TAK-242
TAK-242 ethyl (6R)-6-[N-(2-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)sulfamoyl]cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate, also known as resatorvid, is a cyclohexene derivative and a small inhibitor molecule of TLR4 signaling, which was first represented as a novel anti-sepsis treatment that may inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators. Research on the mechanisms of action has revealed that TAK-242 specifically binds to Cys747 in the TIR domain of TLR4, which ensuingly prevents TLR4 from interacting with TIRAP. TAK-242 is the only small-molecule substance that is declared to control the interactions between TLR4 and its adaptor molecules, but when it comes to other identified TLRs, TAK-242 has no specific binding affinity.
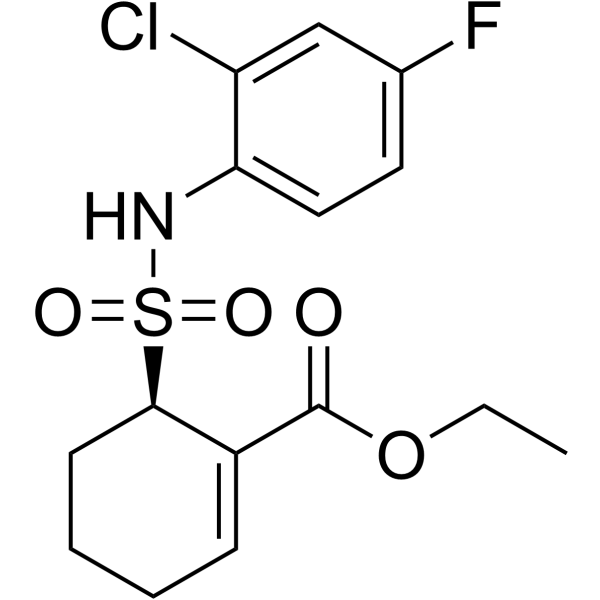
Figure showing the structural representation of TAK-242.
TLR4 inhibitor,TAK-242 specifically binds to TLR4 and disrupts its interaction with adaptor molecules,In the human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells, overexpression of TLR4, MD-2, and TIRAP or TRAM resulted in the restriction of the association of TLR4 with Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor protein (TIRAP) or Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor protein inducing interferon-β-related adaptor molecule (TRAM). In HEK cells that were stably expressing TLR4, MD-2, and CD14, it was found that the same overexpression reduced the TIRAP-mediated activation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) as well as the TRAM-mediated activation of NF-κB and interferon-sensitive response element.
TAK-242 can be employed to characterize the involvement of TLR4 in insulin resistance brought on by LPS and saturated NEFA, as well as to analyze the separate contributions of these endogenous TLR4 ligands in the activation of the MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Stearate, one of the most prevalent saturated NEFA in human plasma, and LPS both have effects on TLR4, and TAK-242 would guard against the inflammation and insulin resistance both TLR4 agonists would produce. TAK-242 offers full and partial protection against insulin resistance and inflammation brought on by NEFA and LPS, respectively.
TAK-242 particularly inhibits the Toll-like receptor 4-mediated signaling. It impedes several other types of inflammatory mediators which include prostaglandin E2 from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages, nitric oxide (NO), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, IL-10, and macrophage inhibitory protein (MIP)-2. The consequences of TAK-242 were analyzed by using a mouse model with endotoxin shock. One hour before the LPS challenge inject TAK-242 intravenously, which results in a reducing the blood levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, MIP-2, and NO metabolites production particularly caused by LPS in a dose-dependent manner. TAK-242 salvaged 100% of the mice at a 1mg/kg dose and exhibited a comparable dose-dependent protective effect against LPS-induced mortality. It is intriguing that TAK-242 rapidly determined the function and continued to have desirable consequences even after an LPS challenge.
