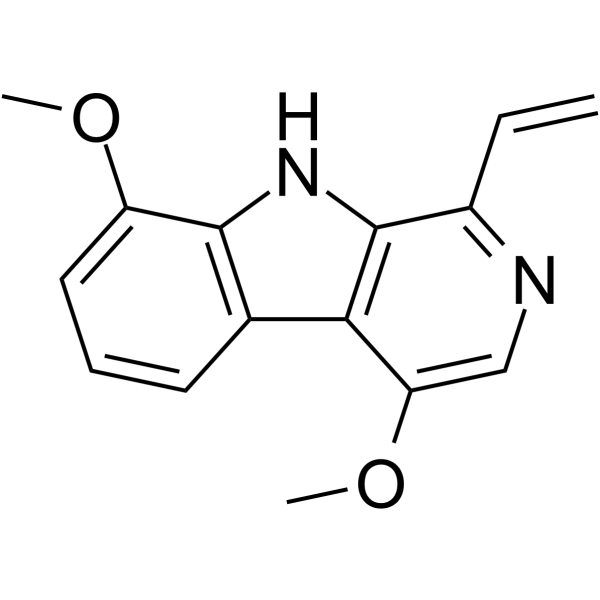
Dehydrocrenatidine |
| Catalog No.GC72012 |
Dehydrocrenatidine, un alcaloide natural, es un inhibidor específico de JAK.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
Cas No.: 65236-62-6
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Dehydrocrenatidine inhibits JAK-STAT3 dependent DU145 and MDA-MB-468 cell survival and induces cell apoptosis. Dehydrocrenatidine inhibits JAKs-JH1 domain over-expression induced STAT3 and STAT1 phosphorylations[1].
Dehydrocrenatidine diminishes IL-6, IFNα and IFNγ stimulated STAT3 phosphorylation as well as constitutive STAT3 phosphorylation[1].
DHCT suppresses both tetrodotoxin-resistant (TTX-R) and sensitive (TTX-S) voltage-gated sodium channel (VGSC) currents with IC50 values of 12.36 µM and 4.87 µM, respectively[2].
Dehydrocrenatidine inhibits JAK-STAT3 dependent DU145 and MDA-MB-468 cell survival and induces cell apoptosis. Dehydrocrenatidine inhibits JAKs-JH1 domain over-expression induced STAT3 and STAT1 phosphorylations[1].
Dehydrocrenatidine diminishes IL-6, IFNα and IFNγ stimulated STAT3 phosphorylation as well as constitutive STAT3 phosphorylation[1].
DHCT suppresses both tetrodotoxin-resistant (TTX-R) and sensitive (TTX-S) voltage-gated sodium channel (VGSC) currents with IC50 values of 12.36 µM and 4.87 µM, respectively[2].
References:
[1]. Jing Zhang, et al. Dehydrocrenatidine is a novel janus kinase inhibitor. Mol Pharmacol. 2015 Apr;87(4):572-81.
[2]. Fang Zhao, et al. Dehydrocrenatidine Inhibits Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels and Ameliorates Mechanic Allodia in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain. Toxins (Basel). 2019 Apr 18;11(4):229.
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 30 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




















