241
ω-Conotoxin GVIA (trifluoroacetate salt)
ω-Conotoxin GVIA is a peptide originally isolated from the marine mollusk C.

-
GA24016
ω-Conotoxin MVIIA
ω-Conotoxin MVIIA (SNX-111), a peptide, is a potent and selective block of N-type calcium channels antagonist.
-
GC64899
ω-Conotoxin MVIIC TFA

-
GN10612
(+)- Praeruptorin C

-
GC30933
(+)-Kavain
Kawain, NSC 112162
An Analytical Reference Standard

-
GC63940
(-)-Denudatin B
(-)-Denudatin B is an antiplatelet agent.

-
GN10445
(-)-pareruptorin A

-
GC14484
(-)-Xestospongin C
XeC, Araguspongine E
IP3-dependent Ca2+ release inhibitor

-
GC50536
(2R/S)-6-PNG
(±)-6-PN
CaV3.2 blocker; active in vivo
-
GC13895
(R)-(+)-Bay K 8644
NI 105, R 4407
L-type Ca2+-channel blocker
-
GC66419
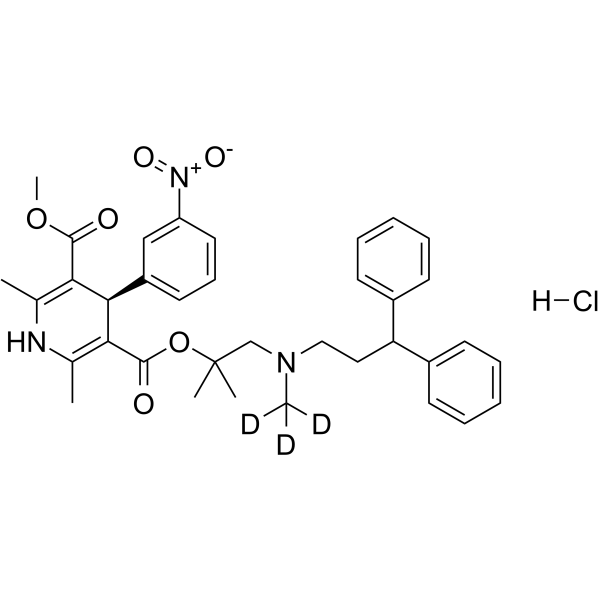
(R)-Lercanidipine-d3 hydrochloride
(R)-lercanidipine D3 (hydrochloride) is a deuterium labeled (R)-Lercanidipine hydrochloride. (R)-Lercanidipine D3 (hydrochloride), the R-enantiomer of Lercanidipine, is a calcium channel blocker.
-
GC68475
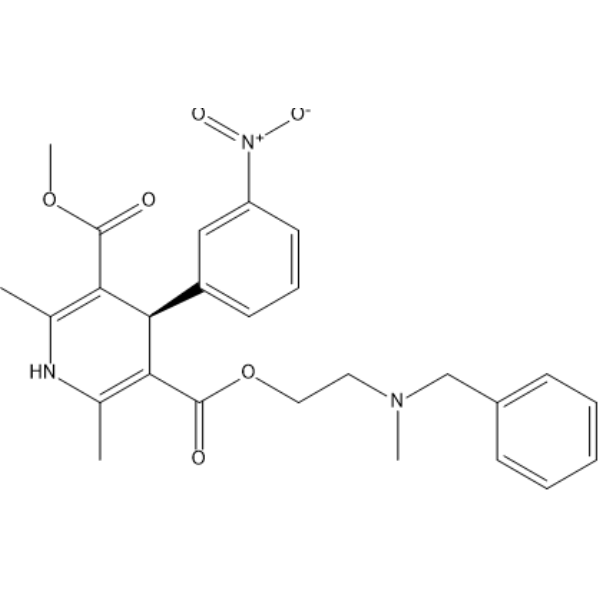
(R)-Nicardipine
(R)-YC-93 free base
-
GC61873
(Rac)-MEM 1003
(Rac)-MEM 1003 is the racemate of MEM 1003.