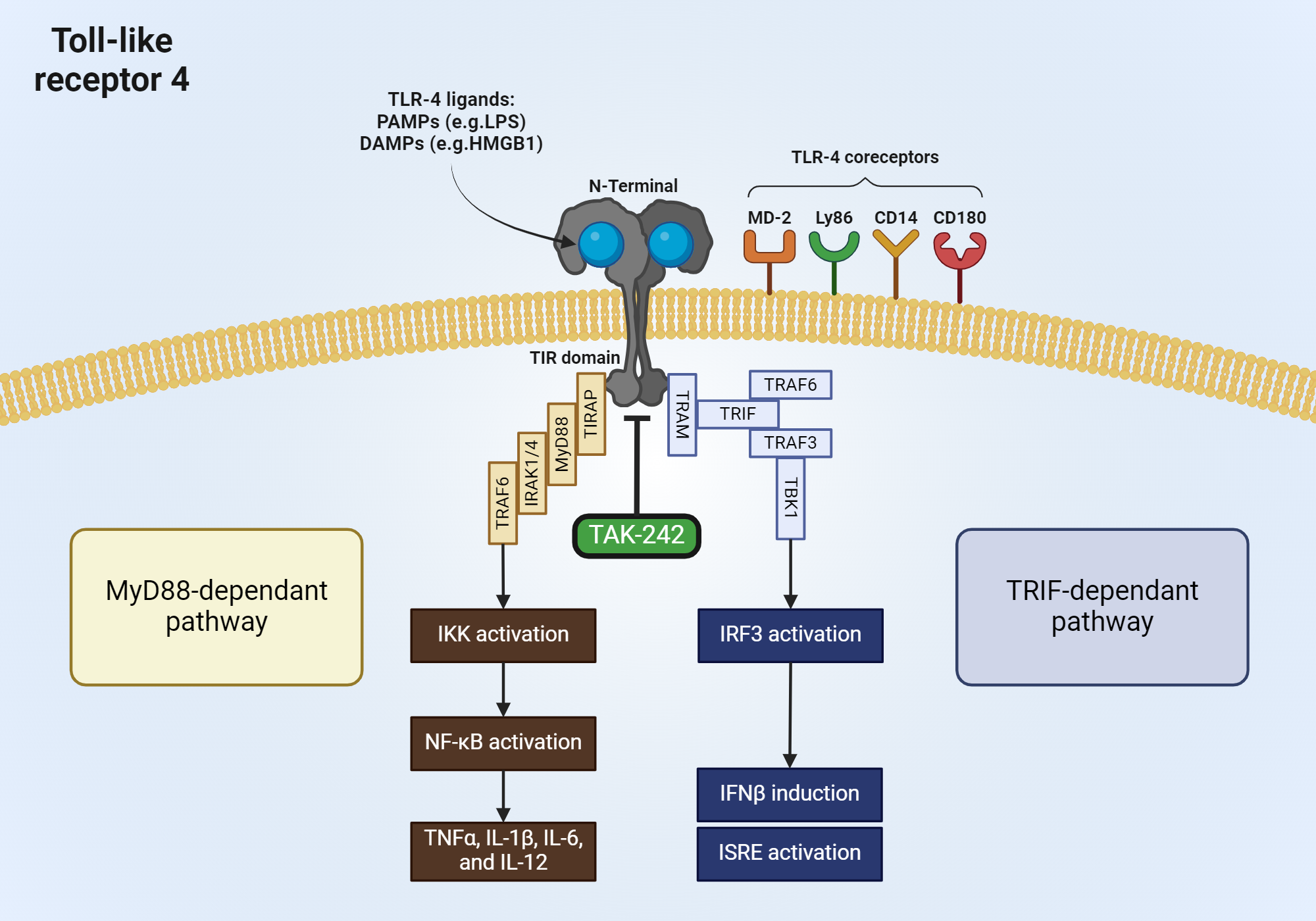
Figure demonstrating TLR4 pathway and TAK-242 interaction.
TAK-242 averts endotoxemia-induced skeletal muscle wasting in mice,Patients with sepsis or other diseases related to bacterial translocation from the gut were diagnosed with elevated levels of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) content, which leads to involuntary muscle loss, known as muscle wasting, that can harm patients' survival and functional outcomes induced by endotoxemia. No drugs are readily accessible to treat this endotoxemia-induced skeletal muscle wasting right now, but to address this, researchers tested the effects of a Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-specific signaling inhibitor called TAK-242 on myotube atrophy in vitro and muscle wasting in vivo induced by endotoxins. When LPS was implemented in C2C12 myotubes in mice, it resulted in an inflammatory response that included elevated expression of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and nuclear factor-κB activity. Activating the autophagy proteolytic and ubiquitin-proteasome pathways led to myotube atrophy (increased expression of LC-II, MuRF1, and atrogin-1/MAFbx), which induces the same inflammatory and proteolytic pathways when heightened in mice's skeletal muscle by LPS injection. Pretreatment with TAK-242 significantly decreases or eliminates every negative effect of LPS in vivo and in vitro in cells or animals. TAK-242, the pharmaceutical specific inhibitor of TLR4 might be a potential treatment approach for endotoxemia-induced muscle atrophy.
