Atherosclerosis
Products for Atherosclerosis
- Cat.No. Nombre del producto Información
-
GC48283
α-Linolenic Acid-d14
ALAd14
An internal standard for the quantification of αLinolenic acid
-
GC40467
(±)11-HETE
(±)11-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acid
(±)11-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid.
-
GC41649
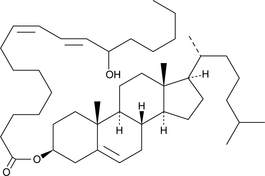
(±)13-HODE cholesteryl ester
(±)13-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions and shown to be produced by Cu2+-catalyzed oxidation of LDL.
-
GC41666
(±)9-HODE cholesteryl ester
(±)9-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions and shown to be produced by Cu2+-catalyzed oxidation of LDL.

-
GC49690
(3R,5R)-Rosuvastatin (calcium salt)
A potential impurity found in bulk preparations of rosuvastatin

-
GC46496
1-Stearoyl-2-Arachidonoyl-d8-sn-glycero-3-PC
18:0/20:4-d8-PC, PC(18:0/20:4-d8), SAPCd8, 1-Stearoyl-2-Arachidonoyl-d8-sn-glycero-3-Phosphatidylcholine, 1-Stearoyl-2-Arachidonoyl-d8-sn-glycero-3-Phosphocholine
An internal standard for the quantification of 1-stearoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-PC
-
GC41893
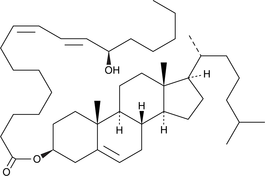
13(R)-HODE cholesteryl ester
13(R)-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions.
-
GC41895
13(S)-HODE cholesteryl ester
13(S)-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions.

-
GC41897
13(S)-HOTrE
13(S)-HOTrE is the 15-lipoxygenase (15-LO) product of linolenic acid.

-
GC49671
2,3-Oxidosqualene
(3R,S)-Oxidosqualene, Squalene 2,3-oxide
An intermediate in the biosynthesis of sterols
-
GC41614
24-dehydro Cholesterol
Desmosterol
El 24-deshidrocolesterol es una molécula similar al colesterol.

-
GC46243
24-dehydro Cholesterol-d6
Desmosterol-d6
An internal standard for the quantification of 24-dehydro cholesterol
-
GC46528
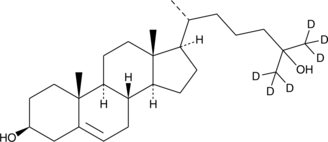
25-hydroxy Cholesterol-d6
An internal standard for the quantification of 25hydroxy cholesterol
-
GC42411
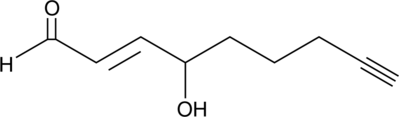
4-hydroxy Nonenal Alkyne
Click Tag 4HNE Alkyne
4-hydroxy Nonenal (4-HNE) is a major aldehyde produced during the lipid peroxidation of ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as arachidonic acid and linoleic acid.
-
GC40053
5α,6α-epoxy Cholestanol
NSC 18176
An oxysterol and a metabolite of cholesterol produced by oxidation
-
GC45357
5-Chlorouracil

-
GC49629
6β-hydroxy Prednisolone
A metabolite of prednisolone

-
GC40202
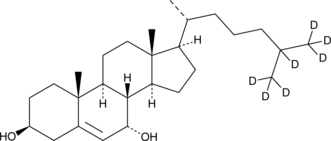
7α-hydroxy Cholesterol-d7
7α-hydroxycholesterol-d7
7α-hydroxy Cholesterol-d7 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of 7α-hydroxy cholesterol by GC- or LC-MS.
-
GC46241
7-keto Cholesterol-d7
7-oxo Cholesterol-d7
7-keto Cholesterol is a bioactive sterol and a major oxysterol component of oxidized LDL

-
GC42634
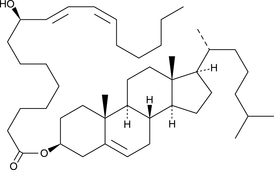
9(R)-HODE cholesteryl ester
9(R)-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions.
-
GC19460
9(S)-HODE
9(S)-HODE is produced by the lipoxygenation of linoleic acid in both plants and animals.
-
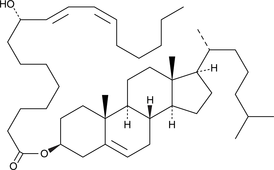
GC42635
9(S)-HODE cholesteryl ester
9(S)-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions.
-
GC49784
AZD 2716
An sPLA2 inhibitor

-
GC42890
Azelaoyl PAF
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) particles contain low molecular weight species which promote the differentiation of monocytes via the nuclear receptor PPARγ.
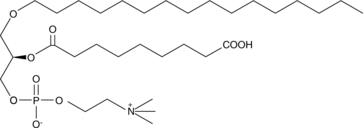
-
GC46912
Beauveriolide III
Beauveriolide III es un inhibidor de la formaciÓn de gotas de lÍpidos en macrÓfagos de ratÓn.