-
GC14229
(S)-(-)-Bay K 8644
L-type Ca2+-channel activator

-
GC63321
(S)-(-)-Felodipine-d5

-
GC60418
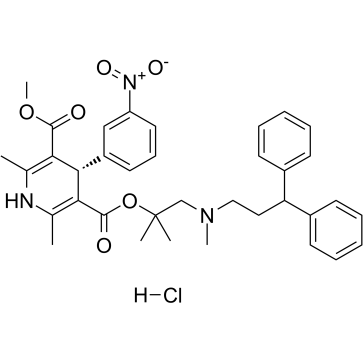
(S)-Lercanidipine hydrochloride
(S)-Lercanidipine hydrochloride is the S-enantiomer of Lercanidipine hydrochloride.
-
GC68476
(S)-Nicardipine
(S)-YC-93 free base
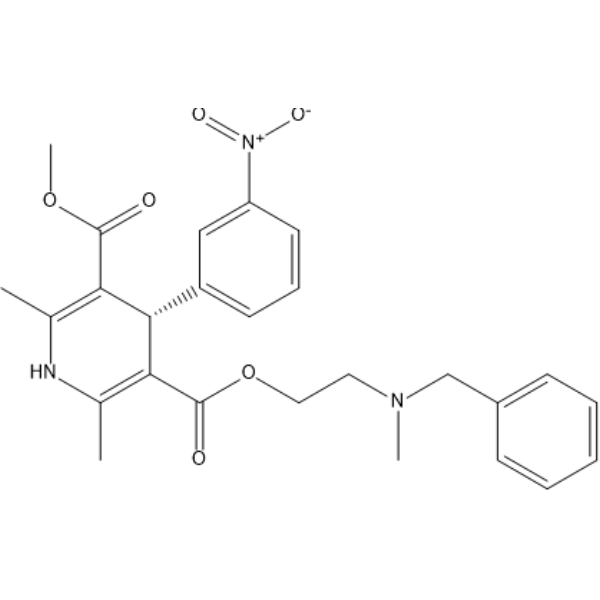
-
GC60425
(S)-Verapamil D7 hydrochloride
(S)-(-)-Verapamil D7 hydrochloride
(S)-Verapamil D7 hydrochloride ((S)-(-)-Verapamil D7 hydrochloride) is a deuterium labeled (S)-Verapamil hydrochloride. (S)-Verapamil hydrochloride (S(-)-Verapamil hydrochloride) inhibits leukotriene C4 (LTC4) and calcein transport by MRP1. (S)-Verapamil hydrochloride leads to the death of potentially resistant tumor cells.
-
GC60008
(S)-Verapamil hydrochloride
(S)-Verapamil hydrochloride (S(-)-Verapamil hydrochloride) inhibits leukotriene C4 (LTC4) and calcein transport by MRP1. (S)-Verapamil hydrochloride leads to the death of potentially resistant tumor cells.
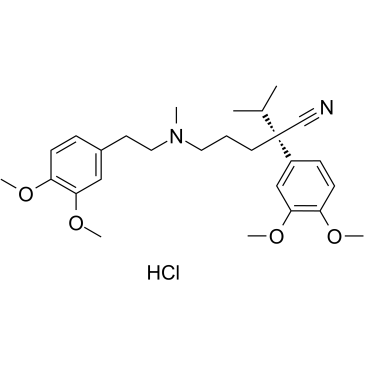
-
GC18603
(±)-Methoxyverapamil (hydrochloride)
Gallopamil, NSC 274966
(±)-Methoxyverapamil (hydrochloride) (Methoxyverapamil hydrochloride), a methoxy derivative of Verapamil, is a phenylalkylamine calcium antagonist.
-
GC61898
1,2,4-Trihydroxybenzene
1,2,4-Trihydroxybenzene (Hydroxyhydroquinone), a by-product of coffee bean roasting, increases intracellular Ca2+ concentration in rat thymic lymphocytes.
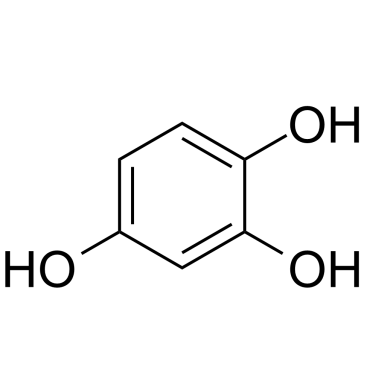
-
GC45980
1,3-Dipalmitoyl-2-Octanoyl-rac-glycerol
1,3-Dipalmitin-2-Octanoin, TG(16:0/8:0/16:0)
A triacylglycerol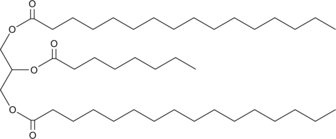
-
GC39470
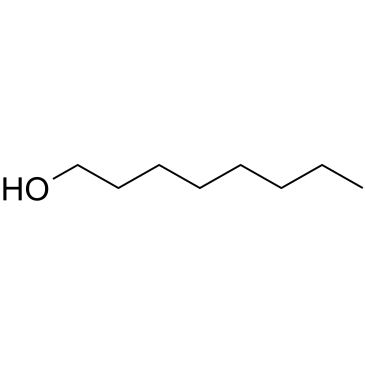
1-Octanol
1-Octanol (Octanol), a saturated fatty alcohol, is a T-type calcium channels (T-channels) inhibitor with an IC50 of 4 μM for native T-currents.
-
GC74657
1-Octanol-d17
Octanol-d17
1-Octanol-d17 is the deuterium labeled 1-Octanol.
-
GC49820
10,11-dihydro-10,11-dihydroxy Carbamazepine
10,11-dihydro-10,11-dihydroxy CBZ, CBZ-diol, Dihydroxycarbazepine, Dihydroxycarbamazepine
A metabolite of carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine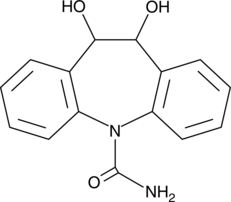
-
GC90815
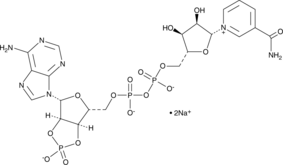
2',3'-cyclic NADP+ (sodium salt)
A substrate for CNP
-
GC17562
2-APB
2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl borate, 2-APB, NSC 17107
2-APB is a nonspecific antagonist of calcium channels, commonly used in studies of calcium signaling, such as in apoptosis, muscle contraction, and neural transmission.
-
GC42475
4α-Phorbol 12,13-didecanoate
4α-PDD, 4α-Phorbol 12,13-dicaprinate
4α-Phorbol 12,13-didecanoate is a negative control for phorbol esters, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and phorbol 12,13-didecanoate (PDD).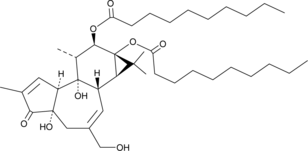
-
GC42346
4-bromo A23187
4-Bromocalcimycin
4-bromo A23187 is a halogenated analog of the highly selective calcium ionophore A23187.
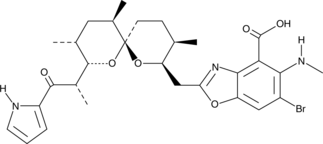
-
GC90867
8-bromo NAD+ (sodium salt)
A prodrug form of 8-bromo-cADPR
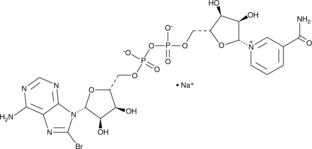
-
GC10119
8-Bromo-cGMP, sodium salt
8-bromo-cGMP, 8-bromo Guanosine 3’,5’-cyclic monophosphate
8-Bromo-cGMP is a cell-permeable cGMP analog that induces PKG activation.
-
GC42621
8-bromo-Cyclic ADP-Ribose (sodium salt)
8-bromo-cADPR, 8-bromo-cADP-Ribose
Cyclic ADP-ribose (cADP-ribose) is a calcium mobilizing nucleotide that is biosynthesized from NAD+ by cADP-ribose synthases, including CD38.
-
GC11178
A-7 hydrochloride
calmodulin antagonist
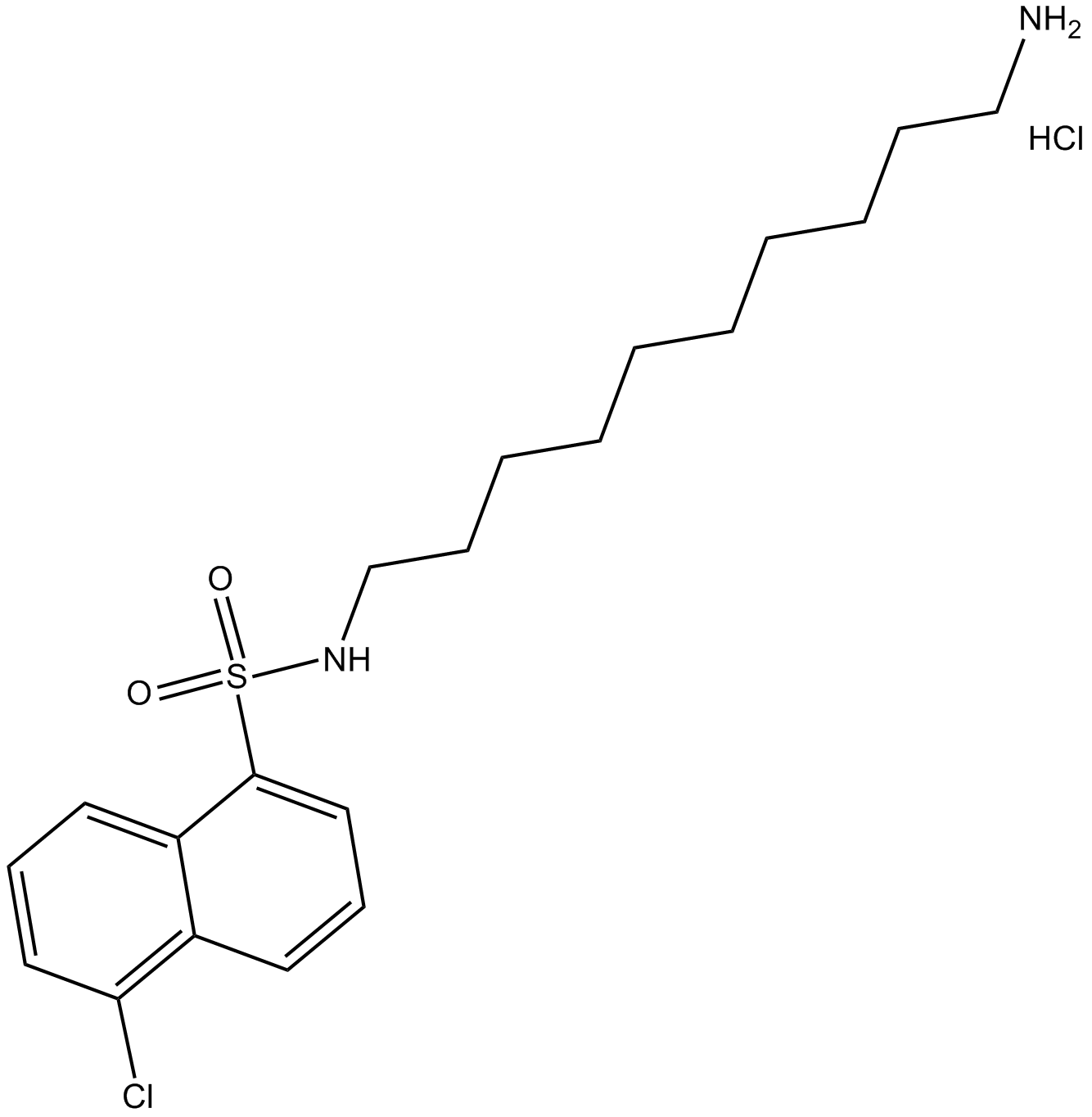
-
GC11200
A23187
Calcimycin
A23187, free acid is a Ca2+ ionophore
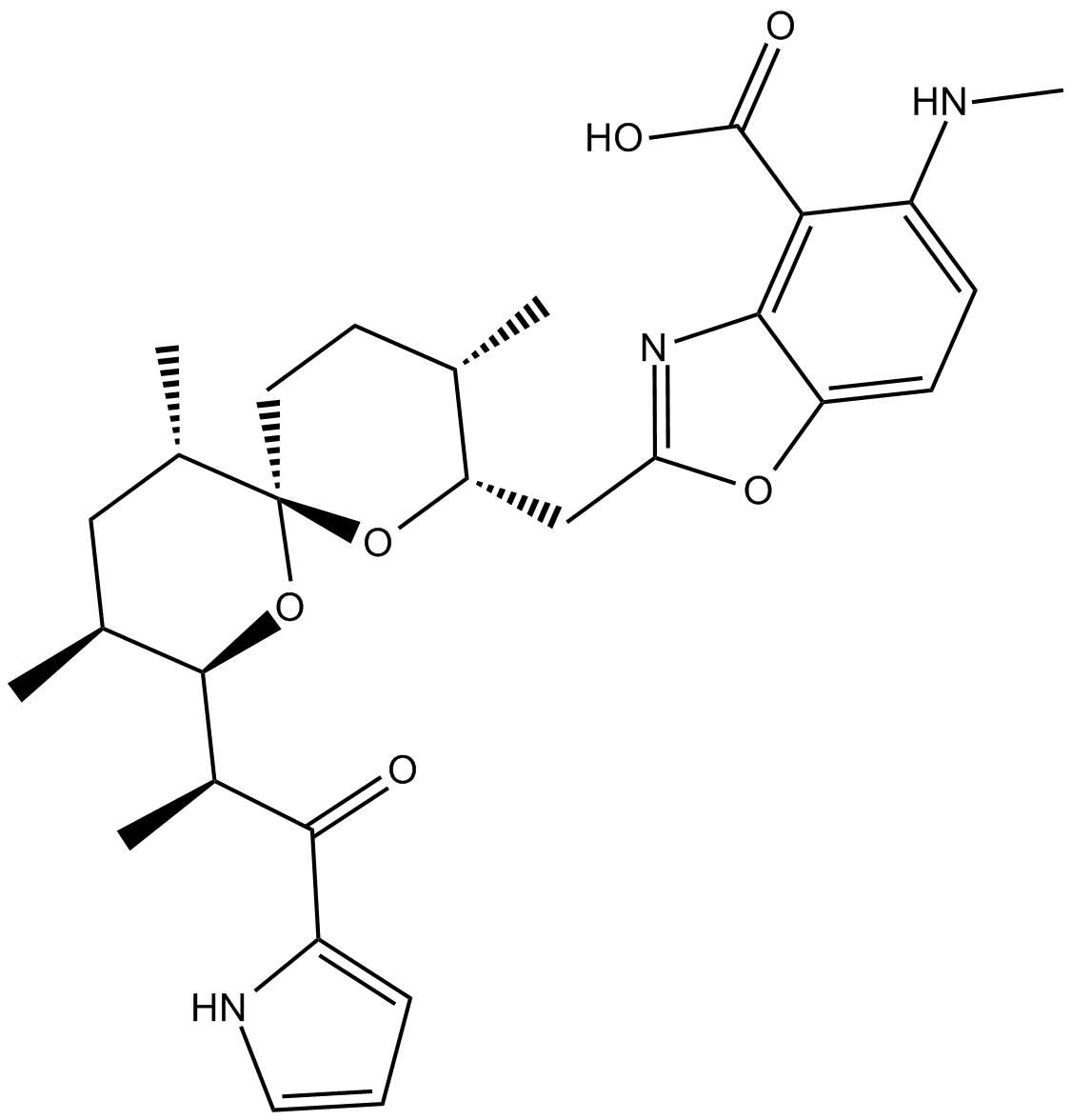
-
GC19016
ABT-639
ABT-639 is a novel, peripherally acting, selective T-type Ca2+ channel blocker.

