Ionomycin free acid |
| Catalog No.GC15446 |
Ionomycin free acid es un portador selectivo y potente de iones de calcio que actúa como un portador activo de Ca2+.
Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
Cas No.: 56092-81-0
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Ionomycin free acid es un portador selectivo y potente de iones de calcio que actúa como un portador activo de Ca2+. Al estimular la entrada de cationes regulados por almacenamiento a través de biopelículas, mejora efectivamente el influjo de Ca2+[9].
Las células NK humanas tratadas con Ionomycin free acid pierden su capacidad para desgranular y secretar IFN-γ en respuesta a una variedad de estímulos, pero la estimulación con IL-2 puede compensar estos defectos[2]. Al probar la hipótesis mediante la hiperpolarización de células HL-60 usando Ionomycin free acid antes de la electroporación. La hiperpolarización de las células antes de la electroporación altera los umbrales de intensidad del campo eléctrico pulsado para la electroporación reversible y la IRE, permitiendo un mayor control y selectividad de los resultados de la electroporación[3]. Ionomycin free acid induce el influjo de calcio en la región intracelular y la producción de especies reactivas de oxígeno en las células N1E-115. La producción de hidroperóxido lipídico se indujo en células N1E-115 tratadas con ionomicina[5]. Ionomycin free acid, al menos en parte, ejerce sus efectos mediante la unión específica a un receptor acoplado a proteínas G, provocando así eventos celulares posteriores como la liberación de araquidonato con la formación subsiguiente de prostaglandinas[6]. Una alta concentración de Ionomycin free acid aumentó la frecuencia y amplitud de los patrones de oscilación de calcio, afectando el equilibrio del metabolismo energético mitocondrial, lo que llevó a un aumento de las especies reactivas de oxígeno (ROS) y una disminución del ATP[1].
La inyección intratumoral de Ionomycin free acid en tumores subcutáneos HT1376 redujo la tumorigenicidad en ratones desnudos. Además, estos efectos inhibitorios del crecimiento in vivo de Ionomycin free acid se vieron significativamente aumentados por el pretratamiento con cisplatino[8]. La secreción evocada por acetilcolina (ACh) por el ionóforo de calcio, ionomicina, se estudió en terminaciones nerviosas motoras de rana. La aplicación en baño de Ionomycin free acid estimuló un aumento irreversible en la tasa de liberación espontánea, cuántica, de ACh en presencia de Ca2+ extracelular. En contraste, la aplicación local de Ionomycin free acid estimuló una rápida y reversible aceleración de la liberación espontánea de ACh[4]. Tras la estimulación con Ionomycin free acid, las células CD4+ PD-1+ICOS+ expresaron niveles significativamente más bajos de IL-17A, pero no de IFNγ, en ratones GF BXD2 en comparación con ratones SPF BXD2[7].
References:
[1]. Chen C, Sun T, et,al. Ionomycin-induced mouse oocyte activation can disrupt preimplantation embryo development through increased reactive oxygen species reaction and DNA damage. Mol Hum Reprod. 2020 Oct 1;26(10):773-783. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaaa056. PMID: 32697831.
[2]. Romera-CÁrdenas G, Thomas LM, et,al. Ionomycin Treatment Renders NK Cells Hyporesponsive. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 23;11(3):e0150998. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150998. PMID: 27007115; PMCID: PMC4805247.
[3]. Aiken EJ, Kilberg BG, et,al. Ionomycin-Induced Changes in Membrane Potential Alter Electroporation Outcomes in HL-60 Cells. Biophys J. 2018 Jun 19;114(12):2875-2886. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.05.018. PMID: 29925024; PMCID: PMC6026377.
[4]. Hunt JM, Silinsky EM. Ionomycin-induced acetylcholine release and its inhibition by adenosine at frog motor nerve endings. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;110(2):828-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13887.x. PMID: 8242258; PMCID: PMC2175912.
[5]. Nakamura S, Nakanishi A, et,al. Ionomycin-induced calcium influx induces neurite degeneration in mouse neuroblastoma cells: analysis of a time-lapse live cell imaging system. Free Radic Res. 2016;50(11):1214-1225. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2016.1227074. Epub 2016 Sep 29. PMID: 27573976.
[6]. Leis HJ, Windischhofer W. Ionomycin induces prostaglandin E2 formation in murine osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells via mechanisms independent of its ionophoric nature. Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Jun;94(3):236-40. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2015-0148. Epub 2016 Feb 9. PMID: 27065246.