-
GC42924
Beraprost (sodium salt)
ML 1129, Procyclin, TRK 100
Beraprost is an analog of prostacyclin in which the unstable enol-ether has been replaced by a benzofuran ether function.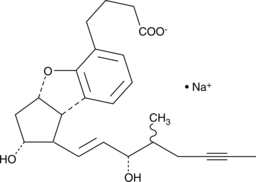
-
GC42994
Butanoyl PAF
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) particles contain low molecular weight species which promote the differentiation of monocytes and activate polymorphonuclear leukocytes.

-
GC43136
Campestanol
24-Methyl-5α-cholestan-3β-ol
El campestanol es un fitosterol que se puede encontrar en los alimentos vegetales.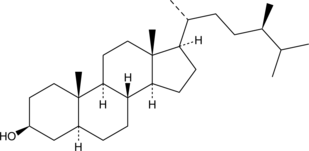
-
GC43160
CAY10485
3,4dihydroxy Hydrocinnamic acid (LAspartic acid dibenzyl ester) amide
Acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase-1 and -2 (ACAT-1 and ACAT-2) catalyze the formation of cholesterol esters from cholesterol and long chain fatty acyl-coenzyme A, and may play a role in the development of atherosclerosis.
-
GC41636
CAY10487
3,4Dihydrocinnamic Acid (Lalanine methyl ester) amide
The early stage of atherosclerosis is characterized by the aggregation of foam cells, so called a fatty streak, in the inner arterial wall.
-
GC40203
Cholesterol-d6
Provitamin D-d6
Cholesterol-d6 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of cholesterol by GC- or LC-MS.

-
GC47085
Cholesterol-d7
Provitamin D-d7
An internal standard for the quantification of cholesterol
-
GC19433
Cholesteryl Heptadecanoate
Cholesteryl Margarate, Heptadecanoic Acid cholesteryl ester, Margaric Acid cholesteryl ester
Cholesteryl heptadecanoate is a cholesterol ester (CE) formed by the condensation of cholesterol with heptadecanoic acid, a C-17 saturated fatty acid that does not occur in any natural animal or vegetable fat at high concentrations.
-
GC43263
Cholesteryl Stearate
18:0 CE, 18:0 Cholesterol ester, CE(18:0), Cholesterol Stearate, NSC 59693
Cholesteryl stearate is a cholesterol ester.
-
GC45439
Docosahexaenoic Acid-d5 MaxSpec• Standard
Cervonic Acid-d5, C22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-d5, C22:6 n-3-d5, DHA-d5, 4,7,10,13,16,19-Docosahexaenoic acid-d5
Ácido docosahexaenoico-d5 MaxSpec• EstÁndar (DHA-d5) es el Ácido docosahexaenoico marcado con deuterio.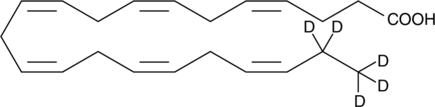
-
GC52193
Eptifibatide
La eptifibatida es un heptapéptido cÍclico, actÚa como antagonista competitivo del receptor activado de la glicoproteÍna plaquetaria IIb/IIIa, con actividad antiplaquetaria.

-
GC33760
ETC-1002 (ESP-55016)
Bempedoic Acid, ESP-55016
ETC-1002 (ESP-55016) (ETC-1002) es un inhibidor de ATP-citrato liasa (ACL).
-
GC47397
Gemfibrozil-d6
CI-719-d6
An internal standard for the quantification of gemfibrozil
-
GC48744
Gliclazide-d4
An internal standard for the quantification of gliclazide

-
GC18788
Graphislactone A
Graphislactone A is an antioxidant produced by Cephalosporium IFB-E001 and M.

-
GC43803
HA-1077 (hydrochloride)
Fasudil
Fasudil (HA-1077; AT877) dihidrocloruro es un inhibidor rhoa/roca inespecÍfico y también tiene un efecto inhibitorio en las proteÍnas quinasas, con un KI de 0.33 ⋼ m para el rock111&&&&&&77TRESTO. offlineefficient_models_2022q2.md;M, 1.650 μM for ROCK2 and PKA, PKC, PKG, respectively.en_es_2021q4.mdHA-1077 (hydrochloride) is also a potent Ca2+ channel antagonist and vasodilator.en_es_2021q4.md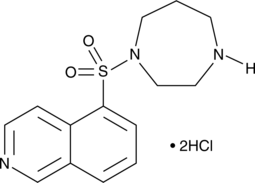
-
GC45469
Hexacosanoic Acid-d4

-
GC49496
Homocitrulline-d3
ε-Carbamyllysine-d3, L-ε-Amino-Carbamoyl-Lysine-d3
An internal standard for the quantification of homocitrulline
-
GC43997
KDdiA-PC
KDdiA-PC es un tipo de LDL oxidada (oxLDL) y es un ligando para el receptor eliminador de macrÓfagos CD36.