-
GC33720
ABT-639 hydrochloride
ABT-639 hydrochloride is a novel, peripherally acting, selective T-type Ca2+ channel blocker.

-
GC14142
Acetylcholine Chloride
ACh
Major transmitter at many nervous sites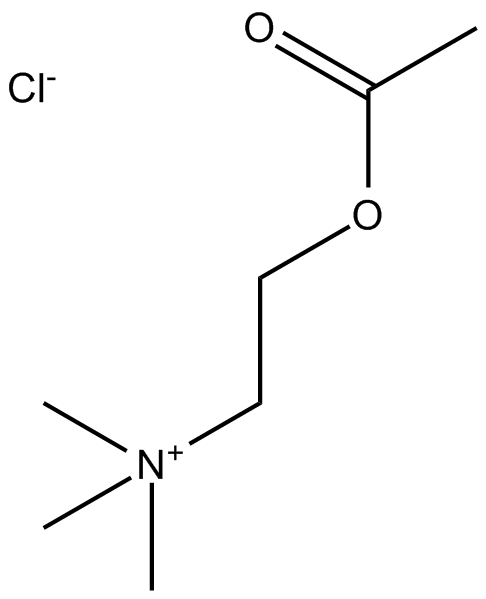
-
GC31100
ACT-709478
ACT-709478
ACT-709478 is a potent, selective, orally active, and brain penetrating T-type calcium channel blocker.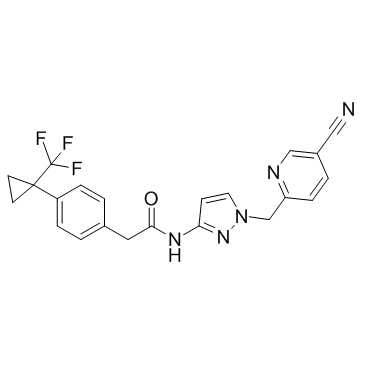
-
GC32672
AE0047 Hydrochloride
AE0047 Hydrochloride is a calcium blocker, used in the research of hypertensive disease.
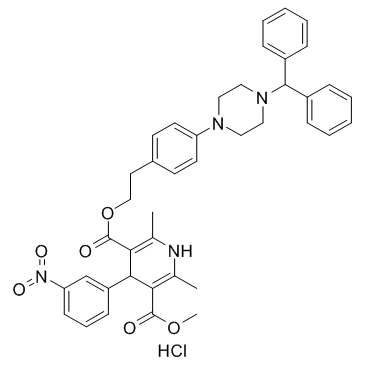
-
GC18274
Amiprofos-methyl
APM, NSC 313446
Amiprofos-methyl (APM) is a phosphoric amide herbicide.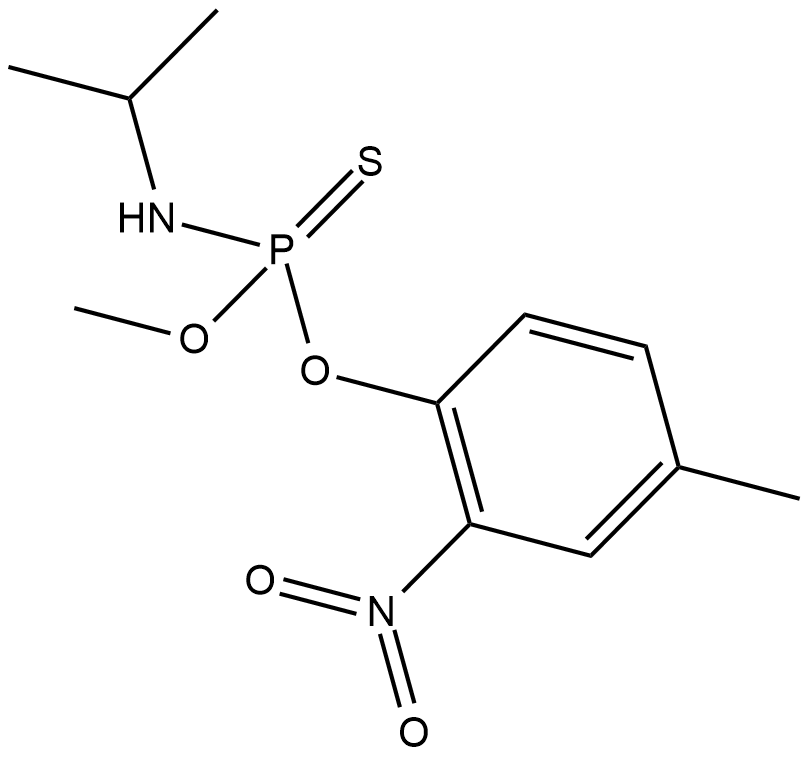
-
GC13523
Amlodipine
Intervask, Pelmec
Calcium channel blocker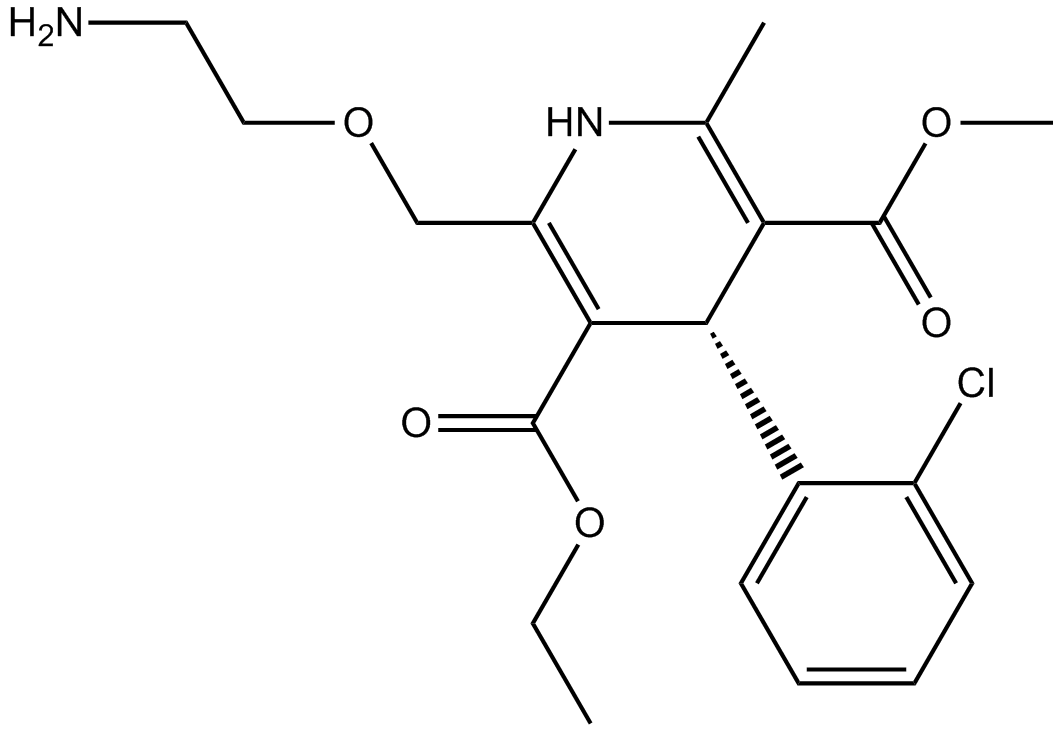
-
GC13146
Amlodipine Besylate
Block of L-type calcium channel