[7]. Hong H, Alduraibi F, et,al. Host Genetics But Not Commensal Microbiota Determines the Initial Development of Systemic Autoimmune Disease in BXD2 Mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022 Apr;74(4):634-640. doi: 10.1002/art.42008. Epub 2022 Feb 10. PMID: 34725967; PMCID: PMC9071869.
[8]. Miyake H, Hara I, et,al. Calcium ionophore, ionomycin inhibits growth of human bladder cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo with alteration of Bcl-2 and Bax expression levels. J Urol. 1999 Sep;162(3 Pt 1):916-21. doi: 10.1097/00005392-199909010-00090. PMID: 10458408.
[9]. Erdahl WL, Chapman CJ, et,al. Ionomycin, a carboxylic acid ionophore, transports Pb(2+) with high selectivity. J Biol Chem. 2000 Mar 10;275(10):7071-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.10.7071. PMID: 10702273.
| Experimentos celulares [1]: | |
Líneas celulares | Células NK |
Método de preparación | Las células fueron tratadas con 1 µM de ácido ionomicina o DMSO como control vehicular y cultivadas durante 16 horas. Las células control y tratadas con ionomicina fueron luego lavadas y se dejaron en reposo durante 24 horas a una densidad de 2x10^6 células/mL en RPMI con 10% de FBS. |
Condiciones de reacción | 1 µM de ácido ionomicina durante 16 horas |
Áreas de aplicación | Las células NK humanas tratadas con ácido ionomicina pierden su capacidad de desgranular y secretar IFN-γ en respuesta a diversos estímulos, aunque la estimulación con IL-2 puede compensar estos defectos. |
| Experimentos con animales [2]: | |
Modelos animales | Ratones desnudos atímicos (Balb/c nu/nu, hembras de 6 a 8 semanas de edad) |
Método de preparación | Se probaron los efectos de la inyección intratumoral de ácido ionomicina sobre el crecimiento de tumores subcutáneos HT1376 establecidos en ratones desnudos atímicos. |
Forma de dosificación | Inyección intratumoral de 100 µg de ácido ionomicina 3 veces por semana durante 4 semanas |
Áreas de aplicación | La inyección intratumoral de ácido ionomicina en tumores subcutáneos HT1376 redujo la tumorigenicidad en ratones desnudos. |
Referencias: [1]. Romera-Cárdenas G, Thomas LM, et,al. Ionomycin Treatment Renders NK Cells Hyporesponsive. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 23;11(3) . doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150998. PMID: 27007115; PMCID: PMC4805247. [2]. Miyake H, Hara I, et,al. Calcium ionophore, ionomycin inhibits growth of human bladder cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo with alteration of Bcl-2 and Bax expression levels. J Urol. 1999 Sep;162(3 Pt 1):916-21. doi: 10.1097/00005392-199909010-00090. PMID: 10458408. | |