-
GC44011
KOdiA-PC
Oxidized low-density lipoprotien (oxLDL) particles contain low molecular weight species which are cytotoxic and pro-atherogenic.

-
GC52497
Lactosylceramide (porcine RBC)
LacCer
A sphingolipid
-
GC40142
Lactosylceramides (bovine buttermilk)
LacCer
Lactosylceramide (LacCer) is an endogenous bioactive sphingolipid.
-
GC52281
Losartan Azide
A potential impurity in commercial preparations of losartan
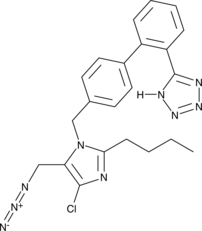
-
GC44093
Lutein
E 161b, Xanthophyll
Lutein is a natural yellow carotenoid, which can be found in plants, egg yolks, and in the human retina.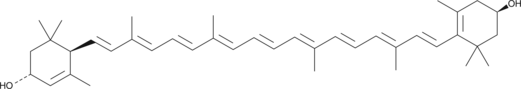
-
GC18241
Lysophosphatidylcholines
Lyso-Lecithins (egg)
Lysophosphatidylcholines are produced by hydrolysis of the fatty acid of phosphatidylcholine at either the sn-1 or sn-2 position by phospholipase A2 (PLA2) or by lecithin-cholesterol acyltranferase (LCAT), which transfers the fatty acid to cholesterol.

-
GC49486
Meglutol-d3
Dicrotalic Acid-d3, 3-hydroxy 3-methyl Glutaric Acid-d3, HMG-d3, 3-methyl-3-Hydroxyglutaric Acid-d3, Medroglutaric Acid-d3, 3-hydroxy-3-Methylglutaric Acid-d3
An internal standard for the quantification of meglutol
-
GC44180
Methylcarbamyl PAF C-16
Methylcarbamyl PAF C-16 is a stable analog of PAF C-16 with a half-life greater than 100 minutes in platelet poor plasma due to its resistance to degradation by PAF-AH.

-
GC40624
MMP-3 Inhibitor VIII
Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 Inhibitor VIII, Stromelysin-1 Inhibitor VIII
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) belong to a family of proteases that play a crucial role in tissue remodeling and repair by degrading extracellular matrix proteins to enable cell migration.
-
GC18616
MMP-8 Inhibitor I
Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 Inhibitor I
MMP-8 Inhibitor I is a selective inhibitor of the neutrophil collagenase matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) with an IC50 value of 4 nM.
-
GC20172
N-Isopropylphthalimide

-
GC44518
Osteocalcin (1-49) (human) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Osteocalcin (1-49) is a non-collagenous peptide that is secreted by osteoblasts and odontoblasts and comprises 1-2% of the total protein in bone.

-
GC44573
PAz-PC
Azelaoyl PC, 1Palmitoyl2Azelaoyl PC
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) particles contain low molecular weight species which are cytotoxic and pro-atherogenic.
-
GC44616
PGPC
1-Palmitoyl-2-glutaryl phosphatidylcholine
PGPC is an oxidized phospholipid that can be formed under conditions of oxidative stress.