-
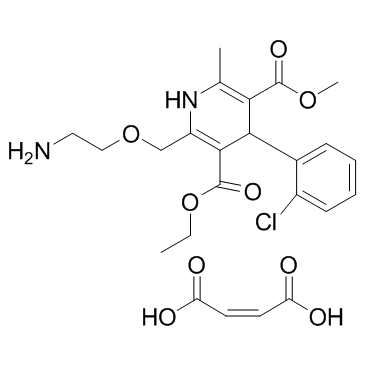
GC35325
Amlodipine maleate
Amlodipine maleate is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker, acts as an orally active antianginal agent.
-
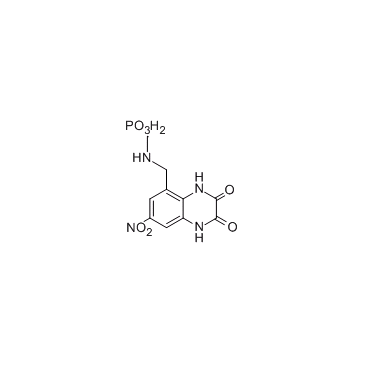
GC32566
Anipamil
Anipamil is a long-acting calcium channel blocker, used for the treatment of cardiovascular disease.
-
GC34049
Aranidipine (MPC1304)
Aranidipine (MPC1304) (MPC1304) is a Ca2+ channel antagonist with potent and long-lasting antihypertensive effects.

-
GC42876
Autocamtide 2 (trifluoroacetate salt)
Autocamtide 2 is a peptide substrate for calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaMK) and CaMKII.

-
GC15099
Autocamtide-2-related inhibitory peptide
inhibitor of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaM-kinase II, CaMKII)
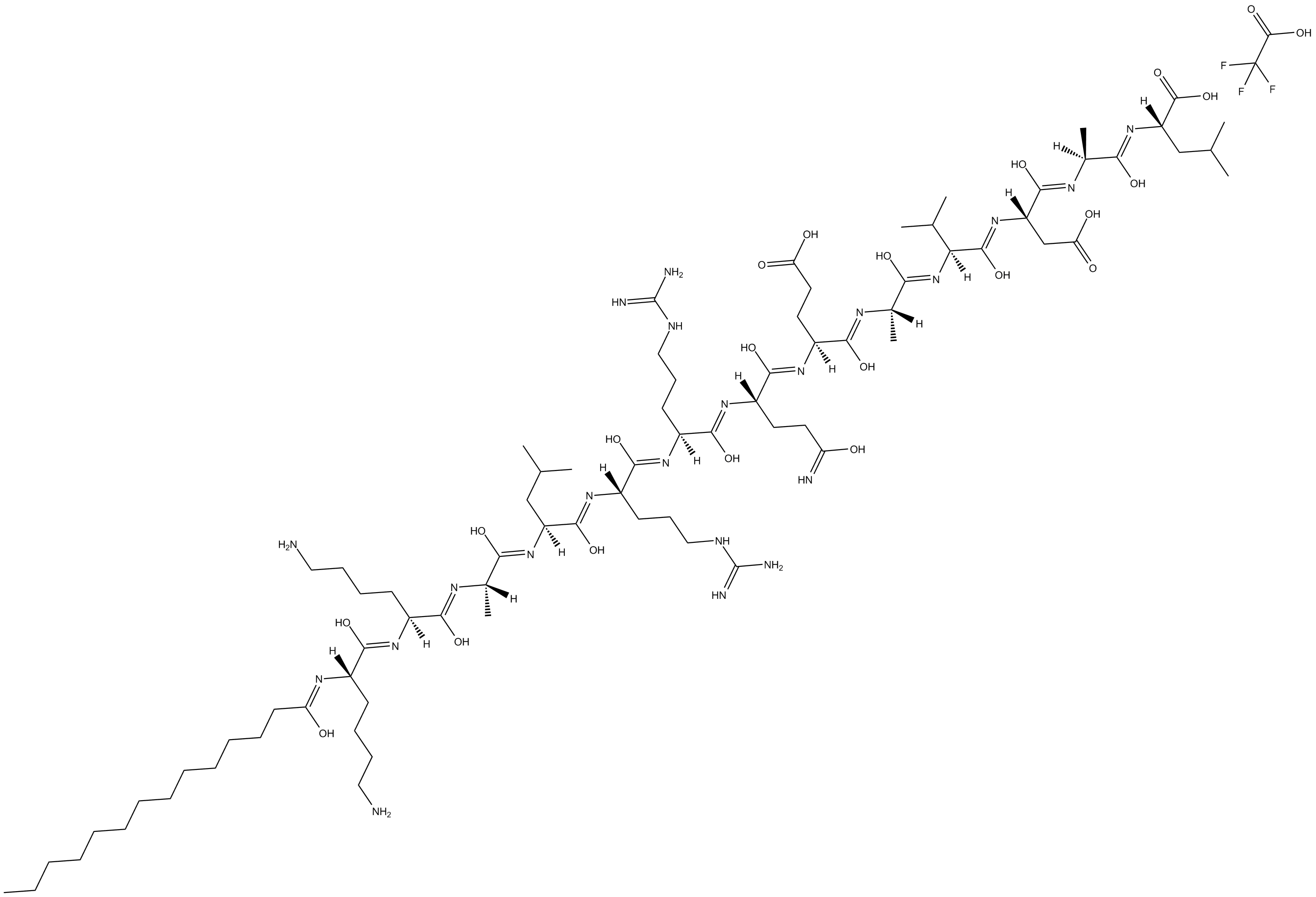

-
GC15101
Azelnidipine
CS 905, RS 9054
L-type calcium channel blocker;antihypertensive
-
GC35451
Azelnidipine D7

-
GC61493
Azumolene
Azumolene (EU4093 free base), a Dantrolene analog, is a muscle relaxant.