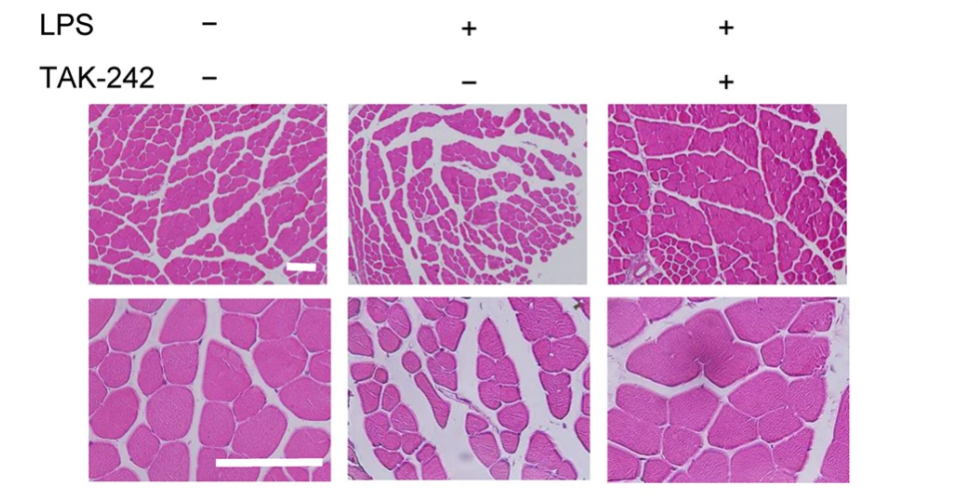
Figure representing the effects of TAK-242 in reduction of LPS-induced muscle atrophy and weakness in mice.
TAK-242 restricts LPS-induced myofibrillar protein loss and atrophy in C2C12 myotubes,In C2C12 myotubes, TAK-242 impedes LPS-induced loss of myofibrillar protein and atrophy. The researchers previously discovered that TLR4 is integrally expressed in myotubes and mouse C2C12 myoblasts22, which suggests that LPS can directly cause myotube atrophy without the immune system getting involved, as the immune system is a significant source of cytokines that promote inflammation. To assess the potential of pharmacologically inhibiting TLR4 signaling to mitigate LPS-induced atrophy and loss of muscle protein in myotubes that have been cultured, examined the expression of myosin heavy chain (MyHC) specific to myofbre, as well as the size and percentage of mature C2C12 myotubes after 48 hours of culture with vehicle, LPS (1μg/mL), or LPS plus TAK-242 (1μM). As Doyle et al. had previously reported, we discovered that LPS significantly reduced the production of MyHC protein; however, pretreatment with TAK-242 largely overrode this. Similarly, exposure to LPS decreased the width and number of mature myotubes, which were likewise saved by TAK-242 pretreatment, according to immunofluorescence labeling of myotubes using a MyHC-specific antibody. According to these findings, LPS-induced muscle protein loss and atrophy in myotubes were inhibited by blocking TLR4 signaling.
TAK-242 is a new potential anti-rheumatoid arthritis drug, It has been proposed that the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can be inhibited by suitably suppressing the toll-like receptor (TLR) activation as the disease progresses. We investigated the possibility of using TAK242, a TLR4 inhibitor, as a treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. The human rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocyte (FLS) line MH7A or primary human FLS, as well as an adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) rat model, were employed to assess the therapeutic impact of TAK-242 in vitro. In LPS-stimulated MH7A cells, TAK-242 dose-dependently suppressed the upregulation of IL-6, IL-8, MMP-1, and VEGF expression. In poly(I: C), TLR3 activator-stimulated primary FLS, also reduced the expression of IL-6 and IL-8, but not in IL-1β-stimulated primary FLS. These results imply that TAK-242 partially inhibits a certain signaling pathway. TAK-242 also marginally reduced NF-κB's ability to mobilize into nuclei. In the AIA rat model, TAK-242 decreased the elevated serum levels of VEGF and IL-6 in AIA rats and dramatically restored the body weight and paw thickness of AIA rats to the normal state at a dose of 5 mg/kg, but not at 3 mg/kg. According to histology and RT-PCR, it also markedly reduced the inflammatory symptoms of joint tissues on day 21 of treatment.
By inhibiting NF-κB and AP-1 activation, TAK-242 has an anti-arthritic effect in AIA rats.For the first time, we were able to show that TAK-242 has anti-arthritic properties in AIA rats. Although TAK-242 did not show a therapeutic impact on our animal model of arthritis, it can progress as a therapeutic agent against rheumatoid arthritis. Further studies on TLR inhibitors are necessary to investigate their potential as cost-effective remedies. TAK-242 has displayed favorable pieces of evidence in inhibiting TLR4-mediated signaling and protecting against inflammation and insulin resistance. Additionally, other TLR inhibitors should be explored for their potential therapeutic uses in various diseases and conditions. With more research on TLR inhibitors, we could use them as a significant tool in the fight against inflammation and related disorders.














コメント