| Cas No. | 56092-81-0 | SDF | |
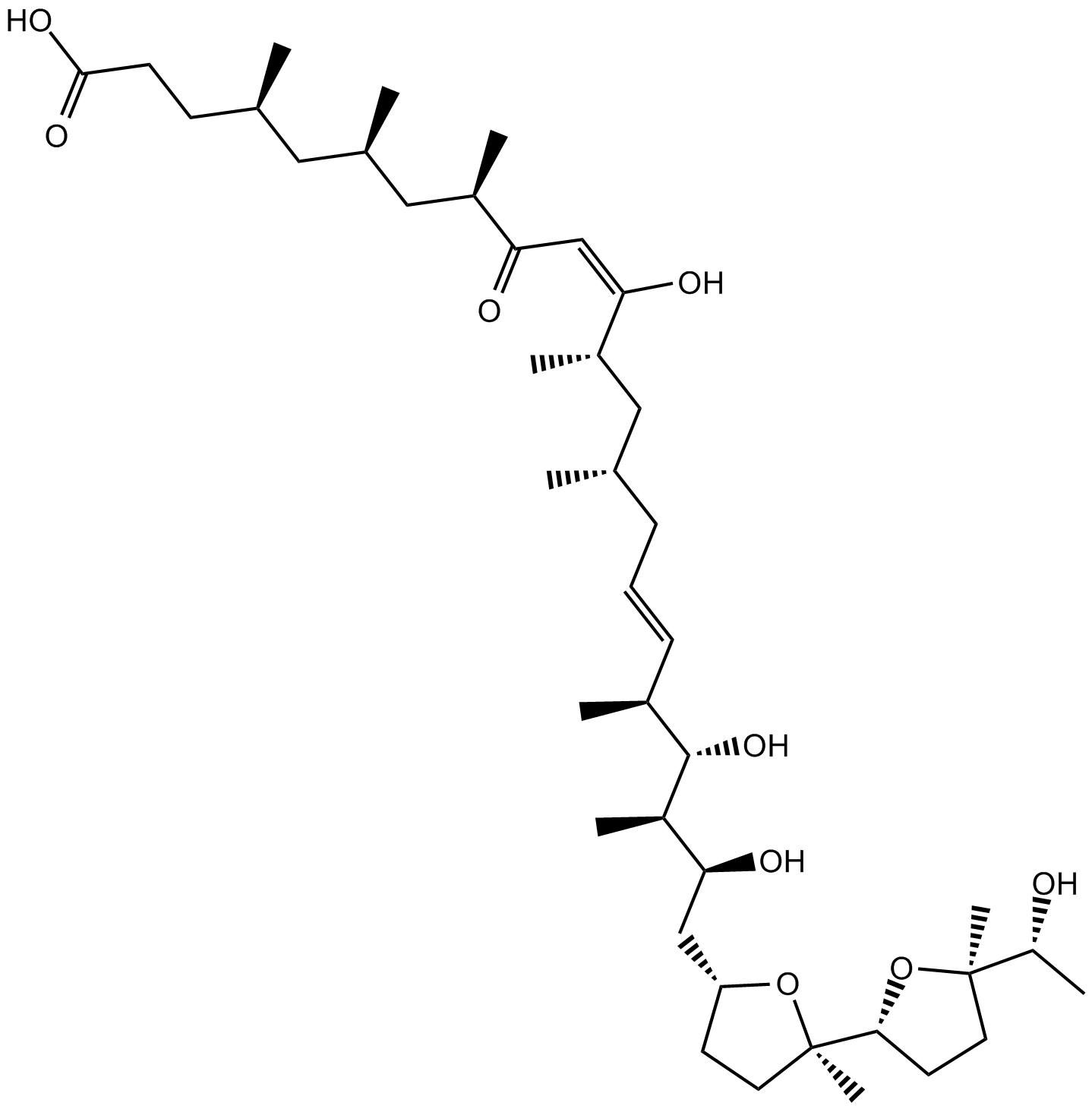
| Chemical Name | (4R,6R,8R,10E,12S,14S,16E,18S,19S,20R,21S)-11,19,21-trihydroxy-22-((2R,2'R,5R,5'R)-5'-((R)-1-hydroxyethyl)-2,5'-dimethyloctahydro-[2,2'-bifuran]-5-yl)-4,6,8,12,14,18,20-heptamethyl-9-oxodocosa-10,16-dienoic acid | ||
| Canonical SMILES | O[C@H](C)[C@]1(C)O[C@H](CC1)[C@]2(C)O[C@@H](C[C@@H]([C@@H](C)[C@H]([C@H](/C=C/C[C@H](C)C[C@H](C)/C(O)=C\C([C@H](C)C[C@H](C)C[C@H](C)CCC(O)=O)=O)C)O)O)CC2 | ||
| Formula | C41H72O9 | M.Wt | 709.01 |
| Solubility | 1.4mg/mL in DMSO, 2.5mg/mL in DMF | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| General tips | Please select the appropriate solvent to prepare the stock solution according to the
solubility of the product in different solvents; once the solution is prepared, please store it in
separate packages to avoid product failure caused by repeated freezing and thawing.Storage method
and period of the stock solution: When stored at -80°C, please use it within 6 months; when stored
at -20°C, please use it within 1 month. To increase solubility, heat the tube to 37°C and then oscillate in an ultrasonic bath for some time. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Evaluation sample solution: shipped with blue ice. All other sizes available: with RT, or with Blue Ice upon request. | ||
| Prepare stock solution | |||

|
1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg |
| 1 mM | 1.4104 mL | 7.0521 mL | 14.1042 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2821 mL | 1.4104 mL | 2.8208 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.141 mL | 0.7052 mL | 1.4104 mL |
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
 g
g
 μL
μL

Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
3. All of the above co-solvents are available for purchase on the GlpBio website.
Quality Control & SDS
- View current batch:
- Purity: >98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- SDS (Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Average Rating: 5 (Based on Reviews and 32 reference(s) in Google Scholar.)
GLPBIO products are for RESEARCH USE ONLY. Please make sure your review or question is research based.
Required fields are marked with *