-
GC42893
Azumolene (sodium salt)
EU4093
Azumolene is a muscle relaxant that inhibits the release of calcium from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum.
-
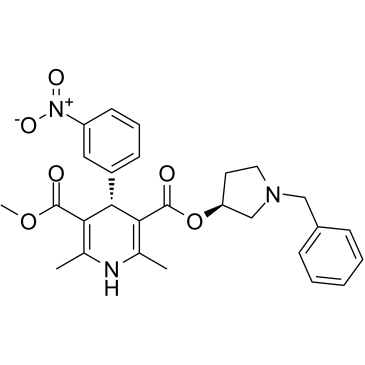
GC35469
Barnidipine
Barnidipine (Mepirodipine) is an L-type calcium antagonist (CaA) with high affinity for [3H] initrendipine binding sites (Ki=0.21 nmol/l), has selective action against CaA receptors.
-
GC13289
Barnidipine (hydrochloride)
YM 09730-5
calcium-channel blocker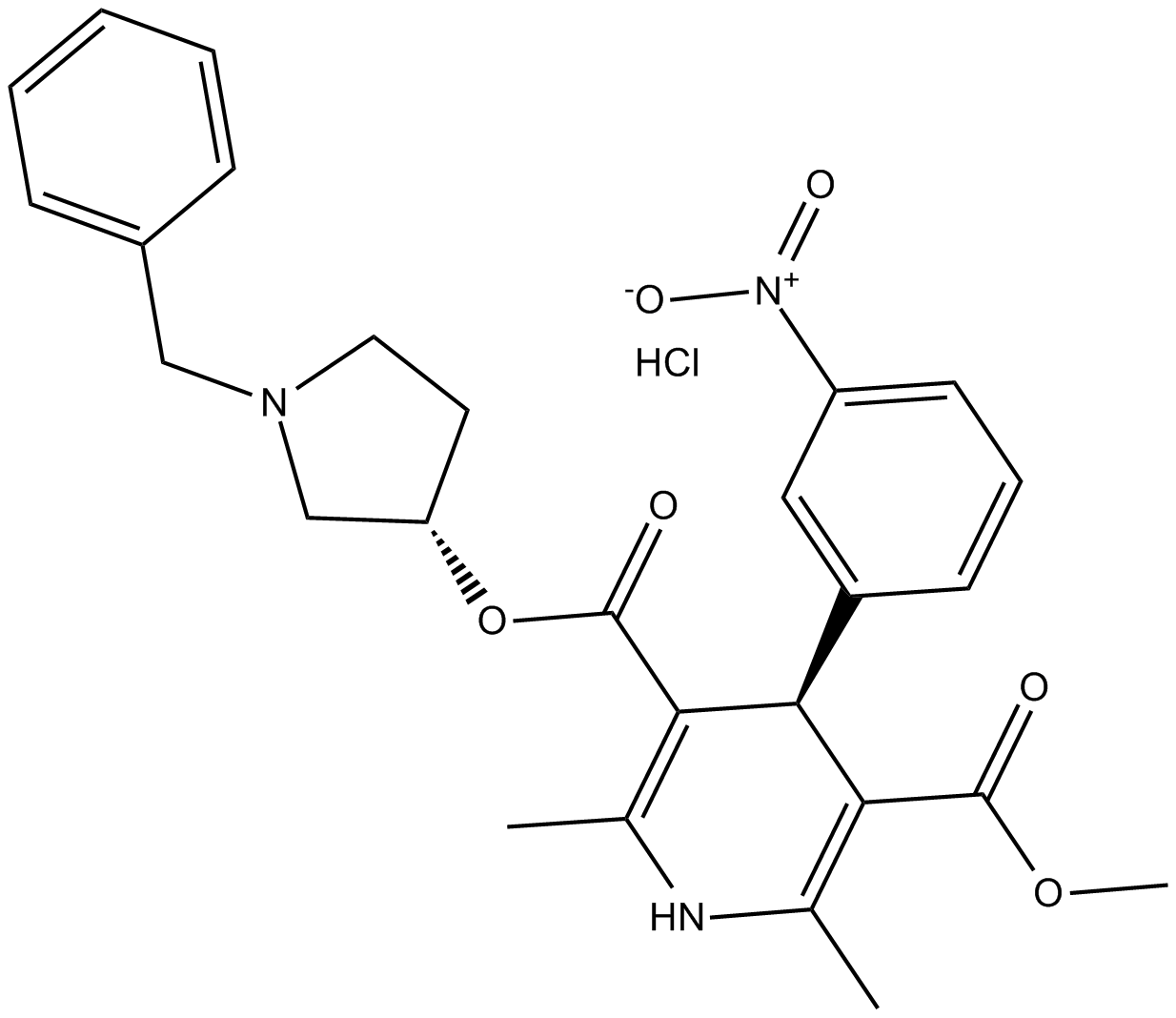
-
GC72475
BBT
BBT is an enhancer of impaired glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS).

-
GC13888
Benidipine HCl
(±)-Benidipine, KW-3049
Benidipine HCl is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker for the treatment of high blood pressure (hypertension).
-
GC15533
Bepridil hydrochloride
Calcium channel blocker

-
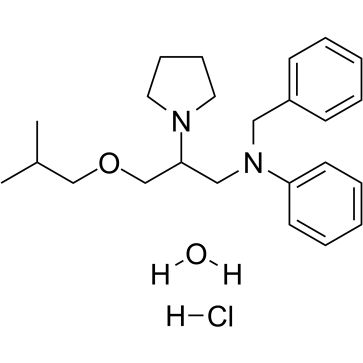
GC39743
Bepridil hydrochloride hydrate
Bepridil hydrochloride hydrate ((±)-Bepridil hydrochloride hydrate) is a non-selective, long-acting Ca+ channel antagonist and Na+, K+ channel inhibitor, with antianginal and type I antiarrhythmic effects.
-
GC39546
Bevantolol hydrochloride
CI-755, DL-Bevantolol, NC-1400
A β1-AR antagonist
-
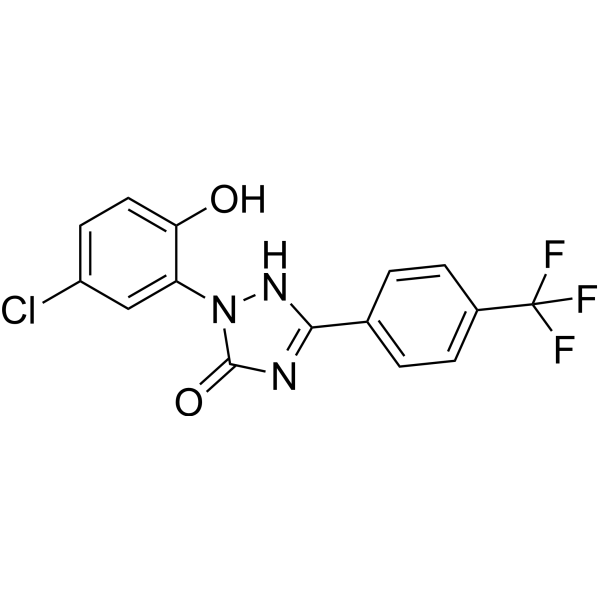
GC70402
BMS-192364
BMS-192364 is targeting the Gα-RGS interaction to produce an inactive Gα-RGS complex.
-
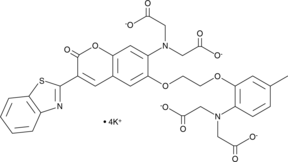
GC42984
BTC (potassium salt)
BTC (potassium salt) is a low affinity calcium indicator (Kd approximately 7-26 μM) featuring many desirable properties for cellular calcium imaging, including long excitation wavelengths (400/485 nm), low sensitivity to Mg2+, and accuracy of ratiometric measurement.
-
GC42985
BTC AM
BTC AM is a cell-permeable acetoxy-methyl ester of BTC.
-
GC50200
BX 430
Blocker of P2X4 Compound 3.0
Selective P2X4 allosteric antagonist
-
GC30977
Ca2+ channel agonist 1
Ca2+ channel agonist 1 is an agonist of N-type Ca2+ channel and an inhibitor of Cdk2, with EC50s of 14.23 μM and 3.34 μM, respectively, and is used as a potential treatment for motor nerve terminal dysfunction.
-
GC43115
Cal Green™ 1 (potassium salt)
Calcium Green-1
Cal Green™ 1 is a cell-impermeant fluorescent calcium indicator that is characterized by high quantum yield and low phototoxicity.
-
GC43116
Cal Green™ 1 AM
Calcium Green-1 AM
Cal Green™ 1 AM is a cell-permeant fluorescent calcium indicator (Excitation 506 nm; Emission 531 nm).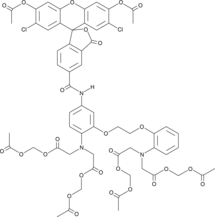
-
GC32616
Calcium channel-modulator-1
Calcium channel-modulator-1 is a calcium channel modulator; blocks aortic contraction with an IC50 of 0.8 μM.

-
GC14326
Calmidazolium chloride
R 24571
Calmodulin antagonist

-
GC43128
Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II (290-309) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (290-309) is a synthetic peptide derived from the rat brain protein sequence that contains the calmodulin binding domain.

-
GC12104
CALP1
Calcium-like Peptide 1
Cell-permeable calmodulin (CaM) agonist

-
GC65081
CALP1 TFA
CALP1 TFA is a calmodulin (CaM) agonist (Kd of 88 ?M) with binding to the CaM EF-hand/Ca2+-binding site.
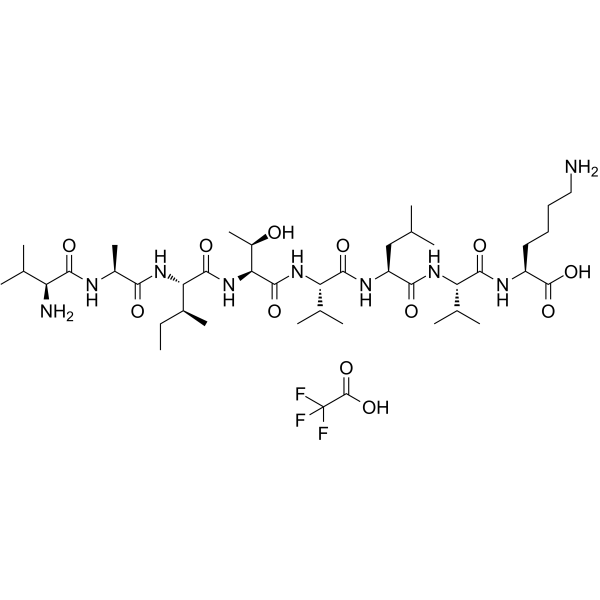
-
GC14889
CALP2
Cell-permeable calmodulin (CaM) antagonist

-
GC61508
CALP2 TFA
CALP2 TFA is a calmodulin (CaM) antagonist (Kd of 7.9 ?M) with high affinity for binding to the CaM EF-hand/Ca2+-binding site.

