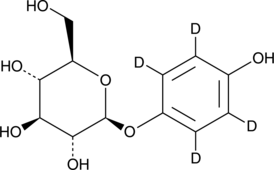
Arbutin-d4 (Synonyms: β-Arbutin-d4) |
| Catalog No.GC48841 |
Arbutina-d4 es Arbutina marcada con deuterio. La arbutina (β-arbutina) es un inhibidor competitivo de la tirosinasa en melanocitos, con valores de Kiapp de 1,42 mM para monofenolasa; 0,9 mM para difenolasa. La arbutina también se utiliza como agente despigmentante. La arbutina es un polifenol natural aislado de la planta de gayuba Arctostaphylos uvaursi, posee propiedades antioxidantes, antiinflamatorias y antitumorales.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Arbutin-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of arbutin by GC- or LC-MS. Arbutin is a glycosylated hydroquinone that has been found in Arctostaphylos plants and has diverse biological activities, including tyrosinase inhibitory, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties.1,2 It inhibits human tyrosinase activity in crude tyrosinase solution isolated from human melanocytes (IC50s = 5.7 and 18.9 mM using L-tyrosine and L-DOPA as substrates, respectively) as well as in intact melanocytes (IC50 = 0.5 mM).3 Arbutin (50 μM) inhibits hemolysis induced by the free radical generator AAPH in sheep erythrocytes and inhibits AAPH-induced decreases in cell viability in cultured human skin fibroblasts when used at concentrations greater than 125 μM.2 In an LPS-induced rat model of acute lung injury, arbutin (50 mg/kg) prevents increases in IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels in lung tissue and serum.4 Formulations containing arbutin have been used in the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.
1.Seo, D.-H., Jung, J.-H., Lee, J.-E., et al.Biotechnological production of arbutins (α- and β-arbutins), skin-lightening agents, and their derivativesAppl. Microbiol. Biotechnol.95(6)1417-1425(2012) 2.Takebayashi, J., Ishii, R., Chen, J., et al.Reassessment of antioxidant activity of arbutin: Multifaceted evaluation using five antioxidant assay systemsFree Radic. Res.44(4)473-478(2010) 3.Maeda, K., and Fukuda, M.Arbutin: Mechanism of its depigmenting action in human melanocyte cultureJ. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.276(2)765-769(1996) 4.Ye, J., Guan, M., Lu, Y., et al.Arbutin attenuates LPS-induced lung injury via Sirt1/ Nrf2/ NF-κBp65 pathwayPulm. Pharmacol. Ther.5453-59(2019)
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 10 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