-
GC44633
Phosphatidylserines (bovine)
PtdSers (bovine)
Phosphatidylserine is a naturally occurring phospholipid that comprises 2-10% of total phospholipids in mammals and is enriched in the central nervous system, particularly the retina.
-
GC18522
Phosphatidylserines (sodium salt)
L-α-Phosphatidylserine, PtdSer (Soy), Soy PS
Phosphatidylserine is a naturally occurring phospholipid that comprises 2-10% of total phospholipids in mammals and is enriched in the central nervous system, particularly the retina.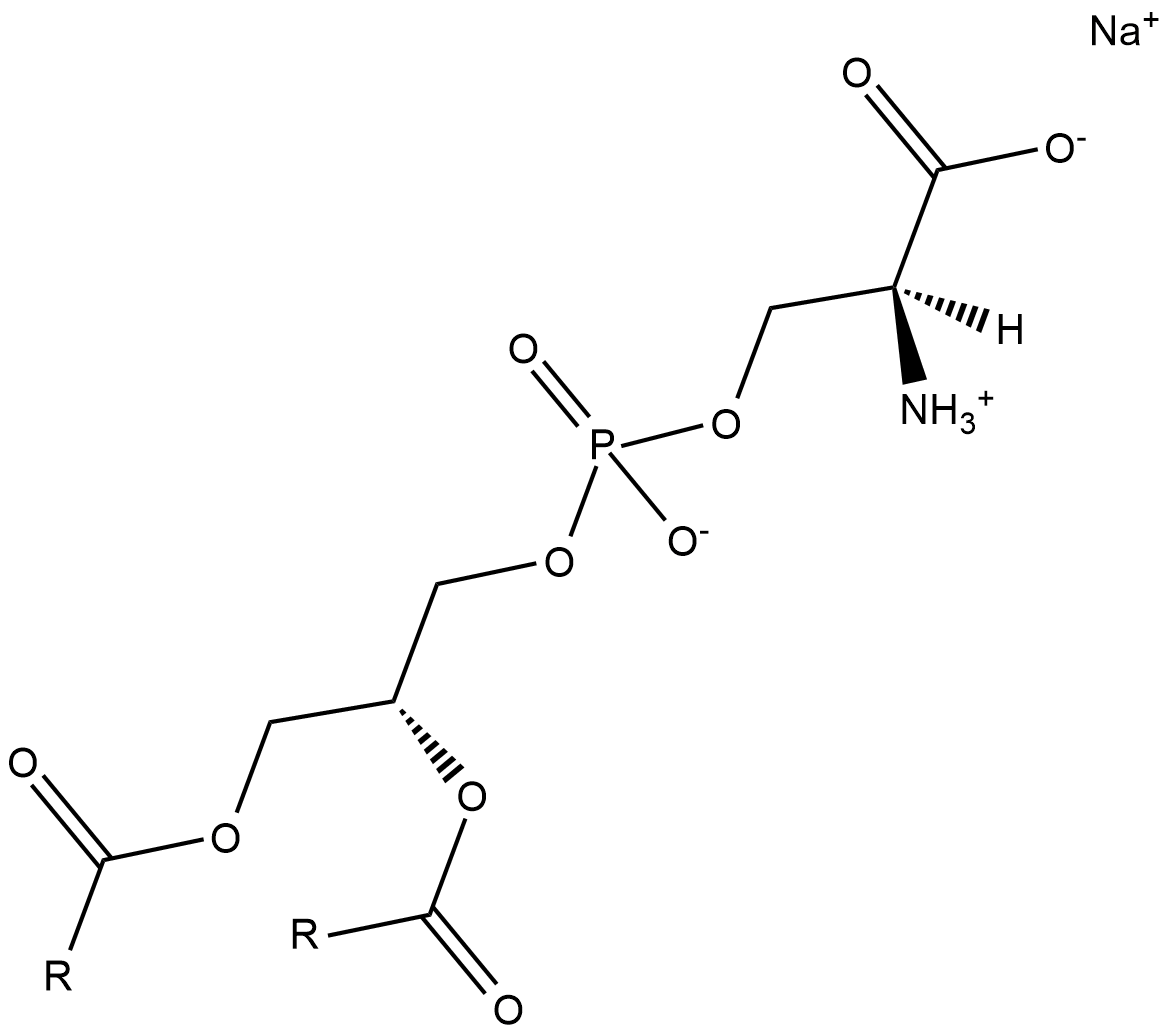
-
GC49340
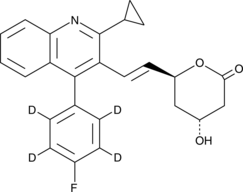
Pitavastatin lactone-d4
An internal standard for the quantification of pitavastatin lactone
-
GC44669
POV-PC
2(5oxovaleryl) Phosphatidylcholine
Oxidized low-density lipoprotien (oxLDL) particles contain low molecular weight species which are cytotoxic and pro-atherogenic.
-
GC49107
Rosuvastatin lactone
(+)-Rosuvastatin lactone, Rosuvastatin-5S-lactone, RSTL
The lactone form of rosuvastatin
-
GC48060
Rosuvastatin-d6 (sodium salt)
An internal standard for the quantification of rosuvastatin

-
GC44910
Sodium Hydrogen Sulfide (hydrate)
NaHS, NSC 158264, Sodium Hydrosulfide
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is, like nitric oxide, an important gaseous mediator that has significant effects on the immunological, neurological, cardiovascular and pulmonary systems of mammals.
-
GC45057
TIQ-A
TIQ-A es un potente inhibidor de TNKS (poli-ART, PARP), con una IC50 de 24 nM para TNKS2.

-
GC48206
Trimethylamine-d9 N-oxide
TMAO-d9
An internal standard for the quantification of trimethylamine N-oxide