-
GC17687
CALP3
Cell-permeable calmodulin (CaM) agonist

-
GC15930
Camstatin
analog of PEP-19 with antagonism of calmodulin

-
GC39646
Carboxyamidotriazole Orotate
L-651582 Orotate; CAI Orotate
Carboxyamidotriazole Orotate (L-651582 Orotate) is the orotate salt form of Carboxyamidotriazole (CAI), an orally bioavailable signal transduction inhibitor.
-
GN10791
Catharanthine
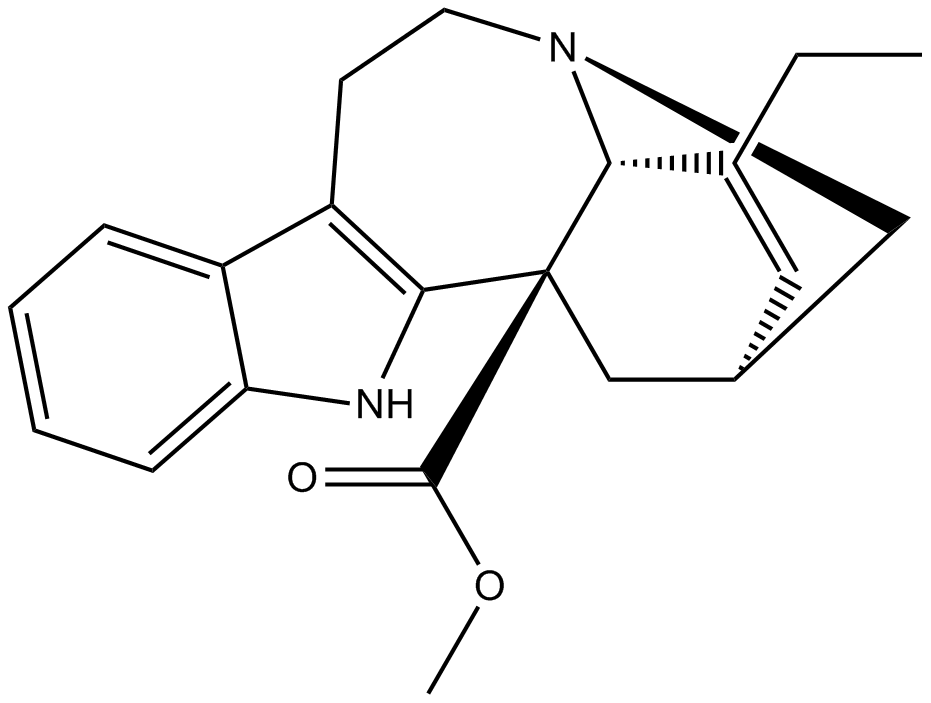
-
GN10715
Catharanthine Tartrate
(+)3,4Didehydrocoronaridine
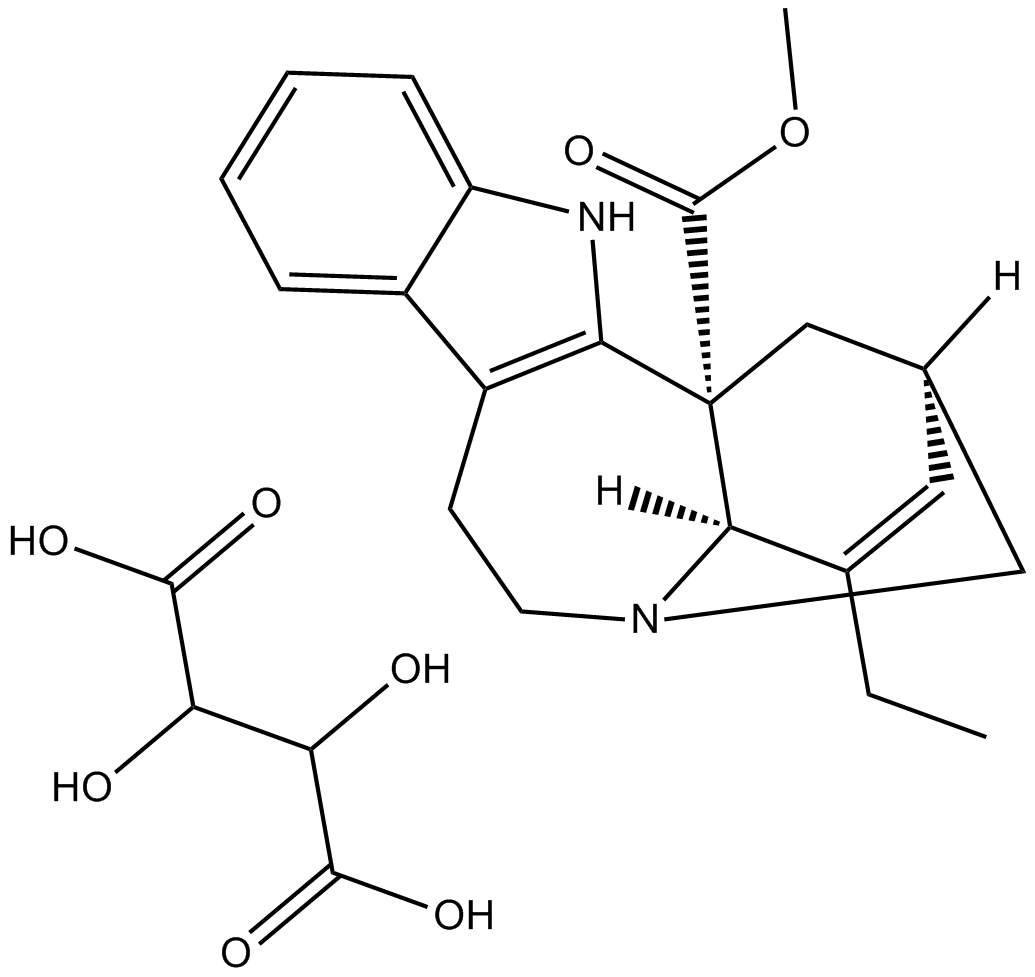
-
GC35619
Cav 2.2 blocker 1
Cav 2.2 blocker 1 (compound 9) is a N-type calcium channel (Cav 2.2) blocker for the treatment of pain, with an IC50 of 1 nM.

-
GC65959
CaV1.3 antagonist-1
CaV1.3 antagonist-1 is a potent and highly selective CaV1.3 L-type calcium channel (LTCC) antagonist with an IC50 of 1.7 μM. CaV1.3 antagonist-1 inhibits CaV1.3 LTCC >600-fold more potently than CaV1.2 LTCC. CaV1.3 antagonist-1, a cyclopentyl derivative, has the potential for Parkinson's disease research.

-
GC31332
CDN1163
An allosteric activator of SERCA2

-
GC16911
CGS 9343B
KW-5617, Zaldaride Maleate
CGS 9343B (CGS-9343B) is a potent, orally active and selective inhibitor of calmodulin.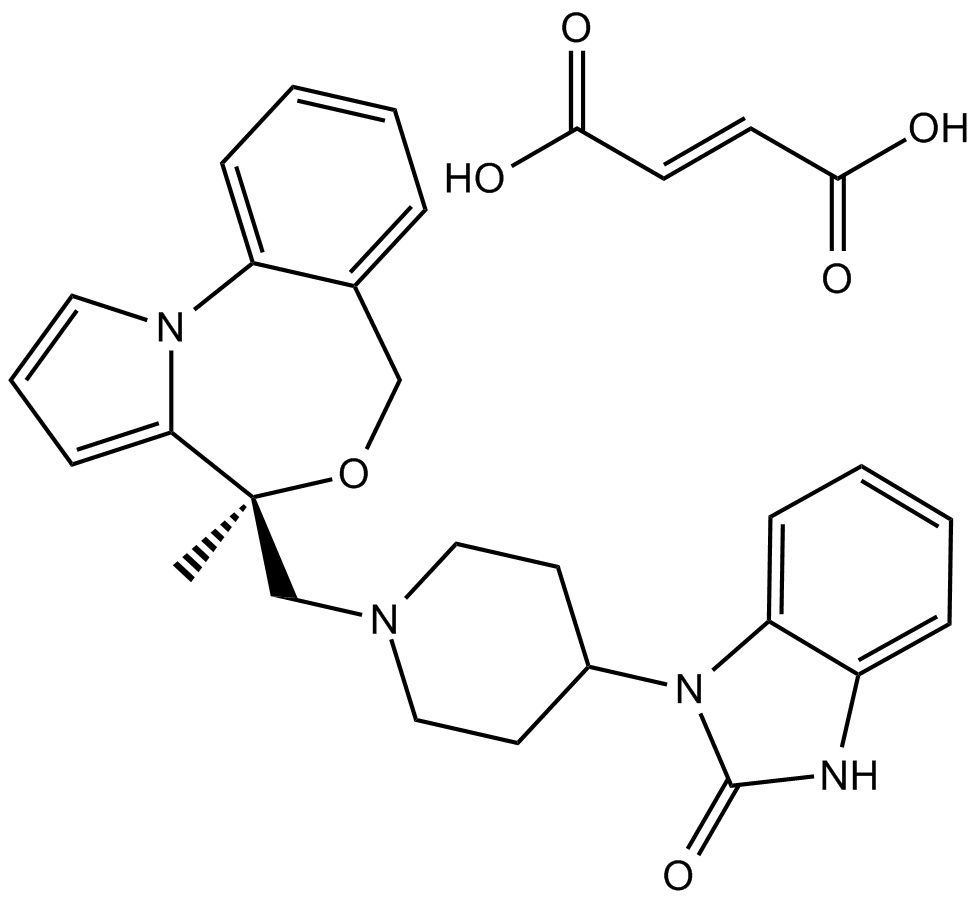
-
GC12312
Cilnidipine
FRC 8653
Blocker of Dual L- and N-type calcium channel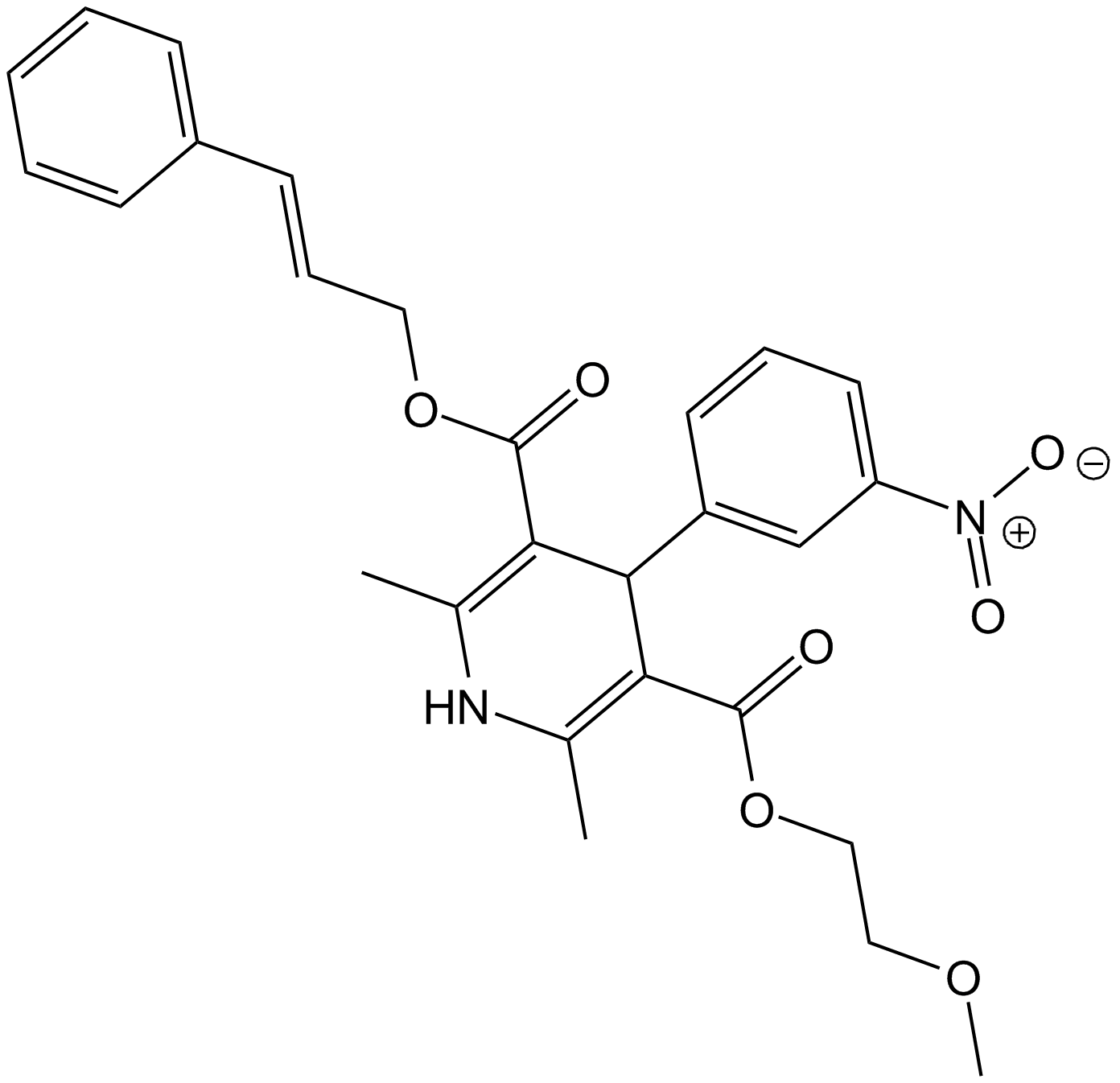
-
GC11695
Cinnarizine
antihistamine and calcium channel blocker

-
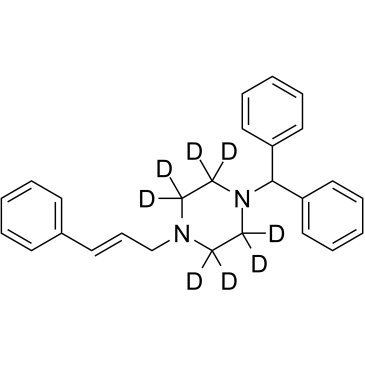
GC60709
Cinnarizine D8
An internal standard for the quantification of cinnarizine
-
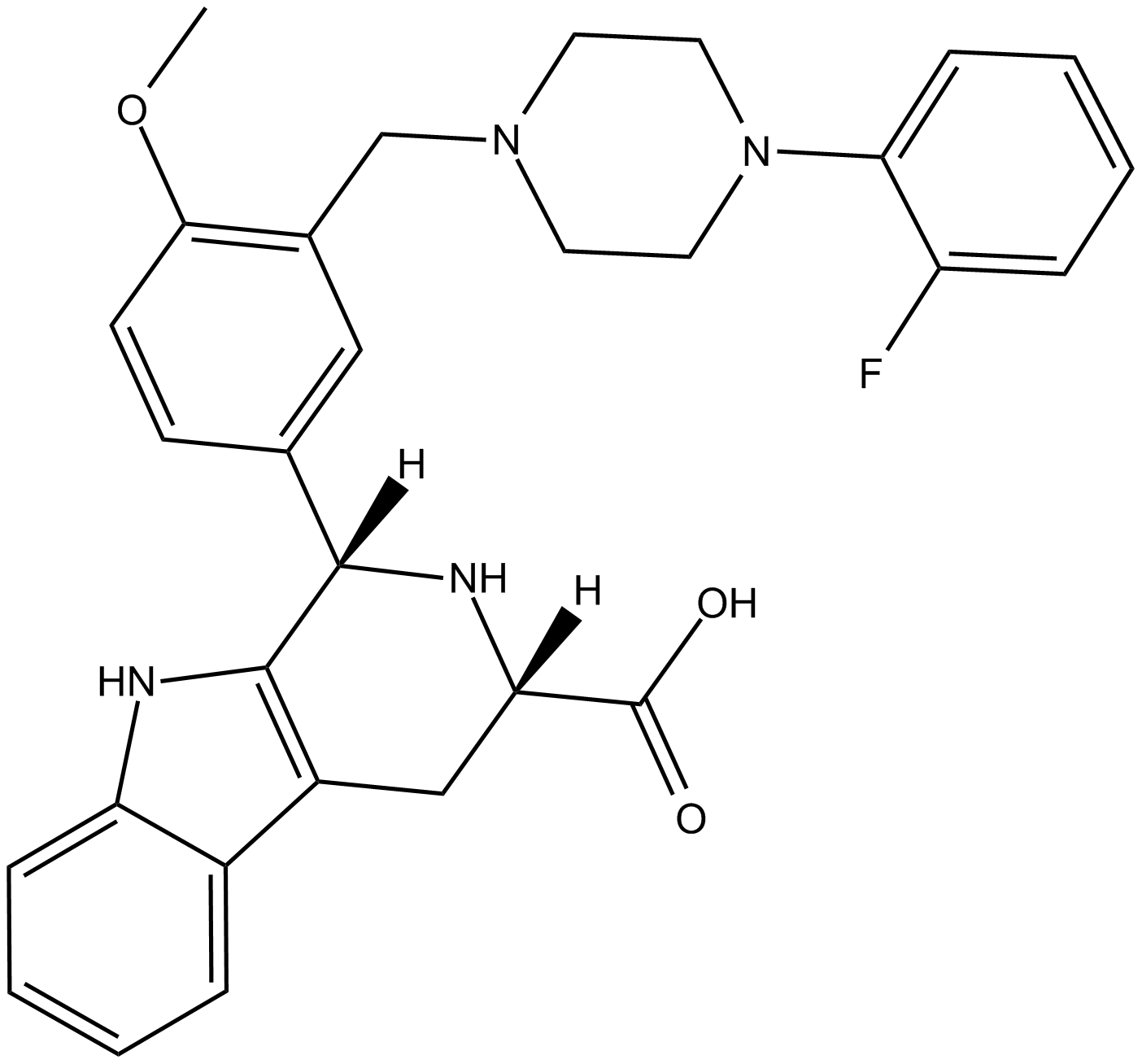
GC12095
cis-Ned 19
nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) antagonist
-
GC16128
Clevidipine Butyrate
rac-Clevidipine
Clevidipine Butyrate is a short-acting dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonist (IC50= 7.1 nM, V(H) = -40 mV ) under development for treatment of perioperative hypertension.
-
GC74202
Coelenterazine h hydrochloride
2-Deoxycoelenterazine hydrochloride; CLZN-h hydrochloride
Coelenterazine h (2-Deoxycoelenterazine) drochloride, a coelenterazine derivative, is a luminescent substrate for RLuc8.
-
GC35738
CP-060
CP-?060 is a potent Ca2+ antagonist, inhibits Ca2+ overload and possesses antioxidant and cardioprotective activities.
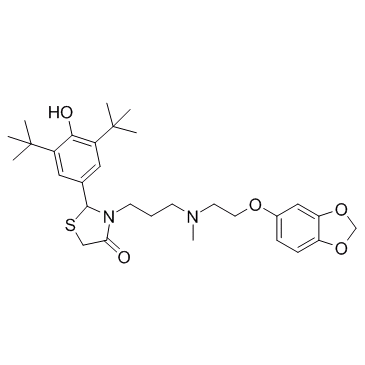
-
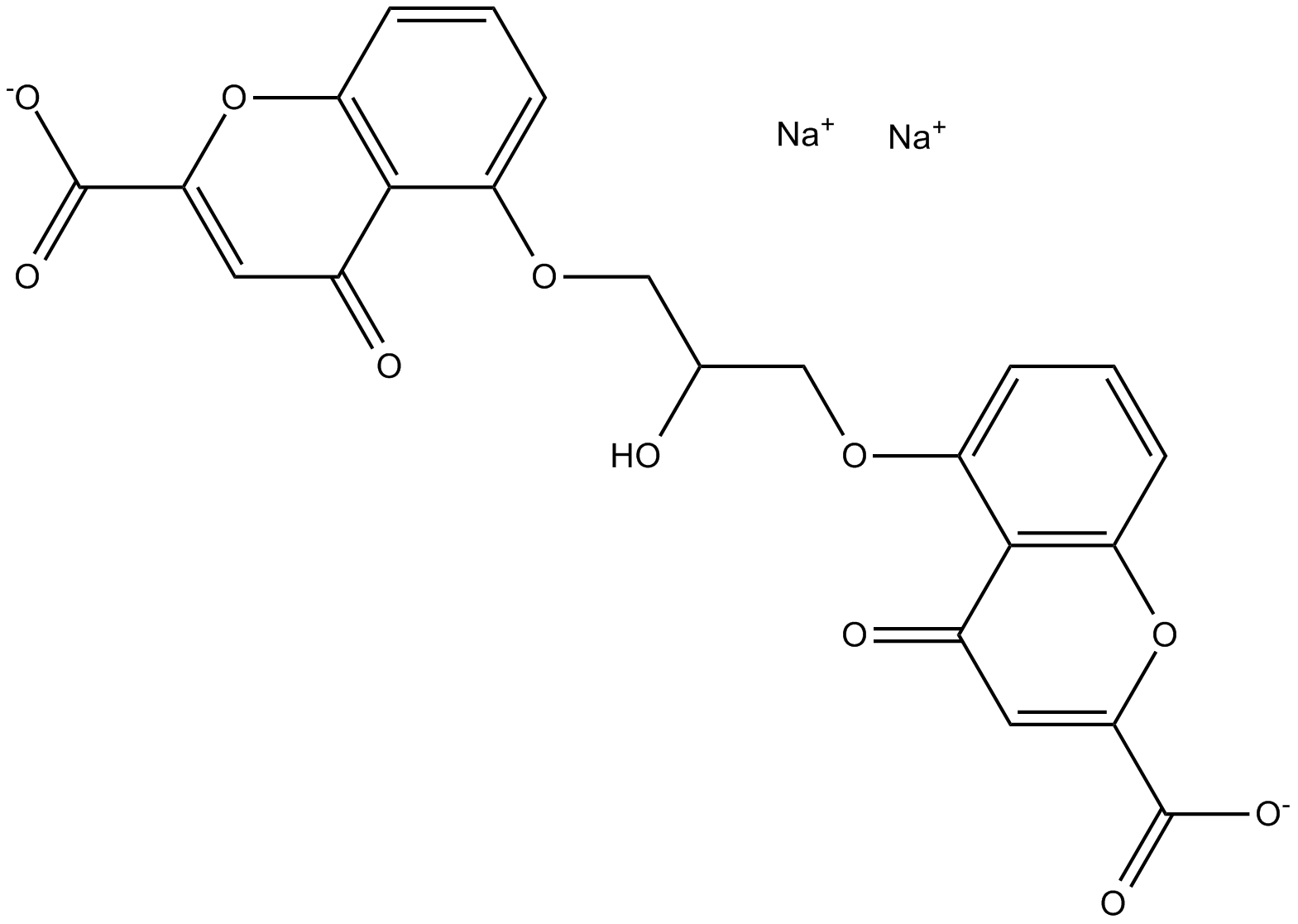
GC17690
Cromolyn sodium
Mast cell membrane stabilizer
-
GC31834
CV-159
CV-159 is a unique dihydropyridine Ca2+ antagonist with an anti-calmodulin (CaM) action, and has antiinflammatory activities.
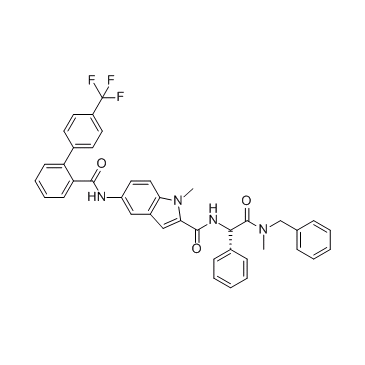
-
GC63967
Cycleanine
O,O-Dimethylisochondrodendrine, O-Methylnorcycleanine
Cycleanine is a potent vascular selective Calcium antagonist.
-
GC62179
Cyclic ADP-ribose
Cyclic ADP-ribose (cADPR) is a potent second messenger for calcium mobilization that is synthesized from NAD+ by an ADP-ribosyl cyclase.

-
GC43338
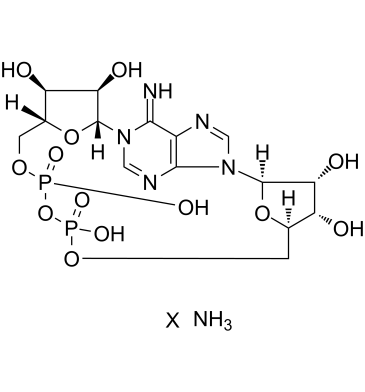
Cyclic ADP-Ribose (ammonium salt)
cADP-Ribose;cADPR
Cyclic ADP-ribose (cADP-ribose) is an endogenous metabolite of NAD+ that mobilizes the release of stored Ca2+ in the endoplasmic reticulum via ryanodine receptors in various cell types.
-
GC61792
Cyclic ADP-ribose ammonium
cADPR ammonium